 |

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Lecture
33
TRAINING/LEARNING
OF TEAM
Training
and Learning of
Team
The
HRM view of training: Training
refers to the methods used to give
new or present employees the
skills
they need to perform their
jobs. Training today plays a
key role in the performance
management
process,
which is a key process for
employers to ensure that employees are
working toward
organizational
goals. Overall, training has a
fairly impressive record of influencing
organizational
effectiveness,
scoring higher than appraisal and
feedback, and just below goal
setting in its effect
on
productivity.
o
Employees
recruited for a flexible
working role rather than a
`job' and for their ability
to learn
rather
than for pre-existing
skills
o
Employees expected
to re-train periodically
o
Training
seen as an investment not a
cost
o
Learning
is an ongoing process in the
organisation, which is integrated
with working
o
Performance,
appraisal and development are
seen as part of a single
process
Purpose
of Training:
Effective
training can raise performance,
improve morale, and increase an
organization's potential.
Poor,
inappropriate, or inadequate training can
be a source of frustration for
everyone involved. To
maximize
the benefits of training, managers
must closely monitor the
training process. Training
ensures
that
Team/Organization meets current and
future performance objectives set by
top management.
Training
also helps in continuous improvement of
performance of individuals and teams,
and
maximizing
people's potential for
growth (and
promotion).
o
Ensure
Team/Organization
meets current and future performance
objectives by...
o
Continuous
improvement of performance of
individuals and teams,
and...
o
Maximizing
people's potential for
growth (and
promotion)
Training
and Development
Trends:
Although
training is often used with
development, the terms are
not synonymous. Training
typically
focuses
on providing employees with specific
skills or helping them to correct
deficiencies in their
performance.
In contrast, development is an effort to
provide employees with the abilities
that the
organization
will need in the future.
Preparing them for
future.
o
Skill
requirements will continue to
increase
o
Workforce
will become significantly better
educated & more diverse
o
Corporate
restructuring reshapes
businesses
o
Technology
will revolutionize certain
training delivery
methods
o
The
role of training departments
will change
o
More
flexible courses aimed
specifically at performance
improvement
o
More
organizations will strive to
become learning-organizations
o
Emphasis
on human performance management will
accelerate
Investing
in people:
"We
must transform the perception of
training expenditure so that it is no
longer seen simply as a
cost,
but
is regarded as an investment, to be evaluated
alongside investments in capital
equipment."
"Sir
Dennis Rooke, Chairman
British Gas,
1987.
Training
Methods:
There
are different training
methods, which are given
below;
On-the-Job
Training (OJT) means
having a person learn a job
by actually doing
o
it,
and involves the following:
141

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Preparing
the learner; presenting the operation;
doing a tryout; and
follow-
up.
Apprenticeship
Training is a structured process by
which people become
skilled
o
workers
through a combination of classroom
instruction and on-the-job
training.
Informal
Learning involves learning
through day-to-day unplanned
interactions
o
between
the new worker and his/her
colleagues.
Job
Instruction Training refers to
teaching a new employee the
logical sequence
o
of
steps in a job step-by-step.
Lectures
quick and simple way to
provide knowledge to large
groups.
o
Programmed
Learning is a step-by-step self-learning
method: 1) presenting
o
questions,
facts, or problems to the learner; 2)
allowing the person to respond;
and
3)
providing feedback on the accuracy of the
answers.
Literacy
Training Techniques Companies
are responding the functional
illiteracy
o
by
testing job candidates'
basic skills, and setting up
basic skills and
literacy
programs.
Audiovisual
Based Training Tools
include: films, PowerPoint
presentations,
o
video
conferencing, audiotapes, and videotapes.
Simulated
Training is a method in which trainees
learn on the actual or simulated
equipment they
o
will
use on the job, but are
actually trained off-the
job.
Computer-Based
Training is where the trainee uses
computer-based and/or DVD
o
systems
to increase his/her knowledge or
skills.
CBT
programs have real
advantages
including reducing learning
time, cost effectiveness once
designed
and
produced, instructional consistency, mastery of
learning, increased retention,
and
increased
trainee motivation.
Electronic
Performance Support Systems (EPSS)
are sets of computerized tools
and
o
displays
that effectively automate and integrate
training, documentation, and phone
support,
thus enabling individuals to
provide support that's faster, cheaper,
and more
effective
than the traditional
methods.
Distance
and Internet-Based Training Distance
learning methods include
traditional
o
paper-and-pencil
correspondence courses, as well as
Tele-training, videoconferencing,
and
Internet-based classes.
o
Tele-training
where a trainer in a central
location teaches groups of
employees
at remote locations via television
hookups.
o
Videoconferencing
allows people in one location to
communicate live
via
a combination of audio and visual
equipment with people in
different
locationsanother
city or country or with groups in several
cities.
o
Training
via the Internet Internet
based learning programs
are
increasingly
popular. Some companies
simply let their employees
take
online
courses offered by online
course providers while
others use their
intranets
to facilitate computer-based
training.
Learning
Principles
o
Participation
o
Repetition
o
Relevance
o
Transference
o
Feedback
Maximizing
Learning:
Selecting
the Stage for
Learning
Provide
clear task instructions
o
Model
appropriate behavior
o
Increasing
Learning during
Training
Provide
for active
participation
o
142
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Match
training techniques to trainees
self-efficacy
o
Ensure
specific, timely, diagnostic, and
practical feedback
o
Provide
opportunities for trainees to practice
new behavior
Maintaining
Performance after Training
Develop
learning points to assist
knowledge retention
o
Set
specific goals
o
Identify
appropriate re-enforcers
o
Teach
trainees self-management skills.
o
Following
up on Training
Evaluate
effectiveness
o
Make
revisions as needed.
o
Models
of learning:
o
Associative
learning: stimulus/response
o
Cognitive
learning: problem
solving
o
Social
learning: watching
others
o
Experiential
learning: learning by
doing
Phases
of Learning Cycles
Understand
and frame problem
o
Create
a shared understanding
o
What
is the problem (or
opportunity)?
o
What
are we trying to do?
o
How
are we going to do
it?
o
Starts
out being general but
becomes more defined as you
proceeds
Plan
Teams
plan actions to produce learning by
answering
o
What
don't we know that we need
to know?
o
What
actions can we take between now &
our next meeting to find
out what we need to
know?
o
How
can we verify that what we
are assuming is actually
true?
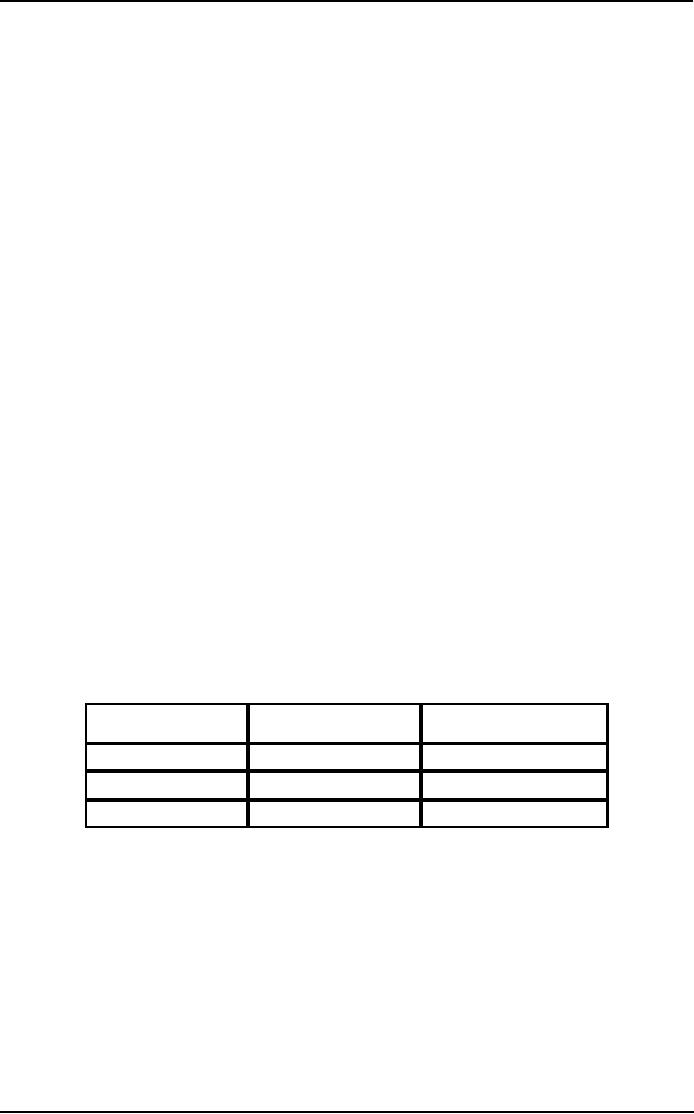
Team
Learning Record
What
we Know?
What
we Think We
What
we Don't Know?
(Facts)
Know?
(Assumption) (Question to be
answered)
Act
Key
to learning is action!
o
Test
assumptions
o
Experiment
o
Gather
new information
o
Try
out hunches
Only
by acting do teams have the opportunity
to learn
143

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Action
Plan for Team
Learning
What
Needs To Be Done?
BY
Whom?
By
When?
Reflect
and Learn
o
Really
when team learning
occurs
o
Teams
need to slow down, reflect
on what has happened and capture
lessons learned
o
Must
occur
�
In a
spirit of openness
�
Not in
a climate of self-protection or
criticism
Assessing
Team Learning
Speed
o
o
Number
of learning cycles should be
completed.
o
The
more cycles completed, the more learning
that takes place.
Depth
o
o
Degree
to which teams "reframe"
their understanding of the original
problem.
Breadth
(Impact)
o
o
The
impact of the results produced by the
team.
o
Degree
to which other projects, functional
areas, or the organization as a whole
is
influenced.
To
Motivate Followers Leaders
Must:
o
Set
clear standards and goals so that the
employee will take more
interest.
o
Expect
the best from
employee.
o
Pay
attention towards employees.
o
Personalize
rewards and recognition. It will
enhance organization performance.
o
Tell a
story about winning
organization etc.
o
Celebrate
ceremonies together.
o
Be a
role model for
employee.
Factors
Affecting Teamwork
Ability
to shape role
o
Common
purpose
o
boundaries
when needed
o
Mutual
respect
Shared
responsibility
o
Good
communication
o
o
Good
leadership
Common
"language"
o
o
Understanding
own role
Professional
culture
o
o
Understanding
role of other
team
members
Learning
Team Assumptions
o
Every
member's participation is essential to the team's
success
o
Members'
roles are fluid
o
Authority
is shared
o
Information
is freely shared with the
team
o
Every
team member has something to
learn and something to teach.
o
Members
don't know precisely what
they will learn or what
they will teach
o
Team
goals include performance and learning
expectations
144

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Key
Characteristics of Successful Learning
Teams
o
Clear
(and shared) sense of
purpose
o
Good
communication
o
Freely
shared information
o
Shared
leadership
o
Interdependence of
team members
o
Utilization
of members' strengths
o
Mutual
encouragement of risk
taking
o
Adaptive
able change/modify plans when
new information and/or
circumstances emerge
o
Pride
in team identity
Team
Learning
o
Continuous
improvement process
o
How
team resolves
conflict
o
How
the team handles diversity
o
Harness
team creativity
145
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION, ORGANIZATION THE STAGE FOR LEADERSHIP:Challenges, Value creation
- FOCUSING ON PEOPLE: THE KEY TO SUCCESS:People in the Process, Developing and Sustaining A World-class Workforce
- LEADERSHIP:Characteristics of Successful Leader, Why Study Leadership?
- LEADERSHIP (CONTD.):Characteristics of Leaders Who Fail, Why Leaders Fail?
- MANAGERS VS LEADERS:Characteristics, Effective Leadership, Respect for Diversity
- FOLLOWER-SHIP:Importance of Followers, Follower-ship Style
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS:Strategies for Cultivating Exemplary Followers, Important Traits of Leaders
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS (CONTD.):Qualities of Leaders, Self-Confidence, Integrity
- LEADERSHIP THEORIES/ APPROACHES:Personal Characteristics of Leaders, Managerial Grid
- CONTINGENCY THEORIES OF LEADERSHIP:The Fiedler Model, Situational Leadership Theory, Path-Goal Theory
- TRANSACTIONAL, CHARISMATIC AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP:Visionary Leadership
- THE LEADER AS AN INDIVIDUAL:Personality, Situation, Heredity, Environment
- ATTITUDE-PERSONALITY:Job Satisfaction, Work Situation, Self - Monitoring
- BIG FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS TYPE INDICATOR (MBTI):Sub-Categories Defined, Information Gathering
- SITUATIONAL FACTORS:Social and psychological climate, Culture of the organization
- BECOMING A LEADER! WHAT DOES IT MEAN & HOW DO YOU GET IT?:Mission Statement, Leading oneself
- BECOMING A LEADER:Elements of Leadership, CONCEPT OF POWER,
- UNDERSTANDING POWER:Sources of Power, Responses to the Use of Power, Managing Political Behavior
- LEADERSHIP POWER & INFLUENCE:Positional Power, Being an Effective Leader
- LEADERSHIP AND EMPOWERMENT:Power sharing and Empowerment, Share Information
- MOTIVATION:Guidelines for Delegating, Human Resource Approach
- MOTIVATION AT WORK, MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:What Factors Diminish Motivation in the Workplace
- LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:Communication & the Four Management Functions
- REVIEW-1:Organizational Performance, That is the Role of Management?, Leaders Vs Managers
- GROUP & TEAM CONCEPT:Groups versus Teams, Deciding When to Use a Team
- TEAM DYNAMICS:Stages of Group Development, Problem-Solving Teams, Benefits of Teams
- BUILDING THE TEAM:Leadership success requires, Strategies for Team Building
- A TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATION:Basic Steps, Span of Control, Categories of Decisions
- DECISION MAKING:Categories of Decisions, The Decision-Making Process
- TEAM DECISION MAKING:Team Problem Solving Techniques, Concept of QC
- EFFECTIVE TEAM COMMUNICATION:Team/Group Communications
- CONFLICT IN TEAM:Sources of Conflict, Scarcity of Resources, Dysfunctional Outcomes
- TRAINING/LEARNING OF TEAM:Training Methods, Phases of Learning Cycles
- LEARNING ORGANIZATION:A Litmus Test, Work Relations
- REWARDING & RECOGNIZING TEAMWORK:Compensating Teams, Individual or Team Rewards?
- MANAGING/LEADING VIRTUAL TEAMS:Communications in Virtual Organizations, Virtual Leadership
- EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS:Better Meetings, Meeting Roles, Meeting Room Facilities
- LEADING TEAM:Team Leadership Structures, Leadership Demands and Duties, Leadership Direction
- REVIEW-II:Types of Teams, Characteristics of High Performance Teams, Sources of Conflict
- STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP:Strategic Management, Determining Strategic Direction, Developing Human Capital:
- LEADING CHANGE:Dynamics of Change, Change Models, Unfreeze
- CREATIVE LEADERSHIP:Awaken Your Senses, How Might These Definitions Be Integrated
- ETHICS IN LEADERSHIP:Character Traits Reflect Ethics, Manifests Honesty
- LOOKING AT THE FUTURE: WHAT COMES NEXT:Benefits of Teams, Ethical Leadership,
- TEAMWORK: LEARNING FROM NATURE:Social Behavior, Termites, Learning from Nature