 |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
19
Facilities
layout corresponds to configuration of
departments, sections, work
centers, equipment
with
focus
being on movement of goods or services or
works. A traveler making use
of the railway platform,
or
bus station or airport would
be a good example of work
being moved through a
facility. Often poor
design
of productive system can
result in poor design of the facilities
layout. After 9, 11, most of
the
airports
in the western world have shown that
they are poorly designed to
handle air traffic
and
passengers
end up paying a heavy price in the
form of long waiting hours and even
people visit airports
to
see of their family or
friend travelers end up reaching the
lobby area. The reason
being no attention
was
paid at the time of design or
construction to separate boarding
lounge form the ticketing counter
or
lounge.
Such short comings plague organizations
and it's the task of the operations
manager to ensure
that
product as well as service layouts
match organizations short as well as
long term plans.
Basic
Layout Types
The
common Basic Layout Types
are
1.
Product/Service layout. A layout that
uses standardized processing operations to
achieve
smooth,
rapid, high-volume
flow
2.
Process layout. A Layout
that can handle varied
processing requirements
3.
Fixed Position layout. A
Layout in which the product or
project remains stationary,
and
workers,
materials, and equipment are moved as
needed
4.
Hybrid/Combination. A Layout that
makes use of the combination of Product,
Process or Fixed
Position
Layout.
PRODUCT
LAYOUT CHARACTERISTICS
1.
Product layouts are used to achieve a
smooth and rapid flow of
large volumes of goods
and
customers
through a system.
2.
The work is divided into a
series of standardized tasks, permitting
specialization of both
labor
and
equipment.
3.
The large volumes handled by
these systems make it
pertinent and necessary to invest
in
equipment
and job design.
4.
Layouts should be arranged to make the
best use of technological
processing abilities to
fulfill
the
requirements of both product and
services.
5.
In manufacturing environments the lines
are referred to as production
lines or assembly
lines,
depending
on the type of activity
involved.
6.
In services side, the word line
may or may not be used
like Healthcare/Hospital Services
line,
Carwash
(absence of word line here) or
Cafeteria Line.
7.
Without standardization, many of the
benefits of the repetitive processing
are lost.
8.
Product Layouts achieve a high degree of
labor and equipment utilization,
which tends to offset
their
high equipment costs.
9.
Operations are so closely tied up
that a mechanical failure or high
absenteeism (rains)
would
increase
vulnerability of the Systems.
10.
We can prevent breakdowns if we
religiously follow preventive maintenance
schedules,
inspection
and replacement of worn
parts.
Advantages
of Product Layout
1.
High rate of output.
2.
Low unit cost.
3.
Labor specialization.
4.
Low material handling
cost.
5.
High utilization of labor and
equipment.
6.
Established routing and
scheduling.
7.
Routing accounting and purchasing.
81
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Disadvantages
of Product Layout
1.
Creates dull, repetitive
jobs.
2.
Poorly skilled workers may
not maintain equipment or
quality of output of service.
3.
Fairly inflexible to changes in
volume.
4.
Highly susceptible to shutdowns.
5.
Needs preventive maintenance.
6.
Individual incentive plans are
impractical.
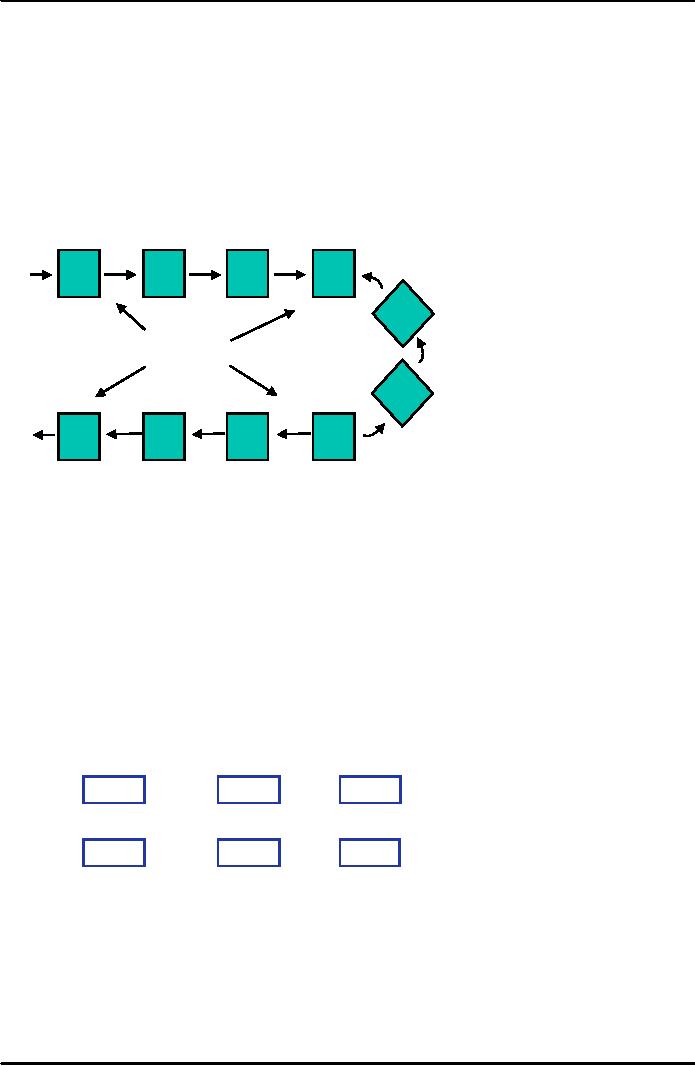
A
U-Shaped Production
Line
1
2
3
4
I
5
Worker
6
Ou
10
9
8
7
A
U-Shaped Production
Line
Straight
Line designs are often
not practical because of
space constraints. U shape Production
Line is
more
compact, and requires often half the
length of a Straight Production
Line.
U
shaped Layouts are a must
for teamwork where communication is
necessary. U shaped Layouts
allow
flexibility
in work assignments as workers
can handle adjacent stations as well as
stations on opposite
ends.
Sometimes U shaped production
line interferes with the
cross travel/movement of workers,
mobile
equipment.
Highly automated processes do not
require teamwork or communication, noise
or
contamination
factors then U shaped Production
Lines are not
required.
Process
Layout
Process
Layout
(Functional)
Dept.
Dept.
Dept.
Dept.
Dept.
Dept.
Used
for intermittent
processing
Job
Shop or Batch
82

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Product
Layout
Product
Layout
(Sequential)
Work
Work
Work
Station
Station
Station
Used
for Repetitive
Processing
Repetitive
or Continuous
Advantages
of Process Layouts
1.
Can
handle a variety of processing
requirements.
2.
Not
particularly vulnerable to equipment
failures.
3.
Equipment
used is less costly.
4.
Possible
to use individual incentive
plans.
Disadvantages
of Process Layouts
1.
In-process inventory costs can be
high.
2.
Challenging routing and
scheduling.
3.
Equipment utilization rates
are low.
4.
Material handling slow and
inefficient.
5.
Complexities often reduce
span of supervision.
83
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model