 |
INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making |
| << INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT |
| INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy >> |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
02
INTRODUCTION
TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS
MANAGEMENT
RECAP
OF 1ST Lecture
Course
Content, Midterm and Final
Exam
Organization
Definition
Finance,
Marketing and Operations
Productive
systems, Production and Service
Systems
Operations
Management (The management of
systems or processes that
create
goods and/or
provide
services)
Operation
Function ( Consists of all
activities directly related to
producing goods or
providing
services)
Manufacturing
and Service Definitions
Manufacturing
is the transformation of raw materials
into finished goods for
sale, or intermediate
processes
involving the production or finishing of
semi-manufactures.
It
is a large branch of industry and of
secondary production. Some
industries, like semiconductor
and
steel manufacturer's use the term
fabrication.
Service
is defined as either as
Services
are deeds, processes, and
performances.
OR
A
service is a time-perishable, intangible experience
performed for a customer
acting in the role of a
co-producer
Definition
of Service Firms
Service
enterprises are organizations
that facilitate the production and
distribution of goods, support
other
firms in meeting their goals, and
add
value to
our personal lives.
Role
of Services in an Economy
Production
and Services Growth in
Pakistan
Can
be attributed to the following
sectors
Private
Public
Public
Private
Government
Key
Areas of Responsibility for an Operations
Manager
Operations
Managers job responsibility
includes but is not limited
to:
Forecasting
Capacity
planning
3
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Scheduling
Inventory
Management
Quality
Assurance and Control
Motivating
employees
Deciding
where to locate facilities
Key
Decision Areas for Operations Managers
5W2H Approach
What
: What resources/what
amounts
Why:
The work is needed to be
done
When:
Needed/ scheduled/ordered
Where:
Work to be done
How
much: Quantity to be produced or
served,
How:
Designed/capacity planning
Who:
To do the work
Decision
Making
Operations
Manager spends most of their
routine hours in making decisions under
certainty or
uncertainty.
The various tools available
to an Operations Manager include
1.
Models
2.
Quantitative approaches
3.
Analysis of trade-offs
4.
Systems approach
Applications
of Models in Operations
Management
Models
Are Beneficial and effective to an
Operations Manager primarily because of
the following
reasons
Easy
to use, less
expensive
Require
users to organize
Systematic
approach to problem solving
Increase
understanding of the problem
Enable
"what if" questions
Specific
objectives
Consistent
tool
Power
of mathematics
Standardized
format
Historical
Development of OM
JIT
and TQC
Manufacturing
Strategy Paradigm
Service
Quality and Productivity
Total
Quality Management and Quality
Certification
Historical
Development of OM (cont'd)
Business
Process Reengineering
Supply
Chain Management
Electronic
Commerce
4
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Current
Trends in Business
Trends
in Business in general and Operations Management
which have shaped the industry and
the
technological
support to the industry include the
following:-
1.
The Internet, e-commerce,
e-business
2.
Management technology
3.
Globalization
4.
Management of supply
chains
5.
Agility
Production
and Operations Management as Nucleus in
the Organizations
Operations
occupy the central figure in
any service or manufacturing
organization. A small decision
as
it
may seem can serious
effect the workings and performance
output in other
units.
Industrial
Engineering
Maintenance
Distribution
Public
Purchasing
Operations
Relations
Legal
Personnel
Accounting
MIS
Current
Issues in OM
The
recent wave of telecom sector
infrastructure consolidation and
deregulation has led to a
lot of
foreign
investors aggressively seeking new
Pakistani partners. With the aid of
operation management
studies
we can foresee the following
current issues in Pakistan . These
issues have already
been
addressed
in Pakistan as well as in other
countries.
1.
Effectively
consolidating the operations resulting
from mergers
2.
Developing
flexible supply chains to enable
mass customization of products and
services
3.
Managing
global supplier, production
and distribution
networks
4.
Increased
"commoditization" of suppliers
5.
Current
Issues in OM (cont'd)
6.
Achieving
the "Service Factory"
7.
Enhancing
value added services
8.
Making
efficient use of Internet
technology
9.
Achieving
good service from service
firms
What
is a Production and Productive
System?
A
productive system is defined as a
user of resources to transform
inputs into some desired
outputs
(products
as well as services) where as production
system refers specifically to only
desired output in
the
form of products or manufactured
goods.
5
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
It
is important to understand that
productive system reflects both
production as well as services
systems.
We
also need to understand the important
transformations through which a
raw material is converted
a
value
added end product or service.
Physical--manufacturing
Location--transportation
Exchange--retailing
Storage--warehousing
Physiological--health
care
Informational--telecommunications
Our
discussion throughout the semester
would focus on what is a Service and what
is a Good? In our
course
of discussion, we will collect
numerous examples to better understand
that Workers working
for
creation
of a product, manufacturing units
are simultaneously working to
create a service? So the
statement
that Services never include
goods and goods never
include services can never
be true.
Production
of Goods vs. Delivery of
Services
�
Production
of goods tangible
output
�
Delivery
of services an action and reaction
between the provider /deliverer of
services and the
demander
of services, bank teller,
hair stylist.
�
Service
job categories
Government
Wholesale/retail
Financial services
Healthcare
Personal services
Business services
Education
Percent
Service Employment for
Selected Nations
Percent
Service Employment for Selected
Nations (Source not
Authenticated)
Country
1980
1987
1993
2000
United
States
67.1
71.0
74.3
74.2
Canada
67.2
70.8
74.8
74.1
Pakistan
13.3
16.0
18.0
23.9
Japan
54.5
58.8
59.9
72.7
France
56.9
63.6
66.4
70.8
Italy
48.7
57.7
60.2
62.8
Brazil
46.2
50.0
51.9
56.5
China
13.1
17.8
21.2
40.6
6
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Stages
of Economic Development in
Pakistan
Pre-
Use
of
Standard
Society
dominant
human
Unit
of
of
living
activity
labor
social
life
measure
Structure
Technology
Pre-
Agriculture
Raw
Extended
Survival
Routine
Simple
Industrial
Mining
(
muscle
household
Traditional
hand
tools
(
1947 to
coal.
Salt)
power
(
Joint
Authoritative
1960)l
Families)
Industrial
Goods
Machine
Individual
Quantity
Bureaucratic
Machines
(
1960
production
tending
of
goods
Hierarchical
todate)
Inter-
Information
Post-
Services
Artistic
Community
Quality
of
dependent
industrial
Creative
life
in
Global
(
Future)
Intellectual
terms
of
health,
education,
recreation
Source
of Service Sector
Growth
Pakistan
is slowly but surely facing
a change in its demographics, economics
and more important social
norms.
This shift has often
proven to be the source of service sector
growth.
Innovation
Push
and
Pull
theory
e.g.
Cash
Management
Services
derived
from
products
e.g.
CD/Automobile/Video
Rental
Information
driven
services
like
finance
brokerage
services.
Social
Trends
Aging
of the population
Increase
in Life expectancy
Two-income
families, both the males and
females of the family are
working
Growth
in number of single people.
Home
as sanctuary
Functions
with in an Organization
The
Operations function consists of all
activities that are directly
related to production of a good
or
service.
Operations
function exist in services
like healthcare, Police, Traffic,
transportation, consultancy,
food
handling, restaurants
etc.
Operations
function forms the core of all
businesses.
Operations
and Marketing
Value
addition refers to conversion of raw
materials to finished goods or
services.
Value
added often refers to the difference
between the cost of the raw material
and the price of
the
finished good.
The
revenues from selling goods
is used in betterment of existing product
or service or R &D,
investment
in new facilities and equipments
Weeding
out or eliminating non value
adding operations. E.g. storage of
goods which have been
produced
ahead of scheduled production,
increases storage and inventory
costs. reducing
storage
cost would reduce
transformation cost and thus
increase value
addition
Marketing
relates to selling of a good or service
of the organization through advertising
and
pricing
decisions.
7
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Marketing
department assesses the customer's needs
and communicate it to the operations
people
on short term and design people on the long term
basis.
Operations
people need information
about demand over a short range in
order to purchase raw
materials
or manage inventory or schedule
production plan where as the design
people need
information
to redesign or simply design new products or
services.
Marketing
provides valuable information
about the competitors customers needs
and
communicate
it to the operations people on short term and design
people on the long term
basis.
Finance
The
finance function focuses on
activities that relate to securing
resources at favorable
prices
and
then allocating these
resources through out the
organization.
Finance
and Operation Personnel exchange
information and expertise in the following
way.
Budgets
Economic
analysis of investment proposals
Provision
of funds
Historical
Evolution of Operations Management
Industrial
revolution (1770's)
Scientific
management (1911)
o
Mass
production
o
Interchangeable
parts
o
Division
of labor
Human
relations movement (1920-60)
Decision
models (1915, 1960-70's)
Influence
of Japanese manufacturers
Simple
Product Supply
Chain
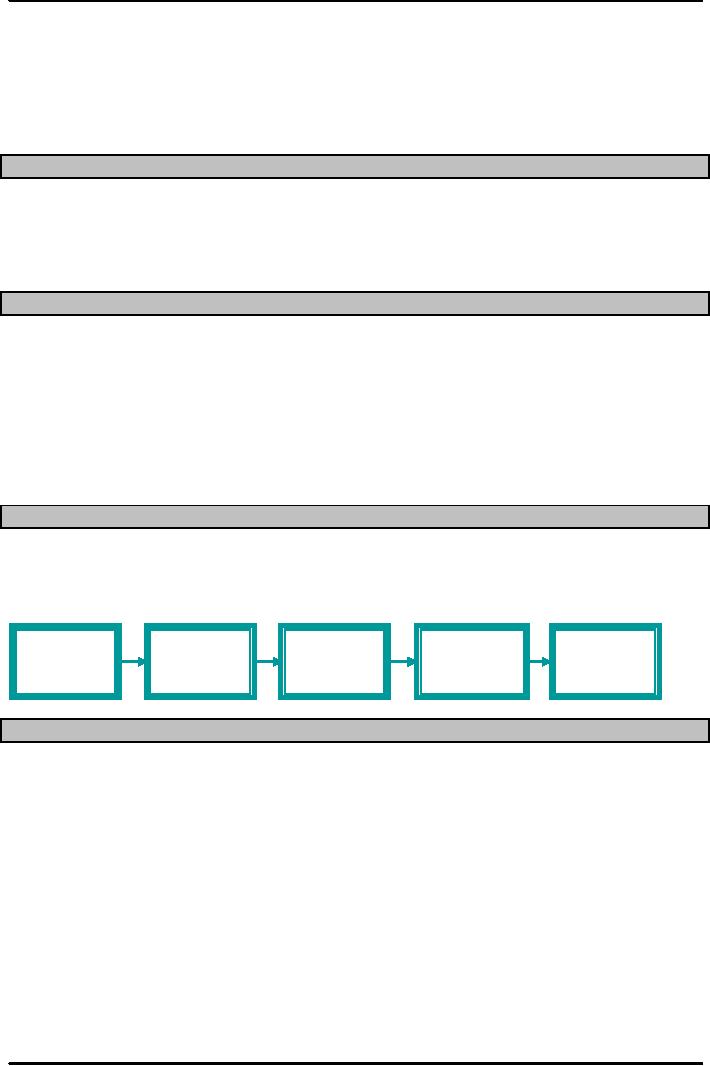
Supply
Chain: A sequence of activities and
organizations involved in producing and
delivering a good
or
service. Let's apply the same
concept to what we have on our breakfast
table every morning, a
simple
loaf
of bread.
Suppliers'
Direct
Final
Distributor
Producer
Suppliers
Suppliers
Consumer
Current
Issues in OM
An
operations manager needs to prepare
himself or herself for the
following issues in the years
to
come
whether its Pakistan or outside
Pakistan.
Effectively
consolidating the operations resulting
from mergers
Developing
flexible supply chains to enable
mass customization of products and
services
Managing
global supplier, production
and distribution
networks
Increased
"commoditization" of suppliers
Current
Issues in OM (cont'd)
Achieving
the "Service Factory"
Enhancing
value added services
Making
efficient use of Internet
technology
Achieving
good service from service
firms
8
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model