 |

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Lecture
39
REVIEW-II
Lecture 39
is a second review and is mainly to
review what ever we covered so
far from lectures 25 to
38.
Second part of our course
was mainly focusing the team
dynamics part. We tried to
understand
group,
team and their dynamics.
We
started our lecture number 25
with group dynamics.
Group
-
two or more people with common
interests or objectives.
Team
-
a small number of people with
complementary skills who are
committed to a common mission,
performance
goals, and approach for which they
hold themselves mutually
accountable
A
team
is
a formal work group in which
there is a high level of interaction
among group members
who
work
intensely together to achieve a common
goal. A group whose members
work intensely with
each
other
to achieve a specific, common goal or
objective is known as Team. All
teams are groups but
not
all
groups are teams.
Teams
often are difficult to
form.
It
takes time for members to
learn how to work
together.
A
group/team is effective
when
it satisfies three criteria:
o
Production
output: the product
of the group's work must
meet or exceed standards of
quality
and
quantity
o
Member
satisfaction: membership in the
group must provide people
with short-term
satisfaction
and facilitate their long-term
growth and development
o
Capacity
for continued cooperation: how the
group completes a task
should maintain or
enhance
the group's ability to work
together; groups that don't
cooperate cannot survive
Groups
versus Teams:
All
teams are groups
Some
groups are just people
assembled together
Teams
have task interdependence whereas some
groups do not..
Why
Rely on Teams? Because as
compared with individuals
working alone, teams tend
to
o
Make
better decisions
o
Make
better products and services due to more
knowledge and expertise
We
also discussed different
development stages of group
formation.
Stages
of Group Development: five
stage of group development
are
o
Forming
o
Storming
o
Norming
o
Performing
o
Adjorning
Types
of Teams
o
Problem-Solving
o
Self-Managed
o
Cross-Functional
o
Virtual
Benefits
of Teams
Synergy:
The
creation of a whole greater than or
equal to the sum of its
parts.
165
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Why
Teams Are Good for
Organizations
o
More
resources for problem
solving
o
Improved
creativity and innovation
o
Improved
quality of decision
making
o
Greater commitments
to tasks
o
Increased
motivation of members
o
Better
control and work
discipline
Characteristics
of High Performance Teams
o
Clear
goals
o
Results-driven
structure
o
Competent
team members
o
Unified
commitments
o
Collaborative
climate
o
Standards
of excellence
o
Leadership
Team:
A
team is a formal work group
in which there is a high level of
interaction and interdependence
among
group members who work
intensely together to achieve a common
goal.
Teamwork:
is the process of people actively
working together to accomplish common
goals.
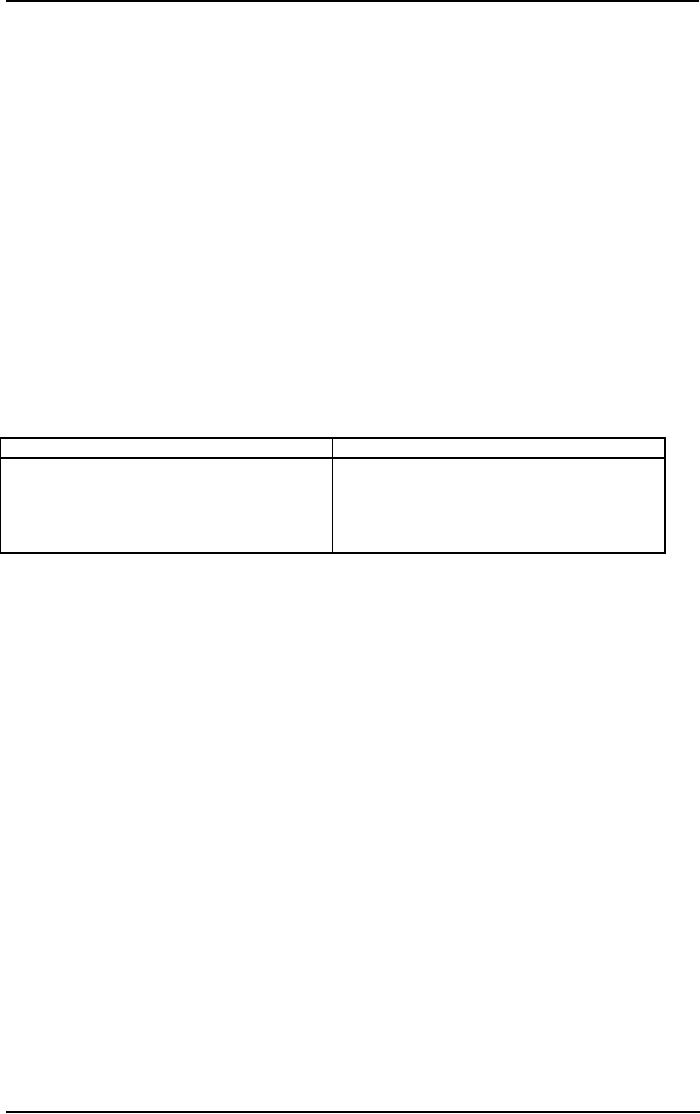
Advantages
and disadvantages of having
team.
Advantages
Disadvantages
o
Blocking
o
Wider
range of knowledge, expertise
o
Dominant
people
and
ideas
o
Status
differential
o
Effective
way to build
consensus
o
Groupthink
o
Effective
way to communicate
complex
information
How
Do We Measure Team Effectiveness?
Effective
teams have confidence in themselves
and
believe
they can succeed--this is
team efficacy. Success
breeds success. Management
can increase
team
efficacy by helping the team to achieve
small successes and skill
training.
Small
successes build team
confidence. The greater the abilities of
team members, more the
likelihood
that
the team will develop
confidence and the capability to deliver
that confidence. We can
measure the
team
effectiveness by measuring their...
o
Productivity
o
Cohesion
o
Learning/
growth & development
o
Integration
with the rest of the
organization.
Leaders
need to put extra efforts to
convert individuals into a
performing team.
Turning
Individuals into Team
Players:
It
starts with the selection of right
type of people, training them and
linking the performance with
proper
reward system.
"NONE
OF US IS AS SMART AS ALL OF
US"
o
When
teams operate effectively, they
can solve more problems, make
better decisions and be
more
creative.
o
"Team
are unique; dynamic, complex
and ever changing." - Ken
Blanchard, author of "the
one
minute
manager".
Leadership
success requires: An
understanding of group behavior.
The ability to tap the
constructive
power
of teams
Team
Building
166

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Get
the right people.
o
Determine
the Challenge.
o
Prepare
the Team Leader.
o
Train.
o
Add
value.
o
See
the Big picture.
Build
and Support the
Team
o
Leadership
Skills
o
Team
Building Strategies
o
Team
Logistics
Team
Building:-The Team Leader's
Responsibility
A
good team leader
o
Fosters
communication among team
members
o
Seeks
to build bonds among team
members (work together, meet
together, get to know
each
other)
o
Creates
positive environment for
collective problem solving and
support; creates
atmosphere
in which differing opinions
are valued but in which
clear decisions can be
reached
o
Is
alert to cliques, bickering,
etc. and acts to address
them; maintains atmosphere in
which
sexual,
racial, ethnic, national or
other harassment is not
acceptable
o
Monitors
individual staff members for
signs of stress and provides
basic support
o
Models
good individual stress
management practices
o
Seeks
to base expatriate/staff interactions on
mutual respect, transparency, and
partnership
Team
Building:-The Organizational
Responsibility
o
The
Organization identifies team-building
skills as an essential qualification
for prospective
managers
o
The
Organization trains staff and
managers in team work skills
(e.g., conflict management)
o
The
Organization helps build team cohesion
(e.g., through common experiences such
as
safety
and security
training)
o
The
Organization regularly reviews
team functioning and has
policies for addressing
the
problems
of dysfunctional teams and of staff
members who have difficulty
functioning in
their
team
Strategies
for Team Building
o
Establish common
goals
o
Understand
each others role in the
Team
o
Find
occasions to celebrate
o
Recognise
effort
o
Improve
communication
Factors
Affecting Teams
o
Work
Design
o
Team
Composition
o
Context
o
Process
Team
Based Organization
Based
on the belief that organizational goals
will be achieved not by individuals
working together
separately,
but by groups of people who
share responsibility for
outcomes and who work
efficiently and
effectively
in teams.
167

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Characteristics
of Traditional Vs Team-based Organizations
Traditional
Team-based
Individual
command structures
Collective
structures
Manager
controls
Team
monitors
Vertical
hierarchy
Horizontal
integration
Stability
and uniformity
Change
and flexibility
One
best way to organize
Organization-specific
Managers
manage
Self-managing
teams
Benefits
of Teams in Organizations:
Enhanced
Performance: Teams may
take many forms, i.e.
including improved
productivity,
quality,
and customer service such the
enhancements result from
pooling individual efforts
in
new
ways and continuously striving to improve
for the benefit of the
team.
Employee
Benefits: Teams always
provide the sense of self-control, human
dignity,
identification
with work, and sense of
self-worth and self-fulfillment for
which current workers
seem
to strive.
Reduced
Costs: Through
empowered teams, an organization can
reduce scrap, make
fewer
errors,
file fewer worker compensation claims,
and reduce absenteeism and turnover.
They
resulting
in significant cost reductions.
Organizational
Enhancements: Teams
improvements in team results a
move from a
hierarchically
based, directive culture to a
team-based culture include
increased innovation,
creativity,
and flexibility in the
organization.
Benefits
of Team-based Organization:
Profitability
and long term viability
organization is increased due to its
working as team based
organization.
Other benefits of team based
organizations are listed
bellow.
o
Efficient
Process
o
Flexible
Response to change
o
Improve
Effectiveness
o
Reduce
Cost
o
Increase
Innovation
o
Customer
Involvement
o
Employee
commitment
o
Skill
utilization
Possible
Pitfalls in the Introduction of
Team Based Organization
(TBO)
o
Introducing
teams regardless of
need
o
Introducing
teams without changing
systems
o
Failing
to train for TBO
o
Not
providing expert support
o
Failure
of communication within, with
and between teams
o
Failure
to establish and support TBO
objectives
Roles
of a Leader in the Team-Based
Organization
o
Defining
the team's mission
o
Building
trust and inspiring teamwork
o
Coaching
team members and group
members toward higher levels
of performance
o
Serving
as a model of teamwork, including
power sharing
o
Facilitating
and supporting team's decisions
o
Expanding
the team's capabilities
o
Creating
a team identity
o
Emphasizing
pride in being
outstanding
o
Anticipating
and influencing change
o
Inspiring
the team toward higher
levels of performance
168

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Enabling
and empowering group members to
accomplish their work
o
Selecting
team-oriented members
o
Using
technology that facilitates
teamwork
Decision
Making and Decision Making
Process:
A
decision
is
a choice made from two or more
alternatives. The decision-making
process is
recognizing
and defining the nature of a decision
situation, identifying alternatives,
choosing the "best"
alternative,
and putting it into practice. An
effective decision is one that
optimizes some set of
factors
such
as profits, sales, employee
welfare, and market share.
Managers make decisions about
both
problems
and opportunities.
Problem
Solving Vs Decision
Making
Problem
solving: finding the root
cause of a deviation (cause
analysis)
o
Decision
making: choosing from alternative
courses of action (choice
analysis)
o
Problem
solving --------------- Decision
making
Types
of Decisions:
Programmed
Decisions: A decision
that is a fairly structured decision or
recurs with some
frequency
or
both. Example: Starting your
car in the morning.
Non-programmed
decisions: A decision
that is relatively unstructured and
occurs much less often
than
a
programmed decision. Example: Choosing a
vacation destination.
Intuitive
decision making: Managers
also regularly use their
intuition. Intuitive decision
making is a
subconscious
process of making decisions on the basis
of experience and accumulated Judgment.
Making
decisions on the basis of gut feeling
doesn't necessarily happen independently of
rational
o
analysis;
the two complement each
other.
Although
intuitive decision making
will not replace the rational
decision-making process, it
does
o
play
an important role in managerial
decision making
Roadblocks
to Good Decision
Making
Human
Cognition
o
o
Our
mental ability to comprehend and understand
something
Human
Perception
o
o
Difficulty
isolating problems
o
Tend
to think of only narrow range of possible
solution
Human
Bias
o
o
Tendency
to shape responses based on
stereotypes, memory, and current
position
Decision-Making
and Technology: In today's
completive world Information
technology can also
help
and
support the decision-making. Different
decision making tools are
available for manager and
leaders
to
use in practical
life.
Team
Decision Making:
Use
Individual Decision Making
When:
o
You
have the information to make a good
decision
o
The
situation is urgent
o
Subordinates
are already committed or
their commitment doesn't
matter
169
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Use
Team/Group For Decision
Making When:
o
No one
knows the answer or the expertise is in the
group
o
You
want to increase the commitment of
subordinates
o
The
situation is not
urgent
in the sense that it requires an
immediate response
o
You,
as manager/leader, can live with
choice
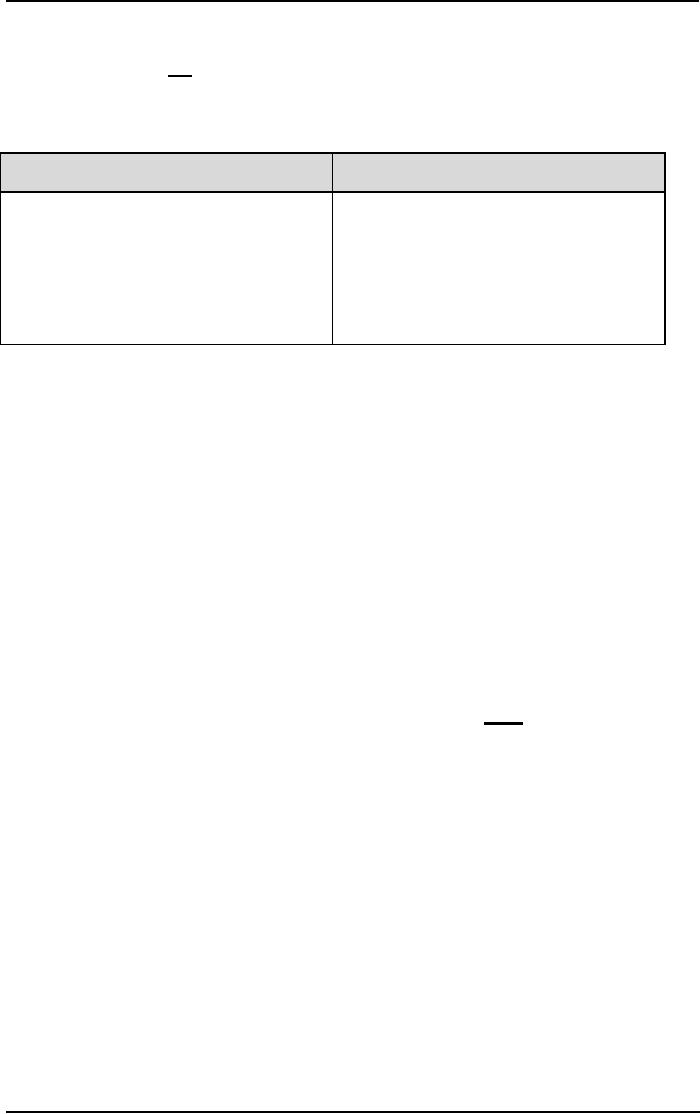
Group/Team
Decision Making
Advantages
Disadvantages
The
process takes longer, so it is
more
More
information & knowledge
are
o
o
costly
Available
Compromise
decisions
due
to
More
alternatives are likely to
be
o
o
indecisiveness
may emerge
generated.
One
person may dominate the
group
More
acceptance of the final
decision
o
o
Groupthink
may occur
is
likely
Enhanced
communication of the
o
decision
may result better
decisions
Methods
of Group/Team Decision Making
(Johnson & Johnson,
1991)
Decision
by authority without
discussion
o
Expert
member
o
Average
of member's opinions
o
Decision
by authority after
discussion
o
Majority
control
o
Minority
control
o
Consensus
o
Decisions
made in groups can be made
by one of four main
methods.
o
Unilaterally
by an individual
o
By
simple majority vote
o
By
consensus everyone agreeing to
support the conclusion
o
Subgroup
of team
Which
one is the best? There is no "best".
Different types fit best for
different situations.
Remember.
Some
decisions will be good! Some decisions
will be bad! BUT
You
will learn something
from
every decision you
make!!!
Communication
is the process by which a person,
group, or organization (the
sender) transmits some
type
of information (the message) to another
person, group or organization
(the receiver) using
some
medium
(Channels).
Communication
encompasses both interpersonal
communication (between two
or more people) and
organizational
communication (all the
patterns, networks, and system of
communication within an
organization).
Communication
and Leadership: The
importance of effective communication
cannot be
overemphasized
because everything a manager/leader does
involves communicating. Effective
leaders
are
also effective communicators. To be
effective, the leader must synchronize
verbal and nonverbal
behavior
Technology has had also a
meaningful impact on leaders'
communication and coordination.
o
Effective
leaders are also effective
communicators
o
To be
effective, the leader must synchronize
verbal and nonverbal
behavior
o
Technology
has had a meaningful impact on
leaders' communication and
coordination
Guidelines
to Team Communication:
o
Be
specific: include
facts and details to avoid
being unclear
170

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Be
accurate: as much as
possible be sure that the information
you are giving is true and
reliable.
o
Be
honest: be truthful
with those you are
communicating with and do not
use questionable
information.
o
Be
logical: make
sure messages are easy to
follow
o
Be
complete: give
all needed information in
regards to your
ideas.
o
Be
concise: be brief-
not unnecessarily wordy.
o
Be
relevant: stay on
task and give information
that is needed.
o
Ask
for feedback: have
recipients give comments on
information.
Responsibilities
of Team Members
o
Open
minded
o
Listen
to what is being said
o
Give
feedback to what is being
said
o
Make
sure all team members have a
chance to communicate their
ideas.
o
If
decisions need to be made discuss
pros and cons, and decide
best option for
TEAM.
o
Take
ownership for what you
say.
o
Take
responsibility for making
sure you are heard and
understood.
o
Use
terminology and examples
that your audience
understands.
o
Be
aware of body language.
o
Always
work to maintain the trust and confidence
of those with whom you
are
communicating/working.
Conflict
in Team: The
process in which one party perceives
that its interests are
being opposed or
negatively
affected by another party.
o
Perceived by the
parties
o
Parties
are in opposition to one another
o
At
least one party is blocking
the goal attainment of the other
party
o
Goals
can be tangible or
psychological
o
Money
o
Task
Achievement
o
Happiness
There
are several common themes which
underlie most
definitions:
o
The
parties to it must perceive
conflict.
o
Commonalties
in the definitions are opposition or
incompatibility and some form
of
interaction.
Many
people and organizations view
conflict as a negative, or something to be
avoided. Yet
conflict,
differences,
or disagreements are a natural
result of people working
together. Also, without
conflict,
teams
can become complacent and
not perform at optimum
levels. The challenge then
becomes, how
should
the team be prepared for this
stage of their existence, and how
should the team leader
facilitate
through
it?
Sources
of Conflict
o
Goal
Incompatibility
o
Different
Values and Beliefs
o
Task
Interdependence
o
Scarce
Resources
o
Ambiguity
o
Communication
Problems
o
Perceived personal
threats
o
Perceived
threat to the organization
o
Personal,
social, cultural differences
o
Others...
171

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Types
of Conflict:
o
Emotional
is personal, defensive, and resentful.
Also known a A-type or
affective.
o
Cognitive
-
is largely depersonalized, it consists of
argumentation about the merits of
ideas,
plans, and projects. Known as C-type.
Often an effective stimulate to
creativity.
We
can have a different type of
conflict classification with reference to
organizational setup.
Task
conflict: Conflict
over content and goals of the work. Low
to moderate levels can
be
o
acceptable
Relationship
conflict: Conflict
based on interpersonal relationships.
Almost always
o
dysfunctional
Process
conflict: Conflict
over how work gets done.
Low levels can be
acceptable
o
We
can also have relationship
conflict (A-type
conflict) and task
conflict (C-type
conflict). We need
to
put
efforts for transforming
relationship into task
conflict. This can be done
through.
o
Agree
on common goal or shared
vision
o
Create
a place for conflict and get it out in
the open
o
Training
in task conflict
We
can also have conflicts
known as;
Intrapersonal:
o
A
person having tension or
stress within...
o
often
due to over competing roles
Interpersonal:
o
between 2 or more
people,
o
disagreement,
values or styles don't match
o
Miscommunication
occurs
Intra-group:
o
Arises
within one group
Inter-group:
o
arises
between groups over issues/goals/solutions
The
Conflict Process:
Four
Stages
o
Potential
opposition
o
Cognition
and personalization
o
Behavior
o
Outcomes
Steps
to Resolve Conflict
o
Identify
the Problem: separate it
from the people
involved--use cause and
effect analysis
o
Gather
and Analyze Data: fact-based
management
o
Clarify
the Interests of Parties:
as
opposed to the positions of
parties
o
Determine
Objective Criteria to Evaluate Fairness
of Outcomes boundary
conditions
o
Identify
New and Creative Options: to resolve
the conflict
o
Choose
an Option: using
team decision-making
tools.
People
Factors That Affect the
Development of the
Conflict:
o
Needs
and wants
o
Self-concept
o
Past
experience
o
Health
172

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Other
Factors That Affect the
Development of the
Conflict:
o
Management
culture
o
Stage
of development of the organization
o
Organizational
structures
o
State
of business
o
Weather
Consequences
of Conflict
Positive
Consequences
Negative
Consequences
Leads
to new ideas
Diverts
energy from work
Stimulates
creativity
Threatens
psychological well-being
Motivates
change
Wastes
resources
Promotes
organizational vitality
Creates
a negative climate
Helps
individuals & groups establish
identities
Breaks
down group cohesion
Serves
as a safety valve to indicate
problems
Can
increase hostility &
aggressive
behaviors
Conflict
Resolution Techniques:
Competing
Avoiding
o
o
Compromising
Withholding
or withdrawing
o
o
Confronting
Smoothing
over/reassuring
o
o
Collaborating
Accommodating
o
o
Bargaining/negotiating
Forcing
o
o
Problem-solving
o
Three
Styles of Resolving
Conflict:
Win-Lose:
strategies
used are power, dominance,
forcing.
Lose-Lose:
common
strategy used is compromise.
Win-Win:
strategies
used are integration,
collaboration, and
problem-solving.
Characteristics
of High Performing
Teams:
o
Common
Purpose
o
Crystal
Clear Roles
o
Accepted
Leadership
o
Effective
Processes
o
Solid
Relationships
Effective
Communication
o
The
3-Cs and 3-Rs of Conflict Resolution
are-
o
Commitment
o
Cooperation
o
Compromise
o
Respect
o
Rights
o
Responsibility
Training
and Learning of
Team
The
HRM view of training: Training
refers to the methods used to give
new or present employees the
skills
they need to perform their
jobs. Training today plays a
key role in the performance
management
173

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
process,
which is a key process for
employers to ensure that employees are
working toward
organizational
goals. Overall, training has a
fairly impressive record of influencing
organizational
effectiveness,
scoring higher than appraisal and
feedback, and just below goal
setting in its effect
on
productivity.
o
Employees
recruited for a flexible
working role rather than a
`job' and for their
ability to learn
rather
than for pre-existing
skills
o
Employees expected
to re-train periodically
o
Training
seen as an investment not a
cost
o
Learning
is an ongoing process in the
organisation, which is integrated
with working
o
Performance,
appraisal and development are
seen as part of a single
process
Purpose
of Training:
Effective
training can raise performance,
improve morale, and increase an
organization's potential.
Poor,
inappropriate, or inadequate training can
be a source of frustration for
everyone involved. To
maximize
the benefits of training, managers
must closely monitor the
training process. Training
ensures
that
Team/Organization meets current and
future performance objectives set by
top management.
Training
also helps in continuous improvement of
performance of individuals and teams,
and
maximizing
people's potential for
growth (and
promotion).
o
Ensure
Team/Organization
meets current and future performance
objectives by...
o
Continuous
improvement of performance of
individuals and teams,
and...
o
Maximizing
people's potential for
growth (and
promotion)
Learning
Principles
o
Participation
o
Repetition
o
Relevance
o
Transference
o
Feedback
Phases
of Learning Cycles
Understand
and frame problem
o
Create
a shared understanding
o
What
is the problem (or
opportunity)?
o
What
are we trying to do?
o
How
are we going to do
it?
o
Starts
out being general but
becomes more defined as you
proceeds
Key
Characteristics of Successful Learning
Teams
o
Clear
(and shared) sense of
purpose
o
Good
communication
o
Freely
shared information
o
Shared
leadership
o
Interdependence of
team members
o
Utilization
of members' strengths
o
Mutual
encouragement of risk
taking
o
Adaptive
able change/modify plans when
new information and/or
circumstances emerge
o
Pride
in team identity
Learning
Organization?
"A
learning organization is one in which
people at all levels,
individually and collectively,
are
continually
increasing their capacity to produce
results they really care
about". Learning organization
is
Creating,
acquiring, interpreting, transferring,
and retaining knowledge. Purposefully
modifying its
behavior
to reflect new knowledge and
insights.
174

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
"Learning
Organization" is a Hot
Topic:
Levels
of Learning
Managers/leaders
need to encourage learning at
four levels:
o
Individual
o
Group
o
Organizational
o
Inter-organizational
The
Basis of the Learning Organization
Strategy need to be
o
Transfer
Knowledge, not just
information.
o
Knowledge
leads to better, safer
decisions.
o
Better-informed.
o
Knowledgeable.
o
Wiser
decisions.
Organizations
Must Learn Faster &
Adapt to the Rapid Changes in the
Environment otherwise they
will
be
history.
The
Bottom Line: Any organization
that has a culture
and
structure
that
promotes learning at all
levels
to enhance its capabilities to produce,
adapt and shape its
future.
The
Knowledge Management
Cycle
o
Create
knowledge
o
Capture
knowledge
o
Refine
knowledge
o
Store
knowledge
o
Manage
knowledgee
o
Disseminate
knowledge
What
Will a Learning Organization
Achieve for You?
o
Develop
effective leadership skills
o
Gain
skills in working as a
team
o
Improve
professional development
o
Understand
change management
skills
o
Overcome
staff inertia
o
Link
theory and practice to solve
organizational problems
o
Create
a non-threatening environment
Through
learning, we:
o
Re-create
ourselves
o
Become
able to do things we never were
able to do before
o
Re-perceive the
world and our relationship to
it
o
Extend
our capacity to create, to be
part of the generative process of
life
Why
is there a Need for a New
Managerial Mindset?
o
Change
o
Globalization
o
New
technology
o
Need
for strategic flexibility
o
Need
for non-linear
thinking
o
Need
to see the whole
o
Need
for changed mental
models
Building,
Maintaining & Sustaining the Learning
Organization
Reward
and Recognition
Systems
o
Team-based
reward and recognition systems
can promote teamwork
175

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Focus
should be rewarding teams
for achieving specific
goals
Why
People Leave Their
Jobs?
o
They
feel they do not make a
difference.
o
They
do not get proper
recognition.
o
They
are not learning anything
new or growing as a
person.
o
They
do not like their
coworkers.
o
They
want to earn more
money.
People
leave organization due to many
reasons but one of them might be the
improper compensation
system.
Compensating
Teams:
Reasons
for tailoring compensation to
individuals:
o
Motivation
comes from within the
individual as opposed to the
group.
o
The
development of skills and behaviors is an
individual undertaking.
o
Fairness
in dealing with teams does
not mean equal pay
for all.
o
Team
compensation is not a payoff but a
means of nurturing behavior
that benefits the
team.
Rewards
and other Employee
Behaviors
Starting
from attracting the good
team members/employees to retain
every thing is revolving on
the
reward
system of organization. Three
important HR related behaviors
like turnover, absenteeism
and
attendance
is directly linked with the
reward system of
organizations.
With
better reward system we can
minimize the turnover, absenteeism and
attendance and vice
versa.
Reward
is also used to reinforce
positive behavior and
reduces the undesirable
behaviors.
Total
compensation comprises of direct like
wages, salary, commission, gain sharing
etc while indirect
benefits,
vacation, insurance, etc. Even
positive behavior of manager/leader also
play important role
in
modifying
the behaviors of the team member/employees. We
can see a wide range of
benefits
organization
use to attract, and retain the
employees.
Objectives
of Reward Systems
o
Attraction
and retention (employees compare to other
firms in the market)
o
Motivating
performance (contingent on expectancy &
equity)
o
Getting
employees to gain skills and
knowledge
o
Reinforce
the organization's culture
o
Not
cost the firm too
much!!
Designing
Rewards
o
Always
remember your basic
motivational theories
o
Options
for reward systems
o
Objectives
of reward systems
o
How
rewards impact organizational
effectiveness
o
Implementing
a reward system
o
Appropriate
rewards practices sometimes
vary between countries
Individual
or Team Rewards?
Individual
rewards
o
fosters
independent behavior
o
may
lead to creative thinking and
novel solutions
o
encourages
competitive striving within a
work team
Team
rewards
o
emphasize
cooperation & joint
efforts
o
emphasize
information sharing
176

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Both
have same purpose.
Types
of Team Pay
o
Incentive
pay
o
Recognition
o
Profit
sharing
o
Gain
sharing
A
Virtual Team is known as a
Geographically Dispersed Team
(GDT) is a group of individuals
who
work
across time, space, and
organizational boundaries with links
strengthened by webs of
communication
technology. They have complementary
skills and are committed to a common
purpose,
have
interdependent performance goals, and share an
approach to work for which
they hold themselves
mutually
accountable. Geographically dispersed
teams allow organizations to
hire and retain the
best
people
regardless of location. A virtual
team does not always
mean Tele-workers. Tele-workers
are
defined
as individuals who work from
home. Many virtual teams in
today's organizations consist
of
employees
both working at home and
small groups in the office but in
different geographic locations
or
during
different shits/time.
Factors
Driving Virtual Organizations
o
Organizational
structure changing to meet the demands of
the fast-paced, dynamic global
economy
o
Many
organizations are moving
from a systems-based organizational
model to a collaborative,
networked
organizational model.
o
The
virtuality of virtual organizations
has been described as having
two key features:
Creation
of a common value chain between distinct
entities and distributed
Information
technology (IT) supported business
processes (Seiber and Griese,
1997).
Communications
in Virtual Organizations
Information
technology is a primary mechanism
for providing support and control to
virtual forms.
Communication
within virtual organizational forms is
increasingly supported by
information
technology.
Organizational
Types
o
Permanent
Virtual Organizations
o
Virtual
Teams
o
Virtual
Projects
o
Temporary
Virtual Organizations
Why
a virtual team?
o
Team
members may not be
physically collocated.
o
It
may not be practical to
travel to meet face-to-face.
o
Team
members may work different
shifts.
o
Organization-wide
project not in the same
location.
o
Alliances
with organizations.
Benefits
of virtual teams
People
can work from anywhere at
anytime.
o
People
can be recruited for their
competencies, not just
physical location.
o
Many
physical handicaps are not a
problem.
o
Expenses
associated with travel,
lodging, parking, and
leasing or owning a building
may
o
be
reduced and sometimes
eliminated.
Apply
most appropriate resources
(from anywhere) to
job
o
Can
schedule to
follow-the-sun/around-the-clock
o
Can
build ongoing relationships/networks
across business
o
Cost
reduction
o
Downside
of virtual teams
o
Time
zones
177

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
"You
can't see me"
attitude
o
No
constant direction
o
Keeping
that motivation and
commitment
o
How do
you celebrate a success?
Characterizations
of virtual teams (Henery and
Hartzler,1998)
o
Members
are mutually accountable for
team results.
o
Members
are dispersed geographically
(nationally or internationally).
o
Members
work apart more than in the same
location.
o
The
team solves problems and makes decisions
jointly.
A
successful virtual
team
A
unified commitment by all
team members
o
Defined
and agreed roles and
responsibilities
o
Clear
concise deliverables
o
Strict
meeting schedules
o
Effective
lines of communication
o
Committed,
enthusiastic leadership - ALWAYS!
o
Setting
Up Virtual Teams
Establish
communication norms procedures to
reconcile differences in
communication
o
practices
Develop
templates for using technology -- e.g.,
store documents on web
pages, expert
o
directories
Set
procedures, responsibilities
o
Establish
leadership that provides procedural
justice
o
Hold
an initial face-to-face startup
meeting
o
Have
periodic face-to-face meetings, especially to
resolve conflict and to maintain
team
o
cohesiveness
Establish
a clear code of conduct and protocols
for behavior
o
Recognize
and reward performance
o
Use
visuals in communications
o
Recognize
that most communications will be
non-verbal use caution in
tone and language
o
Success
Factors in Virtual Teams
o
High
levels of trust among team
members
o
Effective
use of technology
o
Clear
implementation of team
concept
o
Effective
individual performance
Trust
Effective
teamwork depends on trust
o
In
a virtual environment, trust is more
ability/task based than
interpersonal relationship
o
based
o
Level
of member performance over time
results in building or denial of
trust
Like
in case of other team, trust is even more
essential in the effectiveness of virtual
team.
Building
Trust Virtually: Establish trust
through performance consistency
o
Rapid
response to team members
(return emails, task
completion)
o
Set strong
norms around
communication
o
Team leader
role in reinforcing
interactions
Virtual
Team Member
Competencies:
o
Self-disciplined?
o
Strong
communicator?
o
Good
collaborator?
o
Organized?
o
Document
your work well?
178

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Implementation
of Virtual Teams:
o
Must
set out a clear business
reason for the team
o
Team
must understand its
mission/purpose
o
Team
members must develop a sense
of interdependence
o
Must
have accountability and rewards
for team members
Challenges
to Virtual Team
Success:
o
Building
trust within virtual
teams
o
Maximizing
process gains & minimizing process
losses on virtual
teams
o
Overcoming
feelings of isolation & detachment
associated with virtual
teamwork
o
Balancing
technical & interpersonal skills
among virtual team
members
o
Assessment
& recognition of virtual team
performance
Virtual
Team Competencies
o
The
right technology
o
Shared
work space &
processes
o
Established
ground rules
o
Acceptance
of cultural, style & preference
differences
o
Effective
group dynamics
o
Clear
identity
o
Teamwork
skills
o
Leadership
o
True
trust
Virtual
Leadership
Virtual
leadership is about how to pull the
people on a worldwide assignment
together into one
cohesive
partnership. Leadership is about
making things happen and getting
things done. It just
takes
more
work in a virtual
environment.
Key
in Leading a Virtual
Team
o
Build
trust
o
Reward and
recognize
o
Communication
o
Motivation
o
Commitment
Virtual
Team Leadership Competencies
o
Make
the invisible, visible
o
Make
the intangible, tangible
o
Create
& foster a climate of trust
o
Establish &
constantly model standards of
accountability
o
Communicate
clearly, constantly & effectively
within each receiver's
realm
o
Delegate
responsibilities
Virtual
Leadership Key Traits
o
Everyone
gets core information at the
same time.
o
Everyone
has equal input.
o
Everyone's
ideas are weighed against the
alignment tool, not out of
preference.
o
Everyone's
ideas are never judged or
rejected at the onset.
o
Everyone
has equal opportunity to
shine.
o
Everyone
is rewarded or publicly recognized for
contributions to the project.
o
The
leader socializes equally with people
near and far.
o
Even
appearances or suggestions of favoritism
break trust.
179

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Team
Meetings
Team
meetings keep members informed and
provide a forum for problem
solving, decision-making,
and
innovation. Meetings, when
productive, are also one of the
primary ways to develop team
member
relationships,
enthusiasm, and spirit.
Effective
Meetings at Work: Focused,
Crisp and Short
Types
of Meetings
Leadership/Management:
to
review the overall organization
performance, setting up new
o
goals
and targets, headed by CEO, or
Chairman.
Department
Specific: to review
the departmental performance, headed by the head
of
o
department.
Project
Management: to review
the overall project performance, headed
by Project Director
o
or
Project Manager.
Other
Meetings
o
o
Quarterly
Business Review: to review
the quarterly progress report of
all the
departments
in the organization.
o
Client
Specific: to meet
with specific client/customer to
discuss the business
matters
etc.
o
Functional
Team: meeting
with in the department between different
teams exist in one
department.
o
Special
Project: meeting on
special project
o
Performance
Review (1-1): to review
the performance
Others:
a
number of unscheduled meetings has also arranged on
different level of
organization.
o
Meeting
Techniques:
o
Ask
yourself, "Is this meeting
really necessary?"
o
Have
a goal for the meeting. What
do you want to accomplish?
o
Have
an agenda with clearly
stated items and the amount of time to be
allotted each one. Send
out
the agenda at least one day
ahead of the meeting.
o
Limit
attendance and appoint a
leader.
o
Stay
focused on the agenda. If a new
topic is introduced, add it to the list
of future agenda items
or
negotiate with the group if it
should be discussed now.
Have a clock in the
room.
o
Strive
to get everyone involved in the
discussion, avoid domination by
one or two members.
o
Foster
rigorous debate and brainstorming,
while respecting each other's
opinions.
o
Use
visual aids. Have a flip chart
and use it.
o
Keep
minutes of the key points raised
and actions to be taken, then
follow up.
o
Do
a two-minute evaluation of the meeting.
Ask everyone what went
well... what could be
improved.
The
Meeting Process
o
Plan
o
Start
o
Conduct
o
Close
o
Follow
Up
Leading
Team
Having
the leading position or higher
score in a contest; "he is
ahead by a pawn"; "the
leading team in
the
pennant race".
Attributes
of High Performing
Teams:
o
Performance
outcomes
180

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Specific,
shared purpose and
vision
o
Mutual,
internal accountability
o
Coordinated,
shared work roles
o
Inefficiency
leading to efficiency
o
Extraordinarily
high quality
o
Creative
continuous improvement
o
High
credibility and trust
o
Clarity
of core competence
o
Participative
leadership
o
Shared
responsibility
o
Aligned
on purpose
o
High
communication
o
Future
focused
o
Focused
on task
o
Creative
talents
o
Rapid
response
Principles
of Leadership Effectiveness
o
Do
not avoid risks.
o
Believe
in yourself.
o
Take
the offense rather than the
defense.
o
Know
the ways of disagreement and the means of
compromise.
o
Be a
good follower. Effective
leaders lead as they would
like to be lead.
Note
Material
presented during this course
is taken from different
books, presentations and work done
by
great
peoples in this field to
make the material understandable for a
common person and purely
for
learning
purpose. Material/work used from
different sources is highly
acknowledged.
181
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION, ORGANIZATION THE STAGE FOR LEADERSHIP:Challenges, Value creation
- FOCUSING ON PEOPLE: THE KEY TO SUCCESS:People in the Process, Developing and Sustaining A World-class Workforce
- LEADERSHIP:Characteristics of Successful Leader, Why Study Leadership?
- LEADERSHIP (CONTD.):Characteristics of Leaders Who Fail, Why Leaders Fail?
- MANAGERS VS LEADERS:Characteristics, Effective Leadership, Respect for Diversity
- FOLLOWER-SHIP:Importance of Followers, Follower-ship Style
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS:Strategies for Cultivating Exemplary Followers, Important Traits of Leaders
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS (CONTD.):Qualities of Leaders, Self-Confidence, Integrity
- LEADERSHIP THEORIES/ APPROACHES:Personal Characteristics of Leaders, Managerial Grid
- CONTINGENCY THEORIES OF LEADERSHIP:The Fiedler Model, Situational Leadership Theory, Path-Goal Theory
- TRANSACTIONAL, CHARISMATIC AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP:Visionary Leadership
- THE LEADER AS AN INDIVIDUAL:Personality, Situation, Heredity, Environment
- ATTITUDE-PERSONALITY:Job Satisfaction, Work Situation, Self - Monitoring
- BIG FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS TYPE INDICATOR (MBTI):Sub-Categories Defined, Information Gathering
- SITUATIONAL FACTORS:Social and psychological climate, Culture of the organization
- BECOMING A LEADER! WHAT DOES IT MEAN & HOW DO YOU GET IT?:Mission Statement, Leading oneself
- BECOMING A LEADER:Elements of Leadership, CONCEPT OF POWER,
- UNDERSTANDING POWER:Sources of Power, Responses to the Use of Power, Managing Political Behavior
- LEADERSHIP POWER & INFLUENCE:Positional Power, Being an Effective Leader
- LEADERSHIP AND EMPOWERMENT:Power sharing and Empowerment, Share Information
- MOTIVATION:Guidelines for Delegating, Human Resource Approach
- MOTIVATION AT WORK, MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:What Factors Diminish Motivation in the Workplace
- LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:Communication & the Four Management Functions
- REVIEW-1:Organizational Performance, That is the Role of Management?, Leaders Vs Managers
- GROUP & TEAM CONCEPT:Groups versus Teams, Deciding When to Use a Team
- TEAM DYNAMICS:Stages of Group Development, Problem-Solving Teams, Benefits of Teams
- BUILDING THE TEAM:Leadership success requires, Strategies for Team Building
- A TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATION:Basic Steps, Span of Control, Categories of Decisions
- DECISION MAKING:Categories of Decisions, The Decision-Making Process
- TEAM DECISION MAKING:Team Problem Solving Techniques, Concept of QC
- EFFECTIVE TEAM COMMUNICATION:Team/Group Communications
- CONFLICT IN TEAM:Sources of Conflict, Scarcity of Resources, Dysfunctional Outcomes
- TRAINING/LEARNING OF TEAM:Training Methods, Phases of Learning Cycles
- LEARNING ORGANIZATION:A Litmus Test, Work Relations
- REWARDING & RECOGNIZING TEAMWORK:Compensating Teams, Individual or Team Rewards?
- MANAGING/LEADING VIRTUAL TEAMS:Communications in Virtual Organizations, Virtual Leadership
- EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS:Better Meetings, Meeting Roles, Meeting Room Facilities
- LEADING TEAM:Team Leadership Structures, Leadership Demands and Duties, Leadership Direction
- REVIEW-II:Types of Teams, Characteristics of High Performance Teams, Sources of Conflict
- STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP:Strategic Management, Determining Strategic Direction, Developing Human Capital:
- LEADING CHANGE:Dynamics of Change, Change Models, Unfreeze
- CREATIVE LEADERSHIP:Awaken Your Senses, How Might These Definitions Be Integrated
- ETHICS IN LEADERSHIP:Character Traits Reflect Ethics, Manifests Honesty
- LOOKING AT THE FUTURE: WHAT COMES NEXT:Benefits of Teams, Ethical Leadership,
- TEAMWORK: LEARNING FROM NATURE:Social Behavior, Termites, Learning from Nature