 |

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
22
LOCATION
PLANNING AND ANALYSIS
Lecture
Objectives
By
studying location planning and analysis,
an operations management student should be
able to
understand
the
Importance
of Location Planning and
Analysis
Criteria
for Manufacturing and Service Location
selection considerations
Transportation
Model
IMPORTANCE
OF LOCATION
Location
decisions are not limited to one
time strategic planning decisions for
building a new
manufacturing
or service facility rather most of the
organizations face the challenge of
increasing their
capacity
through selection of new locations or
extension of existing
locations.
As
an operations management student, we can focus on the
importance of location for
any organization
through
various departments of the
organization.
Accounting
which prepares cost
estimates for changing
locations as well as operating at
new
locations.
Distribution
which seeks warehouse
layouts that make material
handling easier and
customer
response
shorter.
Importance
of Location
Engineering
which considers the impact of
product /service location
choices.
Finance
which performs the financial analysis
for investments in new
locations.
Human
Resources, which hires and
trains employees to support new locations
or relocations of
operations.
Management
Information Systems which
provide information technologies
that link operations
at
different locations.
Importance
of Location
Marketing
which assesses new locations
and revised locations that are
popular with the
customers.
Operations
Management which seeks and
finalizes locations that
create, sustains, protect
and
project
the best performance criteria for
the whole
organization.
Location
plays an important role for
every business whether new
or existing. We can refer to the
same
airport
example we discussed in our
earlier lectures before. The
airport is not only crowded
but fails to
separate
the different services it provides to
different categories of individuals
present at the airport.
The
airport
may need to explain its
existing facility. In Pakistan too, we
have seen new airports set
up at
Karachi,
Lahore and Islamabad which
cater to greater traffic of the aero
planes and more
passengers.
Location
decisions play an integral part of the
strategic planning process of every
organization. It is
important
to learn about the need and nature of
location decisions. As a part of his
routine
responsibilities
a senior Operations Manager often carries
out the evaluation of different
available
locations.
GLOBALIZATION
AND GEOGRAPHIC DISPERSION OF
OPERATIONS
Globalization
has affected Pakistan tremendously. A
number of Multi National
Corporations are
operating
and functioning in Pakistan. It is
important to spend some time
in understanding how
globalization
makes it necessary and pertinent
for a MNC to disperse and
spread its scope and
function
of
Operation. It would be more correct if
try to understand the philosophy of MNC's
not operating in
certain
regions or certain particular countries.
The western worlds call
these the disadvantages of
Globalization,
if an organization decides to pack up its
business and leave a host
company.
95

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
DISADVANTAGES
TO GLOBALIZATION
The
common disadvantages which lead to a MNC
forgoing globalization
includes.
Handing
over proprietary Technology to
host countries.
Political
risks.
Poor
Employee ( Managers and worker )
skills.
Slow
customer response
time.
Effective
communication between interfaces
difficult
MANAGING
GLOBAL OPERATIONS
When
organizations become global
they often end up paying a
heavy price in terms of
managing
complex
managerial issues and
challenges.
Host
country languages
Host
Country Norms and
Customs.
Workforce
management
Unfamiliar
laws and regulations.
Unexpected
Cost mix.
Need
for Location
Decisions
Quite
often MNC's move to a host
country with a lot of hype
and propaganda of bringing jobs to
the
local
labour but the reality is
its own need to increase
its revenue and profits.
Most of the time the
need
for
location decision focuses
on
Marketing
Strategy
Cost
of Doing Business
Growth
Depletion
of Resources
Nature
of Location Decisions
Location
Decisions are primarily strategic in nature and have
certain objectives and options
attached
Strategic
Importance
1.
Long term commitment/costs
2.
Impact on investments, revenues, and
operations
3.
Supply chains
Objectives
1.
Profit potential
2.
No single location may be
better than others
3.
Identify several locations from
which to choose
Options
1.
Expand existing
facilities
2.
Add new facilities
3.
Move
Making
Location Decisions
1.
Decide
on the criteria
2.
Identify
the important factors
3.
Develop
location alternatives
4.
Evaluate
the alternatives
96

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
5.
Make selection
Location
Decision Factors
Regional
Factors
Location
of raw materials
Location
of markets
Labor
factors
Climate
and taxes
Community
Considerations
Quality
of life
Services
Attitudes
Taxes
Environmental
regulations
Utilities
Developer
support
Site
Related Factors
�Land
�Transportation
�Environmental
�Legal
Multiple
Plant Strategies
1.
Product plant strategy
2.
Market area plant
strategy
3.
Process plant strategy
Mostly
mix of all three
Factors
Affecting Location
Decisions
The
process of determining a geographic site
for firms operations takes
into account both
manufacturing
and
marketing aspects. We just focus on the
manufacturing aspects as its more
closely related to
Operations
Management
Manufacturing
Favorable
Labor Climate
Proximity
to markets.
Quality
of Life
Proximity
of Suppliers and
Resources.
Proximity
to the Parent Company's
facilities.
Utilities,
Taxes and Real estate
costs.
Other
factors ( expansion, construction costs,
and location near the
highway or main
railways)
Dominant
Factors in Services
Look
for concept check
information provided by our
expert. We also present the
following
dominant
factors in selection of locations for
services.
Proximity
to Customers.
Transportation
costs and proximity to
markets.
Location
of competitors.
Site
specific factors.
Trends
in Locations
97
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
�Foreign
producers locating in different
host countries even Pakistan
Currency
fluctuations
Just-in-time
manufacturing techniques
Micro-factories
Information
Technology
Evaluating
Locations
�Cost-Profit-Volume
Analysis
Determine
fixed and variable
costs
Plot
total costs
Determine
lowest total costs
Location
Cost-Volume Analysis
�Assumptions
Fixed
costs are constant
Variable
costs are linear
Output
can be closely
estimated
Only
one product involved
Example
1: Cost-Volume Analysis
The
quantity is 10,000 and the Fixed
and variable costs for
four potential
locations
Location
Fixed
Variable
Cost
Cost
Rs
11
Rs
250,000
A
30
100,000
B
20
150,000
C
35
200,000
D
Example
1: Solution
Fixed
Variable
Total
Costs
Costs
Costs
A
Rs250,000 Rs11(10,000)
Rs360,000
B
100,000
30(10,000)
400,000
C
150,000
20(10,000)
350,000
D
200,000
35(10,000)
550,000
Example
1: Solution
We
calculate the variable costs by
multiplying the unit cost
with the given quantity
and
calculate
total costs for all
four locations
98
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
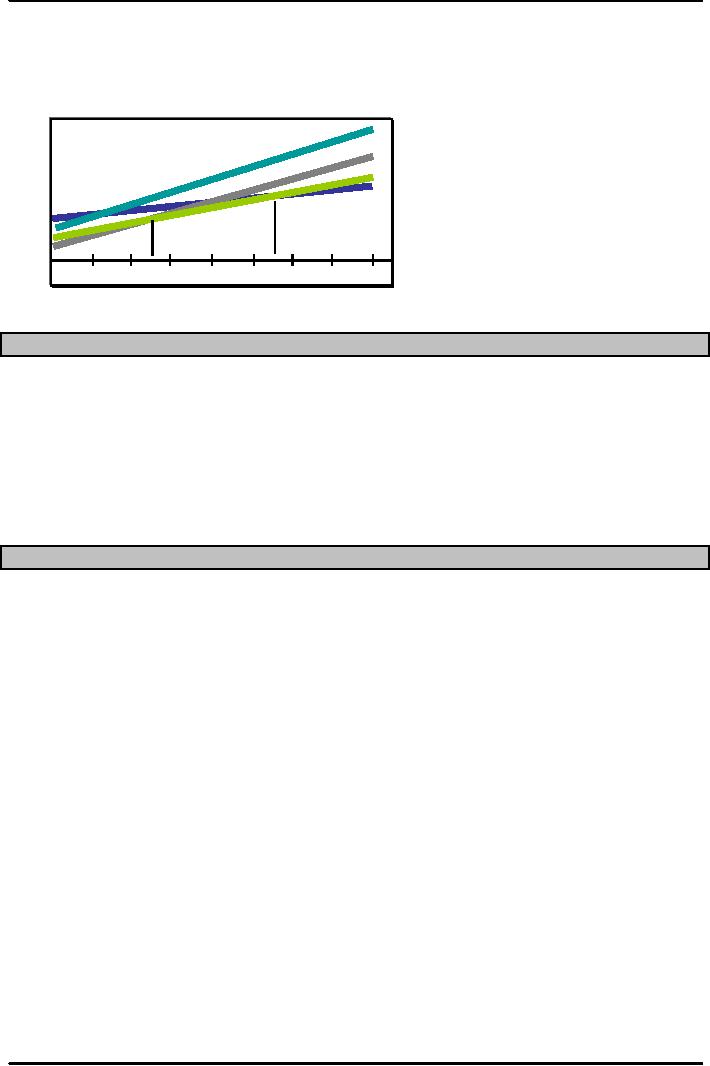
We
also graph them to decide effectively,
the total costs are graphed
and we see that for
10,000
units
clearly location c has an advantage,
beyond 10,000 units,
diseconomies of scales set in
and
makes
Location C look less
lucrative.
We
select the Location for
which the total cost is the
lowest.
Our
Location C, shows the lowest
total cost for an equal
quantity of 10,000
units.
Rs(000)
800
D
700
B
600
500
C
400
A
300
A
200
C
100
B
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Annual
Output (000)
Evaluating
Locations
Operations
Manager can evaluate
business site locations by making
use of the following three
techniques
1.
Transportation Model
Decision
based on movement costs of raw materials
or finished goods
2.
Factor Rating
Decision
based on quantitative and qualitative
inputs
3.
Center of Gravity Method
Decision
based on minimum distribution
costs
Transportation
Method
Transportation
Method is a quantitative approach that
can help solve multiple
facility location problems.
It
is used to determine the allocation
pattern that can be used to
minimize the cost of shipping
products
from
two or more plants or sources of supply
to two or more warehouses or
destinations.
Based
on Linear Programming.
It
does not solve all the
problems of the multiple facility
location.
It
only finds the best shipping
pattern between plants and warehouses
for a particular set
of
plant
locations with a given
capacity.
The
Operations manager or logistics analyst
must try a variety of
location-capacity
combinations
and use this to find the
optimal distribution for
each alternative.
Distribution
costs( variable shipping and possible
variable production costs)
are important
inputs
in evaluating a particular location
allocation combination.
Investments
costs and other fixed
costs are also
considered.
Qualitative
factors ( like land and construction
cost against annual profits)
are also included in
the
analysis for each location
capacity combination.
Transportation
Method
�Step
I
Set
up the initial matrix/tableau. The
basic steps include
Create
a row for each plant (
existing or new) being considered and a
column for each
warehouse.
Add
a column for plant capacities and a
row for warehouse demands
and then insert
specific
numerical
values.
Transportation
Method
�Step
II
Each
cell not in the requirement
row or capacity column
represents a shipping route
from a plant to
warehouse.
Insert the unit costs in the
upper right hand corner of each of
these cells.
99
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Example
Pakistan
Cellular Mobile Company plans to
build a 5000 unit production
plant at Islamabad
because
demand
for mobile phones in Pakistan
has gone up. The tableau on
the next slide shows the
unit cost of
shipping
one truck/loader of mobiles from the
existing plant at Lahore and the possible
location at
Islamabad.
Transportation
Method Ma
Plant
Capacity
WAREHOUSE
1
2
3
Lahore
500.0
600.0
5500
5000
Islamabad
700.0
4500
6000
5000
REQUIREMENTS
2500
4500
3000
10000
10000
Matrix/Tableau
In
transportation method, the sum of the
shipments in a row must
equal the corresponding plants
capacity.
Similarly
the sum of the shipments to a column
must add to corresponding warehouses
demand
requirements.
Thus shipments to Warehouse 1 from Lahore
and Islamabad must equal
2500
mobiles.
Dummy
Plants or Warehouses
The
prime requirement of transportation
model is that the sum of
capacities must equal the
sum
of
demands, which happens to be
10,000 units of mobile
phones.
IN
reality the total capacity
may exceed total requirements or
vice verca.
Dummy
Plants or Warehouses
If
capacity exceeds requirements by say M
units, we add extra column (
a dummy warehouse)
with
a demand of M units and make the
shipping costs in the new
created cell equal to Rs.
0.
Since
no shipments are made to the
dummy warehouse so it represents an
unused plant
capacity.
Dummy
Plants or Warehouses
If
requirements exceed capacity by say M
units, we add extra row ( a
dummy plant) with a
supply
of M units and make the shipping
costs ( stock out costs) in the
new created cell equal
to
Rs.
0.
Since
no shipments are made to the
dummy warehouse or plants so this
step is automatically
taken
care of in Softwares used for
such issues.
Optimal
Solution
We
try to find the least
allocation cost
process.
And
we keep on repeating with various
options till a new solution
with least costs is
obtained
and
we call it the optimal
solution.
Transportation
Method
Plant
Capacity
WAREHOUSE
1
2
3
Dummy
Lahore
1.0
6.0
1.0
0
5000
2500
2500
Islamabad
7.0
2.00
6.00
0
5000
4500
500
0
0
0
0
Dummy
REQUIREMENTS
2500
4500
3000
0
10000
10000
100

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
The
total transportation cost
would be Sum of all Units
time X the Unit Cost
=
2500(1.0)+4500(2.0)+2500(1.0)+500(6.0)
=2500+9000+2500+3000=Rs
17,000.
The
operations manager needs to be judicious
in his approach and may decide to expand
the plant at
Lahore
and build a small plant in
Islamabad.
Summary
The
lecture focused primarily on the
importance of location. Various
aspects relating to
Location
Planning
and Analysis were focused. MNC's
reasons for not selecting
various countries under the garb
of
disadvantages in Global Operations were
also examined. Site
locations for both
manufacturing and
services
were considered. Last but not the
least a detailed study of the
Transportation Model was
also
carried
out. Students should also
know how to make use of cost
volume analysis and transportation
model
to carry out practical
investigation of real life
time Operations Management
problems.
101
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model