 |

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Lesson
19
LEADERSHIP
POWER & INFLUENCE
Leaders
use power as a means of
influencing followers and attaining
group goals. Getting things
done
through
others. Leaders achieve goals, and power
is a means of facilitating their
achievement. Power is
the
capacity of a leader to influence work
actions or decisions.
Sources
of Leadership Power:
�
There are two sources
of the power used by
leaders:
The
power of the position
The
leader's personal qualities
�
�
Position
powers:
Person
powers:
Reward
Expert
Coercive
Referent
Legitimate
Rational
Information
Charisma
Positional
Power:
Coercive
Power
The
coercive power base is being
dependent on fear.
It
rests on the application, or the threat
of application, of physical sanctions
such as the infliction of
pain,
the generation of frustration through
restriction of movement, or the
controlling by force of
basic
physiological or safety needs.
At
the organizational level, A has
coercive power over B if A
can dismiss, suspend, or demote
B,
assuming
that B values his or her
job.
Similarly,
if A can assign B work
activities that B finds unpleasant or
treat B in a manner that B
finds
embarrassing, A possesses coercive
power over B.
Reward
Power
The
opposite of coercive power is
reward power.
People
comply because doing so
produces positive benefits;
therefore, one who can
distribute
rewards
that others view as valuable
will have power over those
others.
These
rewards can be anything that
another person values.
Coercive
power and reward power are
actually counterparts of each
other.
If
you can remove something of
positive value from another or
inflict something of
negative
value
upon him/her, you have
coercive power over that
person.
If
you can give someone
something of positive value or remove something of
negative value,
you
have reward power over that
person.
Legitimate
Power
In
formal groups and organizations, the most
frequent access power is
one's structural position.
It
represents
the power a person receives as a
result of his/her position in the
formal hierarchy.
Positions
of authority include coercive and
reward powers.
Legitimate
power, however, is broader than the
power to coerce and reward.
It includes acceptance
of
the authority of a position by members of
an organization.
63

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Person
Power:
Expert
Power
Expert
power is "influence wielded as a
result of expertise, special skill, or
knowledge."
Expertise
has become a powerful source
of influence as the world has
become more technological.
As
jobs become more specialized, we become
increasingly dependent on experts to achieve
goals.
Referent
Power
Its
base is identification with a
person who has desirable
resources or personal traits. If I admire
and
identify
with you, you can
exercise power over me
because I want to please
you.
Referent
power develops out of admiration of
another and a desire to be like that
person; it is a lot
like
charisma.
Referent
power explains why
celebrities are paid
millions of dollars to endorse products
in
commercials.
Charismatic
Power
Charismatic
power is an intense form of referent
power stemming from an individual's
personality,
physical,
or other abilities that
induces others to believe in and
follow that person.
When
charismatic power exists, other forms of
power lose their
significance because followers
give
the
charismatic leader the right to hold the reins of
power and make the decisions that
define the
vision
and goals of an organization and its
members.
Many
charismatic leaders can excite a
whole organization and propel it to
new heights.
Charismatic
power can have a dark side; charismatic
power can be abused.
Some
argue that charismatic power is an advantage
only when a formal hierarchy
of authority
places
some checks on the power of
this person.
The
Leadership Position
Leadership
is needed in all areas of
society and at all levels of
responsibility
�
Power and responsibility come with
the office of leadership
�
Titles of leadership
include:
President
Chief
Captain
Manager
Director
Supervisor
Power
is important to get things done and
lead the way to get the job
done.
Bases
of Power: following
are the bases of powers;
Legitimate
power based
on formal position of the leader
Reward
Power
leader's ability to deliver
rewards a worker values
Coercive
Power
deliver punishment for wrong
behavior
Expert
Power belief
in superior task knowledge of
leader
Referent
Power
Personal attractiveness of the leader
Sources
of Leader Power:
Furniture
and office arrangements
Prominently
displayed symbols
Appearances
of title and authority
Choice
of clothing
Presence
or absence of crisis
Power
Cues:
Commanding
Large Personal Space
64
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Maximizing
Body Size
Touching
Breaking
Eye Contact
No
Excessive Smiling
Avoiding
Submissive Language
Being
an Effective Leader:
First
Competency- an effective
leader has people waiting to
join the team
Second
Competency - a leader of
commitment and focus with
meaning
Third
Competency the
management of trust
Fourth
Competency
management of self
Fifth
Competency: Focus on
providing appropriate
delegation.
Sixth
Competency: Monitoring
or update meetings
Seventh
Competency: Develop
the skill of letting others
"RUN WITH THE BALL"
Asserting
Leader Influence:
Use
Rational Persuasion
Make
People Like you
Develop
Allies
Ask
for What You Want
Extend
Formal Authority with
Expertise and Credibility
Using
Power and Politics for Leader's
Future:
Use
Persuasion over
Coercion
Use
Patience over
Impatience
Be
Open-Minded Rather Than
Close-Minded
Use
Compassion over
Confrontation
Use
Integrity over
Dishonesty
Contrasting
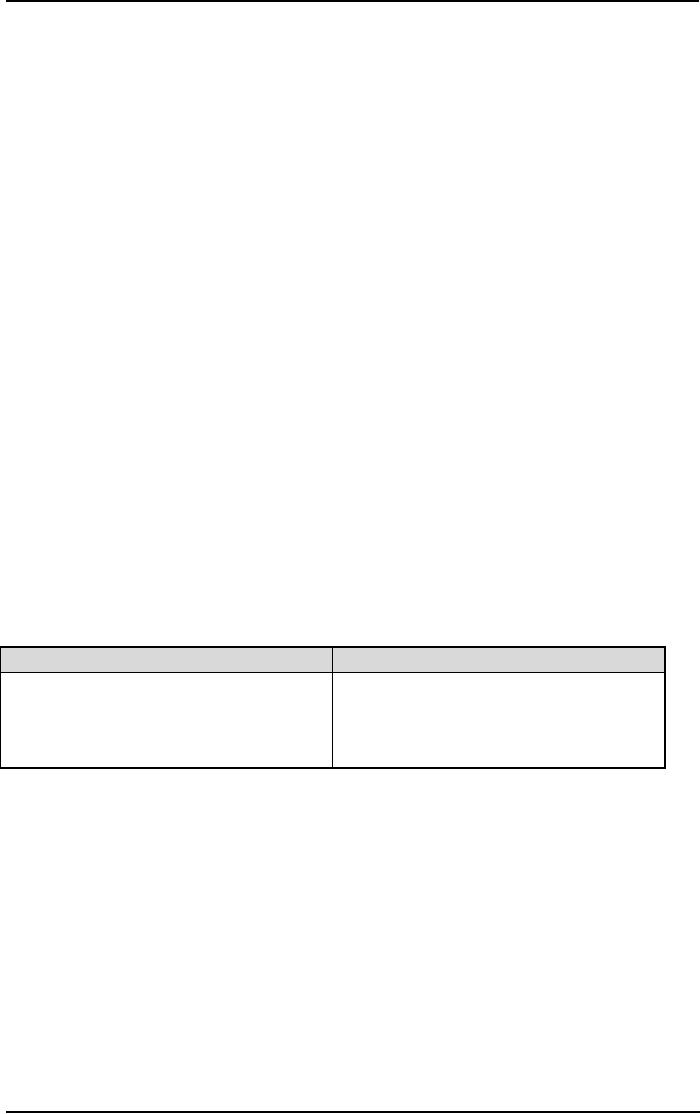
Leadership and Power:
Leadership
Power
1.
Used as a means for achieving
goals.
1.
Focuses on goal achievement.
2.
Requires follower dependency.
2.
Requires goal
compatibility
with
3.
Used to gain lateral and
upward
followers.
influence.
3.
Focuses influence
downward.
How
do Leaders Acquire the Power
Needed for
Leadership?
Acquiring
and using power and influence:
There
are three dimensions of managerial power
and
influence.
Downward.
Upward.
Lateral.
Effective
Leaders /Managers build and
maintain position power and personal
power to exercise
downward,
upward, and lateral
influence.
Leadership
Authority:
Views
on leadership authority:
Top-down
Bottom-up
Lateral
65

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
The
top-down theory holds"
Leadership
authority is based on position in a
social hierarchy. Power flows from the
highest level to
the
lowest
In
an organizational pyramid: Workers
support managers, Managers support executives.
The pyramid
serves
as the basis of most classical
organizational structures
The
top-down concept is the traditional
view of leadership.
The
right of authority is derived
from the right of private
property.
Transfer
of authority:
The
Board appoints executives to manage the
organization.
Executives
give authority to managers and
employees.
Bottom-Up
View:
The
bottom-up
theory
holds
that
Power
flows
from
below
because
people
can reject a
directive by saying
no. Saying yes or
no affirms or
denies
the
authority
of
others.
This
theory
was
first
described
by
Chester
Barnard of AT&T
According
to Barnard, an order will be accepted if
four conditions are
met:
1.
The
person understands the order
what a superior gave.
2.
The
order is consistent with the
organization's goals.
3.
The
person believes that the
order is compatible with
his/her interests and he can
do what the
superior
says.
4.
The
person is mentally and
physically able to comply
with order.
Leaders
must make sure
that:
a.
Directives
fall within their
subordinates' zones of
acceptance.
b.
If
not, orders may be met
with resistance and even
hostility.
Top-Down
vs. Bottom-Up
Both
views have merit that by accepting
employment, employees should acknowledge,
the
authority
of Leaders is to make decisions and give
orders, the employee's duty is to
comply and
obey
the orders.
How
do Leaders Acquire the Power
Needed for
Leadership?
Building
personal power by:
Building
expertise.
Leader
can build expertise by getting
advanced training and
education,
participation
in
professional
associations, and project
involvement.
Learning
political know-how.
Leader
may learn the ways to negotiate,
persuade, and understand goals and means
that others
accept.
Enhancing
likeability.
Through
Pleasant personality characteristics,
agreeable behavior patterns, and
attractive
personal
appearance, he may acquire the
power.
66

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Leaders
increase the visibility of
their job performance
by:
a.
Expanding contacts with senior
people and making a strong network of
strong/professional people
with
in and out side the
organization.
b.
Making oral presentations of written
work.
c.
Participating in problem-solving task
forces and involve in decision
making.
d.
Sending out notices of accomplishment to the
top management.
e.
Seeking opportunities to increase
name recognition.
Servant
Leadership:
Servant
leadership is a calling to serve and is
an approach to leadership development.It begins
with
caring
for and wanting to help
others. All great leaders are servants
first.
67
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION, ORGANIZATION THE STAGE FOR LEADERSHIP:Challenges, Value creation
- FOCUSING ON PEOPLE: THE KEY TO SUCCESS:People in the Process, Developing and Sustaining A World-class Workforce
- LEADERSHIP:Characteristics of Successful Leader, Why Study Leadership?
- LEADERSHIP (CONTD.):Characteristics of Leaders Who Fail, Why Leaders Fail?
- MANAGERS VS LEADERS:Characteristics, Effective Leadership, Respect for Diversity
- FOLLOWER-SHIP:Importance of Followers, Follower-ship Style
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS:Strategies for Cultivating Exemplary Followers, Important Traits of Leaders
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS (CONTD.):Qualities of Leaders, Self-Confidence, Integrity
- LEADERSHIP THEORIES/ APPROACHES:Personal Characteristics of Leaders, Managerial Grid
- CONTINGENCY THEORIES OF LEADERSHIP:The Fiedler Model, Situational Leadership Theory, Path-Goal Theory
- TRANSACTIONAL, CHARISMATIC AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP:Visionary Leadership
- THE LEADER AS AN INDIVIDUAL:Personality, Situation, Heredity, Environment
- ATTITUDE-PERSONALITY:Job Satisfaction, Work Situation, Self - Monitoring
- BIG FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS TYPE INDICATOR (MBTI):Sub-Categories Defined, Information Gathering
- SITUATIONAL FACTORS:Social and psychological climate, Culture of the organization
- BECOMING A LEADER! WHAT DOES IT MEAN & HOW DO YOU GET IT?:Mission Statement, Leading oneself
- BECOMING A LEADER:Elements of Leadership, CONCEPT OF POWER,
- UNDERSTANDING POWER:Sources of Power, Responses to the Use of Power, Managing Political Behavior
- LEADERSHIP POWER & INFLUENCE:Positional Power, Being an Effective Leader
- LEADERSHIP AND EMPOWERMENT:Power sharing and Empowerment, Share Information
- MOTIVATION:Guidelines for Delegating, Human Resource Approach
- MOTIVATION AT WORK, MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:What Factors Diminish Motivation in the Workplace
- LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:Communication & the Four Management Functions
- REVIEW-1:Organizational Performance, That is the Role of Management?, Leaders Vs Managers
- GROUP & TEAM CONCEPT:Groups versus Teams, Deciding When to Use a Team
- TEAM DYNAMICS:Stages of Group Development, Problem-Solving Teams, Benefits of Teams
- BUILDING THE TEAM:Leadership success requires, Strategies for Team Building
- A TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATION:Basic Steps, Span of Control, Categories of Decisions
- DECISION MAKING:Categories of Decisions, The Decision-Making Process
- TEAM DECISION MAKING:Team Problem Solving Techniques, Concept of QC
- EFFECTIVE TEAM COMMUNICATION:Team/Group Communications
- CONFLICT IN TEAM:Sources of Conflict, Scarcity of Resources, Dysfunctional Outcomes
- TRAINING/LEARNING OF TEAM:Training Methods, Phases of Learning Cycles
- LEARNING ORGANIZATION:A Litmus Test, Work Relations
- REWARDING & RECOGNIZING TEAMWORK:Compensating Teams, Individual or Team Rewards?
- MANAGING/LEADING VIRTUAL TEAMS:Communications in Virtual Organizations, Virtual Leadership
- EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS:Better Meetings, Meeting Roles, Meeting Room Facilities
- LEADING TEAM:Team Leadership Structures, Leadership Demands and Duties, Leadership Direction
- REVIEW-II:Types of Teams, Characteristics of High Performance Teams, Sources of Conflict
- STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP:Strategic Management, Determining Strategic Direction, Developing Human Capital:
- LEADING CHANGE:Dynamics of Change, Change Models, Unfreeze
- CREATIVE LEADERSHIP:Awaken Your Senses, How Might These Definitions Be Integrated
- ETHICS IN LEADERSHIP:Character Traits Reflect Ethics, Manifests Honesty
- LOOKING AT THE FUTURE: WHAT COMES NEXT:Benefits of Teams, Ethical Leadership,
- TEAMWORK: LEARNING FROM NATURE:Social Behavior, Termites, Learning from Nature