 |
FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS:The structure of the financial industry |
| << FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS & FINANCIAL MARKETS:Primarily Stores of Value |
| TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Future Value, Present Value >> |
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Lesson
7
FINANCIAL
INSTITUTIONS
Financial
Institutions
Structure
of Financial Industry
Time
Value of Money
Financial
Institutions
Financial
institutions are the firms
that provide access to the
financial markets;
They
sit between savers and
borrowers and so are known
as financial intermediaries.
Banks,
insurance companies, securities firms and
pension funds
A
system without financial
institutions would not work
very well for three
reasons
Individual
transactions between saver-lenders and borrower-spenders
would be extremely
expensive.
Lenders
need to evaluate the creditworthiness of
borrowers and then monitor them,
and
individuals
are not equipped to do
this.
Most
borrowers want to borrow long term,
while lenders favor short-term
loans
Role
of Financial Institutions
Reduce
transactions cost by specializing in the
issuance of standardized securities
Reduce
information costs of screening and
monitoring borrowers.
Curb
information asymmetries, helping to
ensure that resources flow
into their most
productive
uses
Make
long-term loans but allow
savers ready access to their
funds.
Provide
savers with financial instruments (more
liquid and less risky than
the individual stocks
and
bonds) that savers would
purchase directly in financial
markets
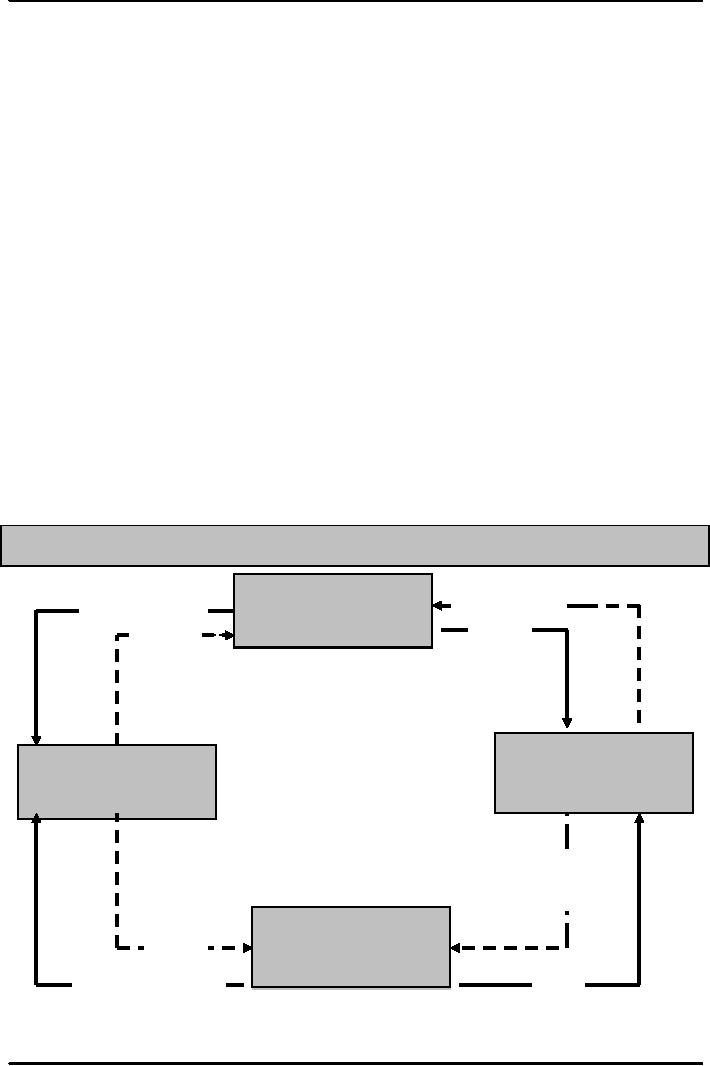
Figure:
Flow of funds through
Financial Institutions: Access to
Financial Markets
Financial
Institutions
Bonds
& Stocks
Bonds &
SStcks s
nds
& toock
that
act as Brokers
Funds
Funds
s
Borooroers/rS/Spends
rs
Br
rw we spendere
Lenders/Savers
(Primarily
Governments
(Primarily
and
Firms)
(Primarily
Households)
Governments
and
Loans,
Bonds,
Stocks
and
Real
Estate
Financial
Institutions
Financial
Institutions
that
transform assets
Funds
that
transform assets
Deposits
& Insurance
Funds
Policies
Indirect
Finance
20

Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
The
simplified Balance Sheet of a
Financial Institution
Assets
Liabilities
Bonds
Deposits
Stocks
Insurance
policies
Loans
Real
estate
The
structure of the financial
industry
The
structure of the financial
industry:
Financial
institutions or intermediaries can be
divided into two broad
categories
Depository
institutions -
take deposits and make
loans.
(Commercial
banks, savings banks, and credit
unions)
Nondepository
institutions
Insurance
companies, securities firms, mutual
fund companies, finance
companies, and pension
funds
Insurance
companies
Accept
premiums, which they invest in securities
and real estate in return
for promising
compensation
to policyholders should certain
events occurs (like death,
property losses, etc.)
Pension
funds
Invest
individual and company contributions into
stocks, bonds and real
estate in order to
provide
payments to retired
workers.
Securities
firms
They
include brokers, investment banks, and
mutual fund companies
Brokers
and investment banks issue
stocks and bonds to corporate customers,
trade them, and
advise
clients.
Mutual
fund companies pool the
resources of individuals and companies
and invest them in
portfolios
of bonds, stocks, and real
estate.
Government
Sponsored Enterprises:
Federal
credit agencies that provide
loans directly for farmers
and home mortgages, as well
as
guarantee
programs that insure the loans made by
private lenders.
HBFC,
ZTBL, Khushhali bank, SME
Bank
The
government also provides
retirement income and medical
care to the elderly (and
disabled)
through
Social Security and
Medicare.
Finance
Companies:
Raise
funds directly in the financial
markets in order to make loans to
individuals and firms.
The
monetary aggregates are made
up of liabilities of commercial banks, so
clearly the financial
structure
is tied to the availability of money and
credit.
21
Table of Contents:
- TEXT AND REFERENCE MATERIAL & FIVE PARTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- FIVE CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND BANKING:Time has Value
- MONEY & THE PAYMENT SYSTEM:Distinctions among Money, Wealth, and Income
- OTHER FORMS OF PAYMENTS:Electronic Funds Transfer, E-money
- FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Indirect Finance, Financial and Economic Development
- FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS & FINANCIAL MARKETS:Primarily Stores of Value
- FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS:The structure of the financial industry
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Future Value, Present Value
- APPLICATION OF PRESENT VALUE CONCEPTS:Compound Annual Rates
- BOND PRICING & RISK:Valuing the Principal Payment, Risk
- MEASURING RISK:Variance, Standard Deviation, Value at Risk, Risk Aversion
- EVALUATING RISK:Deciding if a risk is worth taking, Sources of Risk
- BONDS & BONDS PRICING:Zero-Coupon Bonds, Fixed Payment Loans
- YIELD TO MATURIRY:Current Yield, Holding Period Returns
- SHIFTS IN EQUILIBRIUM IN THE BOND MARKET & RISK
- BONDS & SOURCES OF BOND RISK:Inflation Risk, Bond Ratings
- TAX EFFECT & TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATE:Expectations Hypothesis
- THE LIQUIDITY PREMIUM THEORY:Essential Characteristics of Common Stock
- VALUING STOCKS:Fundamental Value and the Dividend-Discount Model
- RISK AND VALUE OF STOCKS:The Theory of Efficient Markets
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Pooling Savings
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES (CONTINUED):Providing Liquidity
- BANKING:The Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks, Assets: Uses of Funds
- BALANCE SHEET OF COMMERCIAL BANKS:Bank Capital and Profitability
- BANK RISK:Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Interest-Rate Risk
- INTEREST RATE RISK:Trading Risk, Other Risks, The Globalization of Banking
- NON- DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS:Insurance Companies, Securities Firms
- SECURITIES FIRMS (Continued):Finance Companies, Banking Crisis
- THE GOVERNMENT SAFETY NET:Supervision and Examination
- THE GOVERNMENT'S BANK:The Bankers' Bank, Low, Stable Inflation
- LOW, STABLE INFLATION:High, Stable Real Growth
- MEETING THE CHALLENGE: CREATING A SUCCESSFUL CENTRAL BANK
- THE MONETARY BASE:Changing the Size and Composition of the Balance Sheet
- DEPOSIT CREATION IN A SINGLE BANK:Types of Reserves
- MONEY MULTIPLIER:The Quantity of Money (M) Depends on
- TARGET FEDERAL FUNDS RATE AND OPEN MARKET OPERATION
- WHY DO WE CARE ABOUT MONETARY AGGREGATES?The Facts about Velocity
- THE FACTS ABOUT VELOCITY:Money Growth + Velocity Growth = Inflation + Real Growth
- THE PORTFOLIO DEMAND FOR MONEY:Output and Inflation in the Long Run
- MONEY GROWTH, INFLATION, AND AGGREGATE DEMAND
- DERIVING THE MONETARY POLICY REACTION CURVE
- THE AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE:Shifting the Aggregate Demand Curve
- THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE:Inflation Shocks
- EQUILIBRIUM AND THE DETERMINATION OF OUTPUT AND INFLATION
- SHIFTS IN POTENTIAL OUTPUT AND REAL BUSINESS CYCLE THEORY