 |
FIVE CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND BANKING:Time has Value |
| << TEXT AND REFERENCE MATERIAL & FIVE PARTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM |
| MONEY & THE PAYMENT SYSTEM:Distinctions among Money, Wealth, and Income >> |

Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Lesson
2
FIVE
CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND
BANKING
1.
Time has Value
Time
affects the value of financial
instruments.
Interest
payments exist because of
time properties of financial
instruments
Example
At
6% interest rate, 4 year loan of $10,000
for a car
Requires
48 monthly installments of $235
each
Total
repayment = $235 x 48 = $11,280
$11,280
>
$10,000
(Total
repayment)
(Amount
of loan)
Reason:
you are compensating the lender
for the time during which
you use the funds
2.
Risk Requires Compensation
In
a world of uncertainty, individuals
will accept risk only if
they are compensated in
some
form.
The
world is filled with
uncertainty; some possibilities
are welcome and some are
not
To
deal effectively with risk
we must consider the full range of
possibilities:
Eliminate
some risks,
Reduce
others,
Pay
someone else to assume
particularly onerous risks,
and
Just
live with what's
left
Investors
must be paid to assume risk,
and the higher the risk the higher the
required payment
Car
insurance is an example of paying for
someone else to shoulder a
risk you don't want
to
take.
Both parties to the transaction
benefit
Drivers
are sure of compensation in the event of
an accident
The
insurance companies make profit by
pooling the insurance premiums and investing
them
Now
we can understand the valuation of a
broad set of financial
instruments
E.g.,
lenders charge higher rates if there is a
chance the borrower will
not repay.
3.
Information is the basis for
decisions
We
collect information before
making decisions
The
more important the decision the more
information we collect
The
collection and processing of information
is the basis of foundation of the
financial system.
Some
transactions are arranged so that
information is NOT
needed
Stock
exchanges are organized to
eliminate the need for
costly information gathering and
thus
facilitate
the exchange of securities
One
way or another, information is the
key to the financial
system
4.
Markets set prices and
allocate resources
Markets
are the core of the economic system; the
place, physical or virtual,
Where
buyers and sellers
meet
Where
firms go to issue stocks and
bonds,
Where
individuals go to purchase
assets
Financial
markets are essential to the
economy,
Channeling
its resources
Minimizing
the cost of gathering
information
Making
transactions
Well-developed
financial markets are a
necessary precondition for
healthy economic growth
The
role of setting prices and
allocation of resources makes
the markets vital sources
of
information
Markets
provide the basis for the
allocation of capital by attaching
prices to different stocks
or
bonds
3

Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Financial
markets require rules to operate properly
and authorities to police
them
The
role of the govt. is to ensure
investor protection
Investor
will only participate if
they perceive the markets
are fair
5.
Stability improves welfare
To
reduce risk, the volatility
must be reduced
Govt.
policymakers play pivotal
role in reducing some
risks
A
stable economy reduces risk
and improves everyone's
welfare.
By
stabilizing the economy as whole monetary
policymakers eliminate risks that
individuals
can't
and so improve everyone's
welfare in the process.
Stabilizing
the economy is the primary function of
central banks
A
stable economy grows faster than an unstable
one
Financial
System Promotes Economic
Efficiency
The
Financial System makes it
Easier to Trade
Facilitate
Payments - bank checking
accounts
Channel
Funds from Savers to
Borrowers
Enable
Risk Sharing - Classic
examples are insurance and
forward markets
1.
Facilitate Payments
Cash
transactions (Trade "value for
value"). Could hold a lot of
cash on hand to pay for
things
Financial
intermediaries provide checking
accounts, credit cards,
debit cards, ATMs
Make
transactions easier.
2.
Channel Funds from Savers to
Borrowers
Lending
is a form of trade (Trade "value
for a promise")
Give
up purchasing power today in exchange for
purchasing power in the future.
Savers:
have more funds than they
currently need; would like to
earn capital income
Borrowers:
need more funds than they
currently have; willing and
able to repay with interest
in
the
future.
Why
is this important?
A)
Allows
those without funds to
exploit profitable investment
opportunities.
Commercial
loans to growing businesses;
Venture
capital;
Student
loans (investment in human
capital);
Investment
in physical capital and new
products/processes to promote economic
growth
B)
Financial
System allows the timing of income and
expenditures to be decoupled.
Household
earning potential starts
low, grows rapidly until the
mid 50s, and then declines
with
age.
Financial
system allows households to borrow
when young to prop up
consumption (house
loans,
car loans), repay and then
accumulate wealth during
middle age, then live
off wealth
during
retirement.
4
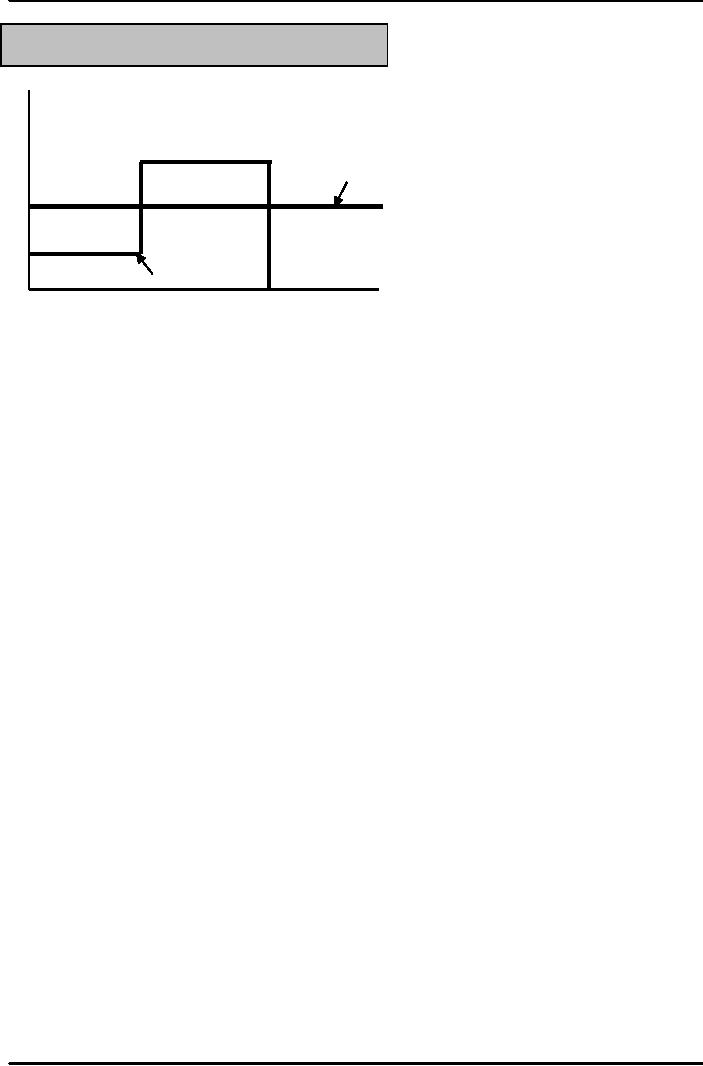
Money
& Banking MGT411
VU
Figure: Channel Funds
from Savers to Borrowers
$
Consumption
Dissavings
Dissavings
Income
Time
Retirement
Begins
3.
Enable Risk
Sharing
The
world is an uncertain place. The
financial system allows trade in
risk. (Trade "value for
a
promise")
Two
principal forms of trade in risk are
insurance and forward contracts.
Suppose
everyone has a 1/1000 chance
of dying by age 40 and one would
need $1 million to
replace
lost income to provide for
their family.
What
are your options to address
this risk?
Summary
Five
Core Principles of Money and
Banking
Time
has Value
Risk
Requires Compensation
Information
is the basis for decisions
Markets
set prices and allocate
resources
Stability
improves welfare
Financial
System Promotes Economic
Efficiency
Facilitate
Payments
Channel
Funds from Savers to
Borrowers
Enable
Risk Sharing
5
Table of Contents:
- TEXT AND REFERENCE MATERIAL & FIVE PARTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
- FIVE CORE PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND BANKING:Time has Value
- MONEY & THE PAYMENT SYSTEM:Distinctions among Money, Wealth, and Income
- OTHER FORMS OF PAYMENTS:Electronic Funds Transfer, E-money
- FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Indirect Finance, Financial and Economic Development
- FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS & FINANCIAL MARKETS:Primarily Stores of Value
- FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS:The structure of the financial industry
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Future Value, Present Value
- APPLICATION OF PRESENT VALUE CONCEPTS:Compound Annual Rates
- BOND PRICING & RISK:Valuing the Principal Payment, Risk
- MEASURING RISK:Variance, Standard Deviation, Value at Risk, Risk Aversion
- EVALUATING RISK:Deciding if a risk is worth taking, Sources of Risk
- BONDS & BONDS PRICING:Zero-Coupon Bonds, Fixed Payment Loans
- YIELD TO MATURIRY:Current Yield, Holding Period Returns
- SHIFTS IN EQUILIBRIUM IN THE BOND MARKET & RISK
- BONDS & SOURCES OF BOND RISK:Inflation Risk, Bond Ratings
- TAX EFFECT & TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATE:Expectations Hypothesis
- THE LIQUIDITY PREMIUM THEORY:Essential Characteristics of Common Stock
- VALUING STOCKS:Fundamental Value and the Dividend-Discount Model
- RISK AND VALUE OF STOCKS:The Theory of Efficient Markets
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES:Pooling Savings
- ROLE OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES (CONTINUED):Providing Liquidity
- BANKING:The Balance Sheet of Commercial Banks, Assets: Uses of Funds
- BALANCE SHEET OF COMMERCIAL BANKS:Bank Capital and Profitability
- BANK RISK:Liquidity Risk, Credit Risk, Interest-Rate Risk
- INTEREST RATE RISK:Trading Risk, Other Risks, The Globalization of Banking
- NON- DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS:Insurance Companies, Securities Firms
- SECURITIES FIRMS (Continued):Finance Companies, Banking Crisis
- THE GOVERNMENT SAFETY NET:Supervision and Examination
- THE GOVERNMENT'S BANK:The Bankers' Bank, Low, Stable Inflation
- LOW, STABLE INFLATION:High, Stable Real Growth
- MEETING THE CHALLENGE: CREATING A SUCCESSFUL CENTRAL BANK
- THE MONETARY BASE:Changing the Size and Composition of the Balance Sheet
- DEPOSIT CREATION IN A SINGLE BANK:Types of Reserves
- MONEY MULTIPLIER:The Quantity of Money (M) Depends on
- TARGET FEDERAL FUNDS RATE AND OPEN MARKET OPERATION
- WHY DO WE CARE ABOUT MONETARY AGGREGATES?The Facts about Velocity
- THE FACTS ABOUT VELOCITY:Money Growth + Velocity Growth = Inflation + Real Growth
- THE PORTFOLIO DEMAND FOR MONEY:Output and Inflation in the Long Run
- MONEY GROWTH, INFLATION, AND AGGREGATE DEMAND
- DERIVING THE MONETARY POLICY REACTION CURVE
- THE AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE:Shifting the Aggregate Demand Curve
- THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE:Inflation Shocks
- EQUILIBRIUM AND THE DETERMINATION OF OUTPUT AND INFLATION
- SHIFTS IN POTENTIAL OUTPUT AND REAL BUSINESS CYCLE THEORY