 |
AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options |
| << ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK |
| AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling >> |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
29
AGGREGATE
PLANNING
Learning
Objectives
Explain
the working and usefulness of Aggregate
Planning.
Identify
the variable decision makers to
work with in aggregate
planning and some of the possible
strategies
they can use.
Describe
some of the graphical and
quantitative techniques planners
use.
Prepare
aggregate plans and compare
their costs.
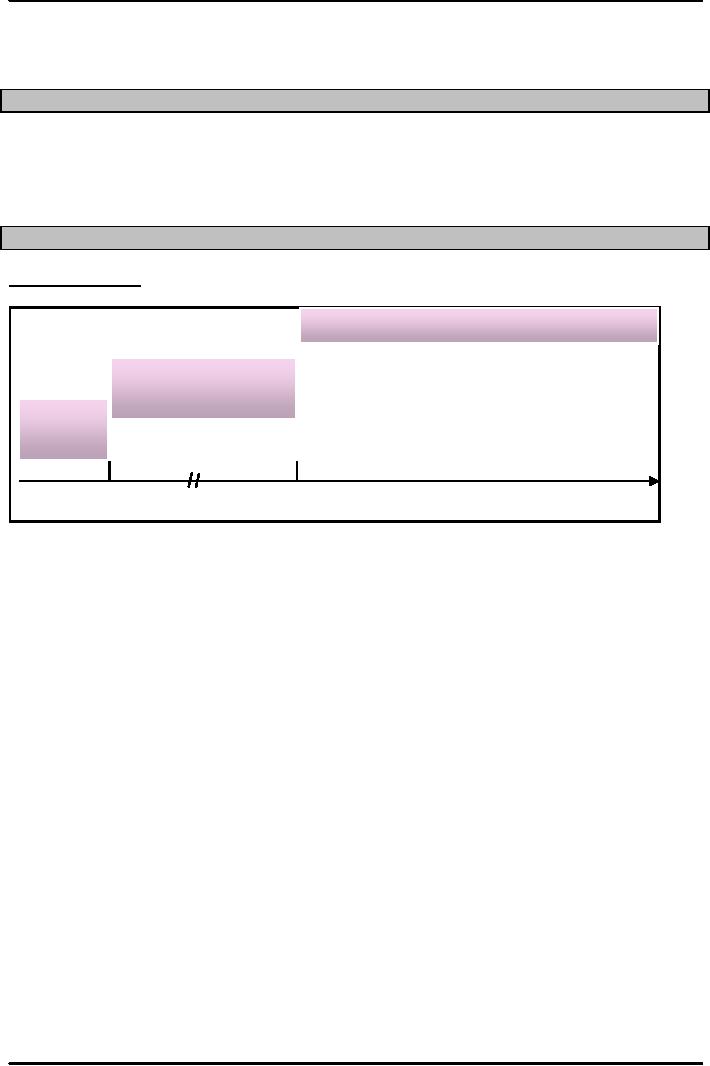
Planning
Horizon
Aggregate
planning:
Intermediate-range capacity planning,
usually covering 2 to 12 months.
Long
Range
Intermediate
Range
Short
Range
Now
2
months
1
Year
As
Operations Manager we should be able to
understand and identify the various
Planning Levels which
are
Short Range Plans,
Intermediate Plans and Long
Range Plans.
Short-range
plans (Detailed plans)
1.
Machine loading
2.
Job assignments
Intermediate
plans (General levels)
1.
Employment
2.
Finished Good
inventories
3.
Subcontracting, Backorders
4.
Output
Long-range
plans
1.
Long term capacity
2.
Location / layout
135

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Planning
Sequence
Aggregate
Planning Inputs
Resources
1.
Workforce
2.
Facilities
Demand
forecast
Policies
1.
Subcontracting
2.
Overtime
3.
Inventory levels
4.
Back orders
Costs
1.
Inventory carrying
2.
Back orders
3.
Hiring/firing
4.
Overtime
5.
Inventory changes
6.
subcontracting
Aggregate
Planning Outputs
1.
Total cost of a plan
2.
Projected levels of inventory
3.
Inventory
4.
Output
5.
Employment
6.
Subcontracting
7.
Backordering
136
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Aggregate
Planning Strategies
Proactive
Strategy: Strategies that
alter demand to match
capacity are known as
Proactive Strategy.
Reactive
Strategy: Strategies that
alter capacity to match
demand are known as Reactive
Strategy.
Mixed.
Strategies that make use of
qualities from both
Proactive and Reactive Strategy
are known
as
Mixed Strategies.
Demand
and Capacity Options
Demand
Options: The four common
demand options primarily focus on
market aspects apart
from
backorders
which is strictly operational
management in nature. The operations
manager should know
all
four
demand options but should be
more interested in back order
option.
1.
Pricing
2.
Promotion
3.
Back
orders
4.
New
demand
Capacity
Options: The common capacity
options primarily focus
on.
1.
Hire and layoff
workers
2.
Overtime/slack time
3.
Part-time workers
4.
Inventories
5.
Subcontracting
6.
Maintain a level
workforce
7.
Maintain a steady output
rate
8.
Match demand period by
period
9.
Use a combination of decision
variables
An
important point to be noted is
that Demand options are short range in
nature while Capacity
options
are
long duration (term or
range).
Which
Strategy to Use
The
organization needs to consider two
factors before choosing a strategy
1.
Costs
2.
Company/Corporate Policy
Policy
can
set
constraints
on
available
options.
E.g.
Layoffs,
subcontracting/Outsourcing
( PIA subcontracting its databases) to
protect secrecy.
As
a rule of thumb, aggregate planners
seek to match supply and
demand within in
constraints
by policies and minimum
costs.
137
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model