 |
BALANCE SHEET OF COMMERCIAL BANKS:Bank Capital and Profitability |
| << BANKING:The Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks, Assets: Uses of Funds |
| BANK RISK:Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Interest-Rate Risk >> |

Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Lesson
24
BALANCE
SHEET OF COMMERCIAL
BANKS
Balance
Sheet of Commercial Banks
Assets:
uses of funds
Bank
Capital and Profitability
Off-Balance-Sheet
Activities
Bank
Risk
Liquidity
Risk
Credit
Risk
Interest
Rate Risk
Trading
Risk
Other
Risks
Liabilities:
Sources of Funds
Checkable
Deposits
Non-transactions
Deposits
Borrowings
Discount
loans
Federal
funds market
Checkable
deposits:
A
typical bank will offer 6 or
more types of checking accounts.
In
recent decades these
deposits have declined because the
accounts pay low interest
rates
Nontransactions
Deposits:
These
include savings and time deposits
and account for nearly
two-thirds of all
commercial
bank
liabilities.
When
you place your savings in a Certificate
of Deposit (CD) at the bank, it is as if
you are
buying
a bond issued by that
bank
CDs
can vary in terms of their
value, the large ones can be
bought and sold in financial
markets
Borrowings:
Banks
borrow from the central bank
(discount loans)
They
can borrow from other
banks with excessive
reserves in the inter-bank money
market.
Banks
can also borrow by using a
repurchase agreement or repo,
which is a short-term
collateralized
loan
A
security is exchanged for cash,
with the agreement that the parties
will reverse the transaction
on
a specific future date
(might be as soon as the next
day)
77
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
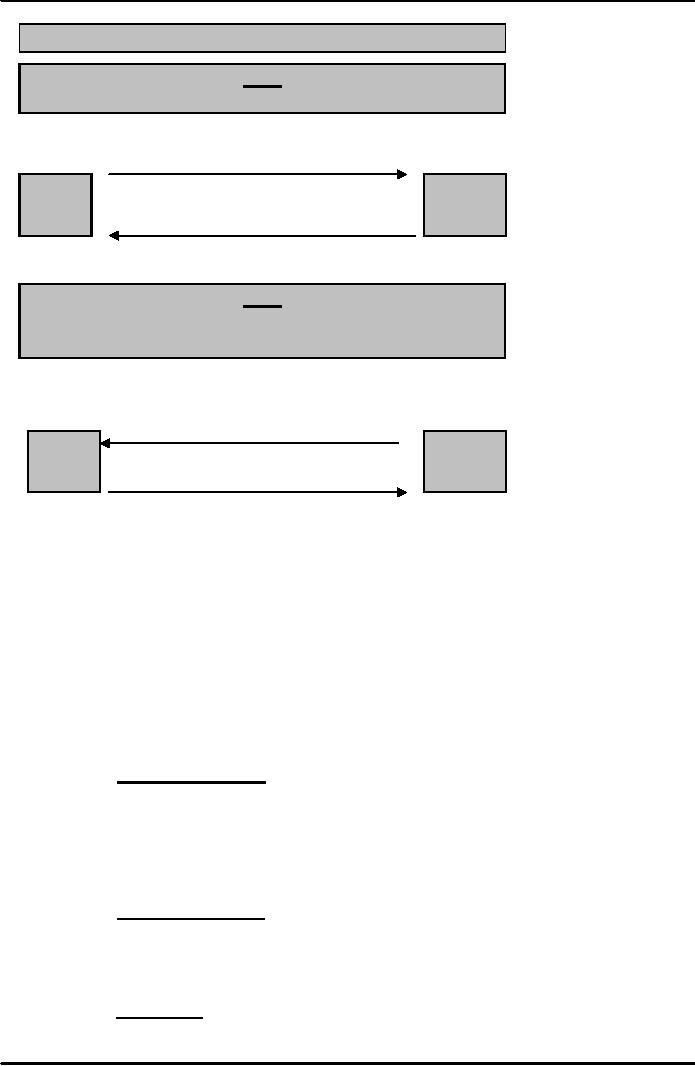
Mechanics
of an Overnight Repurchase
Agreement
Day
1
Bank
sells U.S. Treasury bill to
pension fund in exchange for
cash
U.S
Treasury bill to pension
fund
Pension
Bank
Fund
Cash
to bank
Day
2
Bank
repurchases U.S. Treasury bill
from the pension fund in
exchange
for
cash plus
interest
U.S.
Treasury bill returned to
bank
Pension
Bank
Fund
Cash
+ interest paid to pension
fund
Bank
Capital and
Profitability
The
net worth of banks is called
bank capital; it is the owners'
stake in the bank
Capital
is the cushion that banks have against a
sudden drop in the value of
their assets or an
unexpected
withdrawal of liabilities
An
important component of bank capital is
loan loss reserves, an amount the
bank sets aside to
cover
potential losses from
defaulted loans
It
is reduced by the defaulted loans
written-off
There
are several basic measures of
bank profitability
Return
on Assets,
ROA
= Net profit after
taxes
Total
bank assets
It
is a measure of how efficiently a
particular bank uses its
assets
A
manager can compare the
performance of bank's various lines of
businesses by looking at
different
units' ROA
The
bank's return to its owners is
measured by the Return on
Equity
ROE
= Net profit after
taxes
Bank
capital
ROA
and ROE are related to
leverage
A
measure of leverage is the ratio of
bank assets to bank capital.
Multiplying ROA by this
ratio
yields
ROE
ROA
x Bank Assets
Bank
Capital
78
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
=
Net profit after taxes x
Bank Assets
Total
bank assets
Bank
Capital
=
Net profit after
taxes
=
ROE
Bank
Capital
Return
on equity tends to be higher
for larger banks, suggesting the existence of
economies of
scale
Net
interest income is another measure of
profitability;
It
is the difference between the interest the bank
pays and what it
receives
It
can also be expressed as a
percentage of total assets to
yield (net interest margin). It is
the
bank's
interest rate spread
Well
run banks have high net interest income
and a high net interest margin.
If
a bank's net interest margin is currently
improving, its profitability is
likely to improve in the
future.
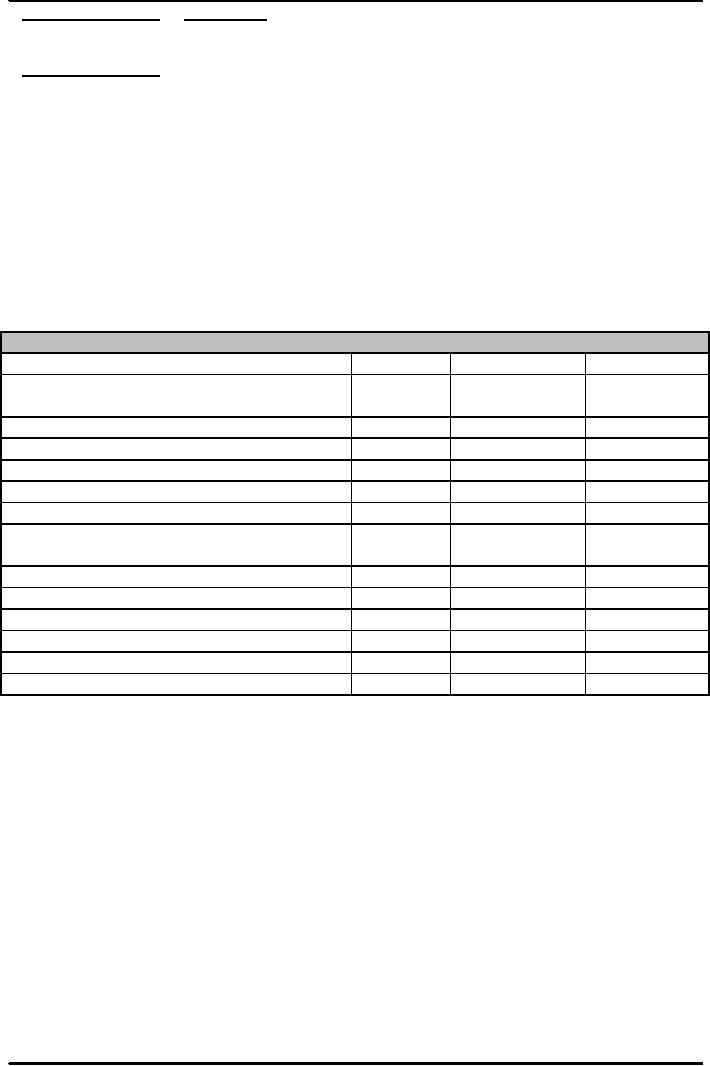
Table:
Profitability of U.S. Commercial Banks(
in millions of $, except bottom
four rows)
Items
1991
1996
2001
A.
Interest
income-interest expense
(Net
$121,,288
$161,172
$210,809
interest
income)
B.
Other
revenue
58,482
92,515
153,734
C.
Operating
costs
124,233
159,241
218,706
D.
Gross
profit (A+B-C)
55,537
94,446
145,837
E.
Loan
losses(provisions)
34,128
15,483
41,008
F.
Net
operating profit
(D-E)
21,409
78,963
104,829
G.
Realized
capital gains from sale of
real
2,971
530
4,434
estate
H.
Net
profits before taxes
(F+G)
24,380
79,493
109,263
I.
Assets
3,420,381
4,554,234
6,454,543
Net
interest margin (A/I)
0.0355%
0.0354%
0.0327%
Return
on assets (H/I) (ROA)
0.0071
0.0175
0.0169
Return
on equity (ROE)
0.1258
0.2147
0.1860
Net
interest income/ Total
income [A/(A+B)]
0.6747
0.6353
0.5782
Off-Balance-Sheet
Activities
Banks
engage in these activities in
order to generate fee income;
these activities
include
providing
trusted customers with lines of
credit
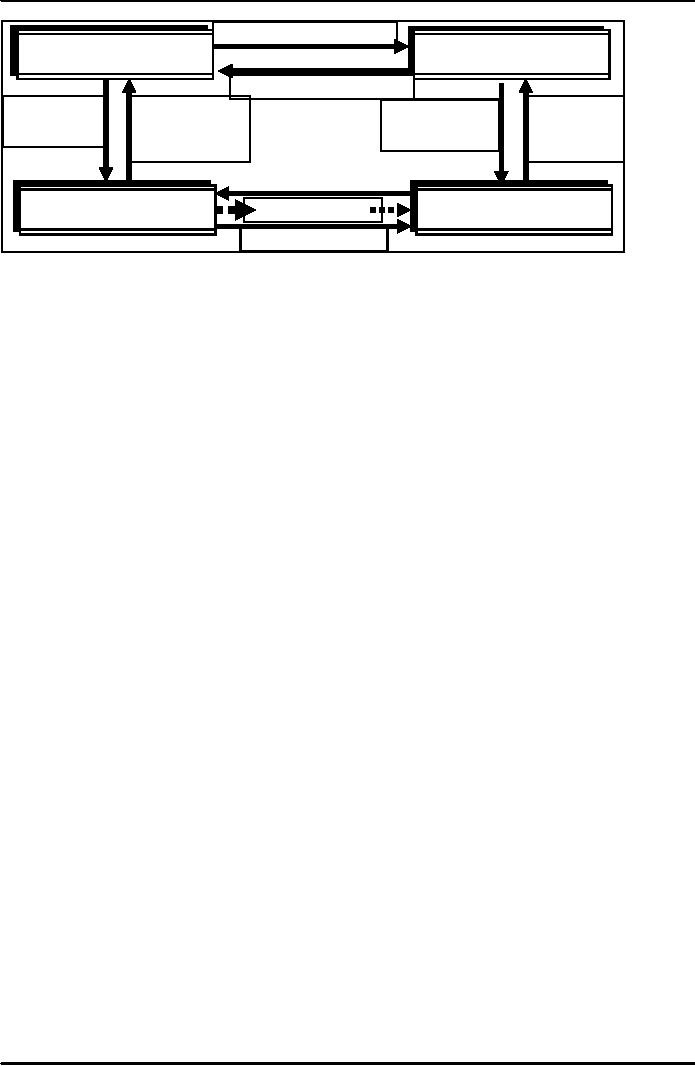
Letters
of credit are another important
off-balance-sheet activity; they
guarantee that a
customer
will
be able to make a promised
payment.
In
so doing, the bank, in exchange
for a fee, substitutes its
own guarantee for that of
the
customer
and enables a transaction to go
forward
79
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Sale
Contract
Buyer
Seller
(Importer)
(Exporter)
Deliver
Goods
Request
Documents
Deliver
Present
for
Credit
&
Claim for
Letter
of
Documents
Payment
Credit
Present
Documents
Importer's
Bank
Exporter's
Bank
Payment
(Issuing
Bank)
(Advising
Bank)
Send
Credit
A
standby letter of credit is a form of
insurance; the bank promises that it
will repay the lender
should
the borrower default
Off-balance-sheet
activities create risk for
financial institutions and so have come
under
increasing
scrutiny in recent
years
80
Table of Contents:
- TEXT AND REFERENCE MATERIAL & FIVE PARTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- FIVE CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND BANKING:Time has Value
- MONEY & THE PAYMENT SYSTEM:Distinctions among Money, Wealth, and Income
- OTHER FORMS OF PAYMENTS:Electronic Funds Transfer, E-money
- FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Indirect Finance, Financial and Economic Development
- FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS & FINANCIAL MARKETS:Primarily Stores of Value
- FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS:The structure of the financial industry
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Future Value, Present Value
- APPLICATION OF PRESENT VALUE CONCEPTS:Compound Annual Rates
- BOND PRICING & RISK:Valuing the Principal Payment, Risk
- MEASURING RISK:Variance, Standard Deviation, Value at Risk, Risk Aversion
- EVALUATING RISK:Deciding if a risk is worth taking, Sources of Risk
- BONDS & BONDS PRICING:Zero-Coupon Bonds, Fixed Payment Loans
- YIELD TO MATURIRY:Current Yield, Holding Period Returns
- SHIFTS IN EQUILIBRIUM IN THE BOND MARKET & RISK
- BONDS & SOURCES OF BOND RISK:Inflation Risk, Bond Ratings
- TAX EFFECT & TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATE:Expectations Hypothesis
- THE LIQUIDITY PREMIUM THEORY:Essential Characteristics of Common Stock
- VALUING STOCKS:Fundamental Value and the Dividend-Discount Model
- RISK AND VALUE OF STOCKS:The Theory of Efficient Markets
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Pooling Savings
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES (CONTINUED):Providing Liquidity
- BANKING:The Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks, Assets: Uses of Funds
- BALANCE SHEET OF COMMERCIAL BANKS:Bank Capital and Profitability
- BANK RISK:Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Interest-Rate Risk
- INTEREST RATE RISK:Trading Risk, Other Risks, The Globalization of Banking
- NON- DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS:Insurance Companies, Securities Firms
- SECURITIES FIRMS (Continued):Finance Companies, Banking Crisis
- THE GOVERNMENT SAFETY NET:Supervision and Examination
- THE GOVERNMENT'S BANK:The Bankers' Bank, Low, Stable Inflation
- LOW, STABLE INFLATION:High, Stable Real Growth
- MEETING THE CHALLENGE: CREATING A SUCCESSFUL CENTRAL BANK
- THE MONETARY BASE:Changing the Size and Composition of the Balance Sheet
- DEPOSIT CREATION IN A SINGLE BANK:Types of Reserves
- MONEY MULTIPLIER:The Quantity of Money (M) Depends on
- TARGET FEDERAL FUNDS RATE AND OPEN MARKET OPERATION
- WHY DO WE CARE ABOUT MONETARY AGGREGATES?The Facts about Velocity
- THE FACTS ABOUT VELOCITY:Money Growth + Velocity Growth = Inflation + Real Growth
- THE PORTFOLIO DEMAND FOR MONEY:Output and Inflation in the Long Run
- MONEY GROWTH, INFLATION, AND AGGREGATE DEMAND
- DERIVING THE MONETARY POLICY REACTION CURVE
- THE AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE:Shifting the Aggregate Demand Curve
- THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE:Inflation Shocks
- EQUILIBRIUM AND THE DETERMINATION OF OUTPUT AND INFLATION
- SHIFTS IN POTENTIAL OUTPUT AND REAL BUSINESS CYCLE THEORY