 |
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
42
POLITICAL
REFORMS
In this
lecture we will examine the
Political reforms, Administrative
structure and Financial
arrangements
(PFC) in greater detail.
Political
Reforms
Elctoral
Arrangements: The
foundation of the electoral structure
for the three tiers of
local
government
is the union council. The union is a
multimember ward for the election of
members of the
union
council that is, each
constituency is on average 25,000,
and each union council is
composed of 21
directly
elected members. The
nazim
and
naib nazim
(mayor
and deputy mayor) are
elected on a joint ticket.
The
remaining 19 seats are, as discussed in
last lecture, as
following:
-
12
Muslim seats, 4 of which are
reserved for women;
-
6
seats for peasants and
workers of which 2 are
reserved for women;
-
1
seat for minority
communities;
Indirect
Elections
The
nazim of the union council then
becomes member of district council
and naib nazim of
union
council
becomes members of tehsil council.
The
union councilors constitute the Electoral
College for the district or tehsil
councilors and for
the
district and tehsil nazim
and naib nazim. 1/3 of seats
are reserved for women
(directly elected at union
council
level and elected by Electoral College of
Union Councilors at tehsil and district
level).
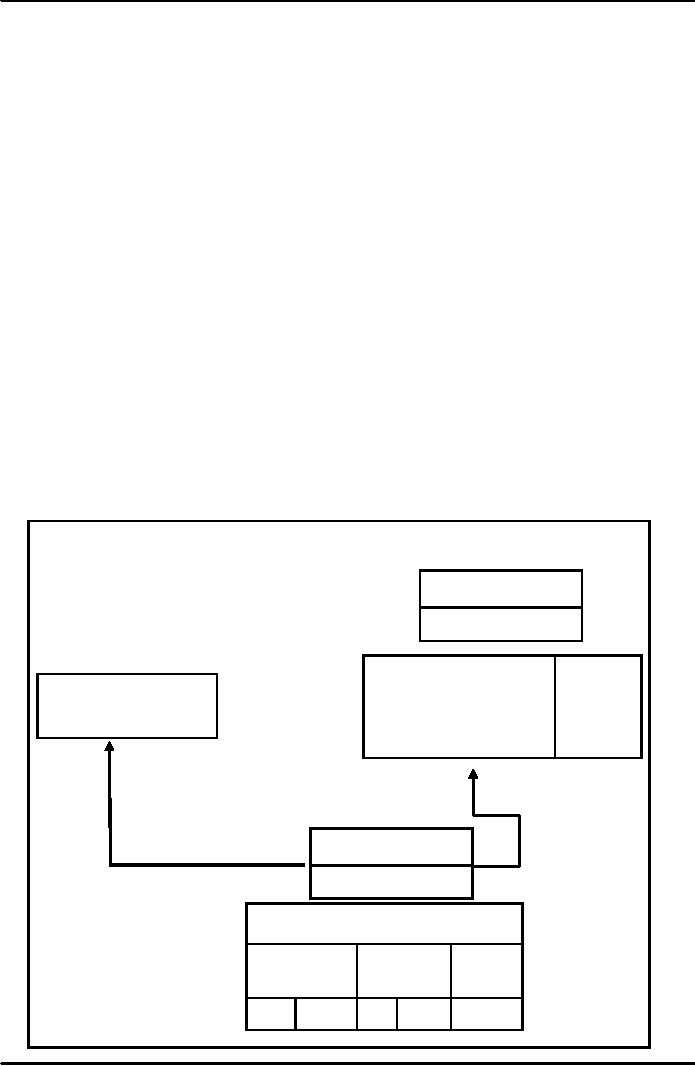
Figure
1
Indirect
Elections
Tehsil
Nazim
Naib
Nazim
2/3
2/3
1/3
Union
Naib Nazims
Union
Nazims
Indirectly
(Ex
Officio)
(Ex
Officio)
Elected
Zila
Council
Tehsil
Council
Union
Nazim
Naib
Nazim
Naib
Nazim
Peasants
Min
General
Seats
(6)
(1)
(12)
8
4
4
2
1
148

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
In
addition 5 percent of district
and tehsil seats have been
reserved for peasants (in
rural
constituencies)
or workers (in urban areas),
and 5 percent for minorities.
Thus overall districts council
and
tehsil
council are made up of about 2/3
directly elected members and
1/3 indirectly elected
including nazim
and
naib nazim. The size of
district and tehsil councils
varies according to the number of union
councils
within
district. Each tier of local government
has a term of office of 4 years,
with 2 term limit for
nazimeen
and
naib nazimeen. The indirect
elections system is illustrated in Figure
1.
District
There
is a departure from convention
and in the Devolution Plan, at
district level representation of
marginalized
groups is intentionally designed in the
election. Thus, there are 33 %
seats for women in
the
District
Council. Similarly 5% seats are for
workers and 5% for
minorities.
In
order to have better quality of
elected representative a condition of
matriculation/secondary
school
has been kept.
Tehsil
Likewise
for better representation of marginalized
groups following seats are
kept at Tehsil level:
-
33%
women seats
-
5%
for workers/peasants
-
5%
for minorities
-
Qualification
of at least matriculation / Secondary
certificate or Equivalent.
Each
tier of local government has a term of
office of four years, with a
two-term limit for nazimeen
and
naib
nazimeen at all
levels of government .
Functions
of Union Council
We
have discussed the functions of
district council. And we have
also discussed the function
of
Tehsil
council. Union Councils as we know
are the lowest local unit in
rural areas (the lowest unit
in urban
area
is town committee. A Union
Council as we know has a
population of 25,000 performs
following
functions:
1.
Municipal function is the function of
sewerage and sanitation i.e.
cleanliness of area.
2.
Finance: Performs financial function of
managing expenditures and rousing
revenues.
3.
Pubic safety: Managing bridges, culvert
etc.
4.
Health: Provision of basic
preventive health care, like
controlling epidemics
etc.
5.
Education: Provision of basic primary
education.
6.
Literacy: Literacy programmes for adults
who were unable to receive
primary education.
7.
Justice: Provision of justice in
civil cases through
"masalihat Councils"
In
addition Union Council also
performs following functions:
a.
Undertake development projects in connection
with above mentioned functions.
b.
Impose taxes, to fund annual development
plan. The proposed revenue
raising authority of
Union
Council is: fee for
licensing of professions and
vocations, fee on sale of
animals in cattle
market,
market fee, fee for
certification of births, marriages and
deaths etc.
c.
Local securities system-union
guards
d.
Creation of villager council, citizen like community
boards.
Structure
within local government
We
have discussed the administrative
structure of local government in the last
lecture and it was
mentioned
that the executive branch of
each district government has 10 to 14
departments, The DCO,
the
highest-ranking
civil servant in the district, heads the
District Coordination department. An
Executive
District
officer (EDO) heads each of
the remaining departments. The staff at
district and tehsil level
was
mentioned.
In addition three groups of
employees were assigned to the
new district governments.
These
were:
149
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
1.
Federal employment groups, primarily
District management Group
(DMG) and the Audit
and
Accounts
Group.
2.
Former rural district council employees;
and
3.
Provincial employment groups, particularly Public
health. Engineering Department (PHED)
Rural
Development, Local Government, health and
Education.
A
large majority of district staff
formerly belonged to the provincial employment group,
particularly
education.
Most are in grades 1-15 (90%
of district staff in NWFP and 83% in
Sindh) Tehsil Municipal
Administration
(TMA) inherited staff from the
former urban council and rural
district council and
also
some
provincial PHED staff where
these have been
devolved.
Fiscal
Reforms
Areas
of expenditure responsibility of the federal and
provincial governments are
set out in the
Constitution
of Pakistan as mentioned before. The
Constitution is silent on the remaining
functions
(functions
other than federal and
provincial government) and assumes by
default that these
remaining
functions
are to be performed by the sub-national
(that is, provincial or
local) governments.
Thus,
according to the Constitution, the
federal government is responsible for
foreign affairs,
defense,
banking and currency, postal
service, transportation (ports, airports,
railways), while the main
provincial
responsibilities are police services,
justice, roads, education and
health.
The
actual assignment of functions
remained much more
centralized than the
Constitutional
provisions
required, as higher levels of government played a
dominant role in areas of
shared responsibility
.
The
Constitution accepts that the
actual or implied assignments of
expenditures and revenues
will
lead
to vertical fiscal imbalances between the
upper two levels of government (Federal
& Provincial) which
are
to be resolved through revenue
sharing. Thus, the Constitution
also sets up the National
Finance
Commission,
an institution assigned the task of
determining appropriate revenue sharing
arrangements
among
the federal and provincial
governments.
Table
1 shows the responsibilities of province,
District and Tehsil
governments.
Table
- 1
Province
District
Tehsil,
Taluka, or Town
Education
Education
Health
Health
Agriculture
Agriculture
extension
On-farm
management
Soil
conservation
Fisheries
Forests
Water
Supply and
water
supply and sanitation
Sanitation
sewerage
Sewerage
transport
Transport
inter
tehsil road
Street
lighting
Parks
and playground
Parks
and playgrounds
Street
light
Municipal
regulation
Municipal
regulation
Irrigation
Police
Mines
and mineral
Development
Industrial
and labor
Regulation
150

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Under
Devolution Plan, there were
no shifts of responsibility from the
federal to the provincial
governments.
The initial attempt was to
bring about changes that
would not require any
constitutional
amendment,
which the devolution of any
function to the local governments from
the Federal Legislative
List
(or even the Concurrent List)
would have required.
As
the previous table indicates, significant functional
transfers did occur from
provincial to local
governments.
Federal-provincial
In
Pakistan, revenue sharing is the
dominant form of federal-provincial
fiscal relations. The
main
source
of provincial revenues is a transfer
based on a share of federal tax
collections. The decision on
the
list
of taxes ("divisible pool"), the
ratio of the provincial-federal share of
the pool and the formula for
its
distribution
to the provinces is to be fixed at least
once every five years by the
National Finance
Commission
(NFC). This has been
discussed in the topic Public
Finance.
ProvincialLocal
Transfer
All
the four provincial government share
resources with district
governments. Just as there
is
Federal
Divisible Pool, there is
Provincial Divisible Pool. This
Pool comprise: transfer from
federal divisible
pool,
straight transfers from federal
government and provincial tax revenue.
Sindh PFC estimates the
shares
of
provincial and district government
for both current and development
expenditure. The Sindh PFC
decided
that for current expenditure, the
Provincial Divisible Pool
comprises:
Federal
divisible pool
transfer
Federal
straight transfers
Provincial
tax revenue
The
transfers to districts were
based on gap between
district expenditure and revenue
transfers
from
provincial government to districts on the
basis of population, tax collection
and backwardness
index
of
districts.
Now
we will examine the weaknesses
and strengths (success) of
Devolution Plan and
Local
Government
Ordinance 2000.
We
will first look at the
weaknesses and then
strengths. Some of the weaknesses of the
local
government
system are:
1.
An
attempt to undermine provincial
autonomy. The
provinces now have to
systematically
evolve
mechanism to share resources.
Also prior to this system,
provinces were
autonomous
and
had centralized system.
People from remove areas in
the provinces had no access
to
provincial
headquarters.
2.
Violation
of a fundamental structure of
constitution. The
Constitution does not
provide
local
government structure.
3.
Resistance
of bureaucracy against system. The
power of bureaucracy has weakness
and at
the
district level DCO is answerable to
elected nazim.
4.
Role of members of legislative
assembly. The members of
legislature have greater
role in the
development
of the area and more
answerable to people.
Some
of the strengths of the system
are:
1.
Unleashed horse of bureaucracy
has been bridled. The
office of DC has been
now
brought
under the control of elected
representative.
2.
Elimination of urban-rural division.
Attempt has been made to
reduce the gap
between
urban
and rural areas.
3.
Formula - based division of
financial resources. The
PFC now has to share
resources under
a
formula, which is logical and
appropriate.
151

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
4.
Grass root organizations. The
local government system has
established grass
root
organizations
like citizen community board to oversea the
working of government
organization.
5.
Enhanced representation of
women.
6.
Political linkage
7.
Autonomy of local
Representatives
Conclusions
Examined
local government structure and
functions in greater detail.
Also
examined the weaknesses and
strengths of local government.
152
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management