 |
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Lesson
23
BANKING
Banking
Types
of banks
Balance
Sheet of Commercial Banks
Assets
Liabilities
Banking
Banking
is a combination of businesses designed to
deliver the services
Pool
the savings of and making loans
Diversification
Access
to the payments system
Accounting
and record-keeping
The
intent of banks is to profit
from each of these lines of
business
There
are three basic types of depository
institutions:
Commercial
banks,
Savings
institutions
Credit
unions
Commercial
banks
They
accept deposits and use the
proceeds to make consumer,
commercial and real estate
loans.
Community
banks
Small
local banks focused on
serving consumers and small
business
Regional
and Super-regional banks
They
make consumer, residential, commercial
and industrial loans
Money
center bank
These
banks rely more on borrowing
for their funding
Saving
Institutions
Financial
intermediaries to serve households and
individuals
Provide
mortgage and lending as well as saving
deposit services
Credit
Unions
Nonprofit
depository institutions that
are owned by people with a
common bond
These
unions specialize in making small
consumer loans
The
Balance Sheet of Commercial
Banks
Balance
Sheet Identity
Total
Bank Assets = Total Bank
Liabilities + Bank
Capital
Banks
obtain funds from individual
depositors and business as well as by
borrowing from other
financial
institutions and through the financial
markets.
They
use these funds to make
loans, purchase marketable securities and
hold cash.
The
difference between a bank's assets
and liabilities is the bank's
capital or Net Worth
The
bank's profits come both
from service fees and the
difference between interest earned
and
interest
paid.
74
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
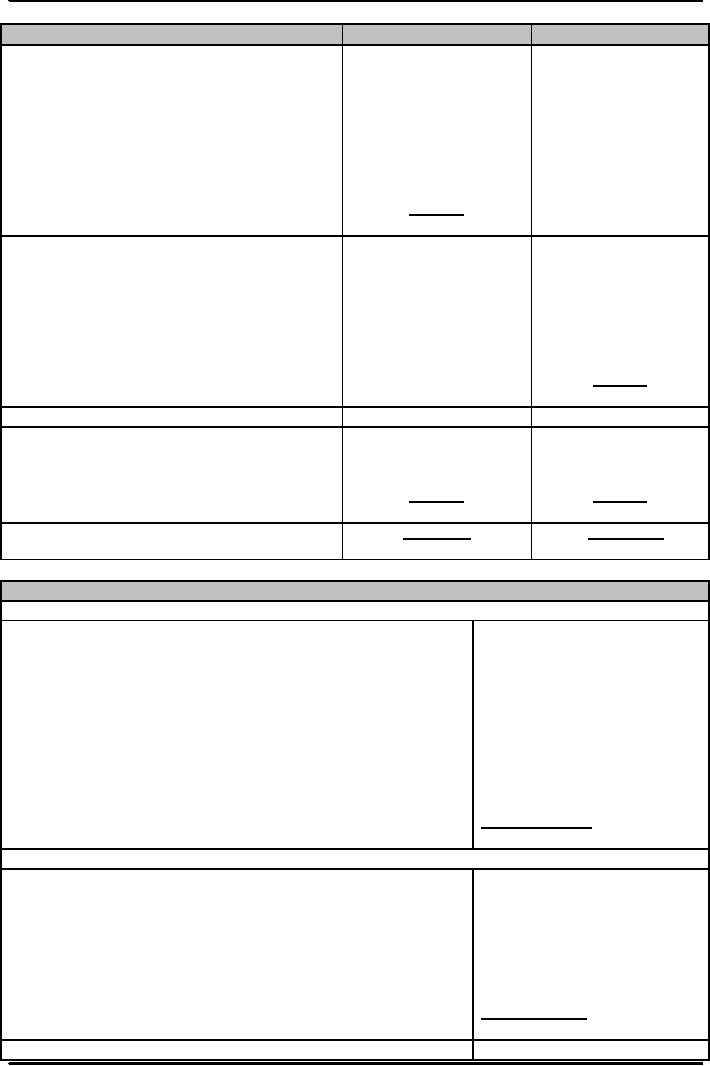
ITEMS
2005
(Rs.000)
2004
(Rs.000)
ASSETS
Cash
and balances with treasury
banks
23,665,549
23,833,253
Balances
with other banks
1,469,333
5,708,323
Lendings
to financial institutions
9,998,828
10,965,297
Investments
net
69,481,487
67,194,971
Advances
net
180,322,753
137,317,773
Other
assets net
5,464,426
6,154,370
Operating
fixed assets
8,182,454
7,999,821
Deferred
tax assets - net
191,967
_________
298,776,797
259,173,808
LIABILITIES
7,566,684
Bills
payable
8,536,674
7,590,864
Borrowings
from financial
institutions
27,377,502
221,069,158
Deposits
and other accounts
229,345,178
1,598,720
Sub-ordinated
loan
1,598,080
----
Liabilities
against assets subject to finance
lease
-----
6,525,999
Other
liabilities
8,611,600
269,499
Deferred
tax liabilities - net
________
275,469,034
244,620,924
NET
ASSETS
23,307,763
14,552,884
REPRESENTED
BY:
3,371,800
Share
capital
4,265,327
5,661,553
Reserves
13,408,005
165,208
Unappropriated
profit
210,662
17,883,994
9,198,561
5,423,769
5,354,323
Surplus
on revaluation of assets - net of
tax
23,307,763
14,552,884
Balance
Sheet of U.S Commercial Banks, August
2004
Assets
in billions of dollars(numbers in parentheses are %age
of total assets)
321.6
(4.1)
Cash
items (including reserves)
1,893.5
(23.9)
Securities
1,1707.7
(14.8)
o
U.S.
Government and agency
722.8
(9.1)
o
State
and local government and
other
5,044.6
(63.7)
Loans
887.1
(11.2)
o
Commercial
and industrial
2,411.6
(30.5)
o
Real
estate (including mortgage)
672.3
(8.5)
o
Consumer
364.7
(4.6)
o
Interbank
708.9
(9.0)
o
Other
655.1
(8.3)
Other
assets
Total
Commercial Bank
Assets
7,914.8
Liabilities
in billions of dollars (numbers in parentheses are
%age of total
liabilities)
645.0
(8.9)
Checkable
deposits
4,487.7
(62.3)
Nontransactions
deposits
3,340.9
(46.3)
o
Savings
deposits and time
deposits
1,146.8
(15.9)
o
Large,
negotiable time
deposits
1,589.0
(22.0)
Borrowings
459.1
(6.4)
o
From
banks in U.S.
1,129.9
(15.7)
o
From
nonbanks in U.S.
487.4
(6.8)
Other
liabilities
Total
Commercial Bank
Liabilities
7,209.1
Bank
assets Bank Liabilities =
Bank Capital
705.7
75

Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Assets:
Uses of Funds
Cash
Items
Reserves
Cash
items in process of collection
Vault
cash
Securities
Secondary
reserves
Loans
Cash
Items
Reserves
Includes
cash in the bank's vault and
its deposits at the central
bank
Held
to meet customers' withdrawal
requests
Cash
items in the process of
collections
Uncollected
funds the bank expects to
receive
The
balances of accounts that
banks hold at other banks
(correspondent banking)
Because
cash earns no interest, it has a
high opportunity cost. So
banks minimize the amount of
cash
holding
Securities:
Stocks
T-Bills
Government
and corporate bonds
Securities
are sometimes called
secondary reserves because
they are highly liquid and
can be
sold
quickly if the bank needs
cash.
Loans:
The
primary asset of modern commercial
banks;
Business
loans (commercial and industrial
loans),
Real
estate loans,
Consumer
loans,
Inter-bank
loans,
Loans
for the purchase of other
securities
The
primary difference among the various
types of depository institutions is in the
composition
of
their loan portfolios
Commercial
banks make loans primarily to
business
Savings
and loans provide mortgages to
individuals
Credit
unions specialize in consumer
loans
76
Table of Contents:
- TEXT AND REFERENCE MATERIAL & FIVE PARTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- FIVE CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND BANKING:Time has Value
- MONEY & THE PAYMENT SYSTEM:Distinctions among Money, Wealth, and Income
- OTHER FORMS OF PAYMENTS:Electronic Funds Transfer, E-money
- FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Indirect Finance, Financial and Economic Development
- FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS & FINANCIAL MARKETS:Primarily Stores of Value
- FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS:The structure of the financial industry
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Future Value, Present Value
- APPLICATION OF PRESENT VALUE CONCEPTS:Compound Annual Rates
- BOND PRICING & RISK:Valuing the Principal Payment, Risk
- MEASURING RISK:Variance, Standard Deviation, Value at Risk, Risk Aversion
- EVALUATING RISK:Deciding if a risk is worth taking, Sources of Risk
- BONDS & BONDS PRICING:Zero-Coupon Bonds, Fixed Payment Loans
- YIELD TO MATURIRY:Current Yield, Holding Period Returns
- SHIFTS IN EQUILIBRIUM IN THE BOND MARKET & RISK
- BONDS & SOURCES OF BOND RISK:Inflation Risk, Bond Ratings
- TAX EFFECT & TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATE:Expectations Hypothesis
- THE LIQUIDITY PREMIUM THEORY:Essential Characteristics of Common Stock
- VALUING STOCKS:Fundamental Value and the Dividend-Discount Model
- RISK AND VALUE OF STOCKS:The Theory of Efficient Markets
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Pooling Savings
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES (CONTINUED):Providing Liquidity
- BANKING:The Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks, Assets: Uses of Funds
- BALANCE SHEET OF COMMERCIAL BANKS:Bank Capital and Profitability
- BANK RISK:Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Interest-Rate Risk
- INTEREST RATE RISK:Trading Risk, Other Risks, The Globalization of Banking
- NON- DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS:Insurance Companies, Securities Firms
- SECURITIES FIRMS (Continued):Finance Companies, Banking Crisis
- THE GOVERNMENT SAFETY NET:Supervision and Examination
- THE GOVERNMENT'S BANK:The Bankers' Bank, Low, Stable Inflation
- LOW, STABLE INFLATION:High, Stable Real Growth
- MEETING THE CHALLENGE: CREATING A SUCCESSFUL CENTRAL BANK
- THE MONETARY BASE:Changing the Size and Composition of the Balance Sheet
- DEPOSIT CREATION IN A SINGLE BANK:Types of Reserves
- MONEY MULTIPLIER:The Quantity of Money (M) Depends on
- TARGET FEDERAL FUNDS RATE AND OPEN MARKET OPERATION
- WHY DO WE CARE ABOUT MONETARY AGGREGATES?The Facts about Velocity
- THE FACTS ABOUT VELOCITY:Money Growth + Velocity Growth = Inflation + Real Growth
- THE PORTFOLIO DEMAND FOR MONEY:Output and Inflation in the Long Run
- MONEY GROWTH, INFLATION, AND AGGREGATE DEMAND
- DERIVING THE MONETARY POLICY REACTION CURVE
- THE AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE:Shifting the Aggregate Demand Curve
- THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE:Inflation Shocks
- EQUILIBRIUM AND THE DETERMINATION OF OUTPUT AND INFLATION
- SHIFTS IN POTENTIAL OUTPUT AND REAL BUSINESS CYCLE THEORY