 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
34
LEADERSHIP
At the
end of the lecture students
will be able to
understand:
-
Leader
ship functions;
-
Leadership
styles;
-
Theoretical
explanations of leadership and
-
Importance
of theories to management;
Leadership
Functions
To
operate effectively groups
need leaders who can
perform two major functions in
the
organizations
to achieve objectives. The
functions of leader in organization
are:
1.
Task-related
or problem-solving functions: While
supervising workers, manager
has to help
group
solve problems. For example
the employees are asked to
process an admission
application
in a college and the computers in
which data is entered is not
working. The
manager
will have to resolve this
problem by asking concerned people to
repair computer.
The
mangers that focus more on
tasks are more concerned
about output.
Group-maintenance
or social functions. Group-maintenance functions
are mediating
2.
disputes
and ensuring that
individuals feel valued by the group.
These problems relate to
people
. Suppose two employees
working have some
differences and now they do
not talk to
each
other. The manager will
have to mediate between two
employees.
Leadership
Styles
Managers
who have a task-oriented style
closely supervise employees to be
sure the task is
performed
satisfactorily. Getting the job done is given
more emphasis than employees'
growth or personal
satisfaction.
Managers with an employee-oriented style
put more emphasis on
motivating, mediating etc.,
rather
than controlling
subordinates.
Tannenbaum
and Schmidt were the first
to describe factors that influence
managers' choice of
leadership
style. They favoured
`employee-centered' style, but they
said that managers
considered three sets
of
forces before choosing a leadership
style. These sets of forces
are:
1.
Forces in manager: his/her knowledge,
background, experience, for example a
managers who
believes
that organization's needs are
more important will be more
directive.
2.
Forces in employees: their
knowledge, experience, background, willingness to
work, attitudes
aptitude
etc.
3.
Organizational force: organizational preferred style,
culture, pressure of time etc.
All
the three forces will combine to
determine what style of leadership is
used by manger.
122
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
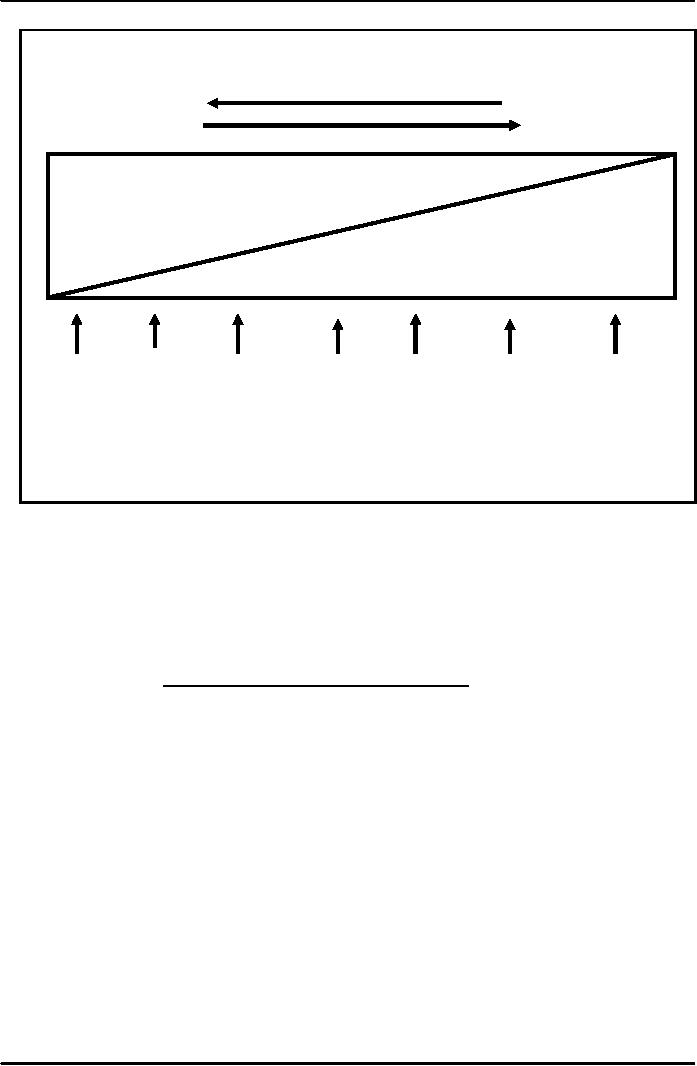
Figure
1
Continuum
of Leadership Behaviour
Subordinate-Centered
Boss-Centered
Leadership
Leadership
Use
of Authority
By
the Manager
Area
of Freedom
For
Subordinates
Manager
Manager
Manager
Manager
Manager
Manager
Manager
Defines
Permits
Presents
Presents
Presents
makes
"sells"
Limits;
employees
Problem,
Ideas
and
Tentative
Decision
and
Decision
Asks
to
function
Gets
Invites
Decision
announces
group
Within
limits
Suggestions,
Subject
to
Questions
it
To
make
Defined
by
Makes
Change
decision
superior
decision
Now
let's look at figure 1 which
shows a scale of leadership
style i.e. whether manager
will have
"subordinate
centre style", in which, area of freedom
for subordinates will be
more. Or whether manager
would
have "boss centered leadership"
where boss will have
more authority. The two
extreme leadership
styles
are shown and in between
these two extremes is the
variation of style that a
manager will adopt
depending
upon the three
forces.
Contingency
Approaches
Researchers
using the trait and behavioral
approaches showed that effective
leadership depended on
many
variables, such as organizational culture
and the nature of tasks. No
one trait was common to
all
effective
leaders. No one style was
effective in all situations. According to
this approach it will be
the
situation
that will determine what should be the
leadership style. And since
every situation is
different,
therefore,
every style is
different.
Contingencies
theories focus on the following
factors that determine
leadership style:
1.
Task
requirements: The style of
leadership depends on what the work
demands. For example,
in
the
battle field the task demands
that orders to be complied
strictly.
2.
Peers'
expectations and behavior: In organizational
situation, people whom we work with
have
certain
expectations, like peers may
expect that you will
cooperate.
3.
Employees'
characteristics, expectations, and
behavior: It is important for manager to
know
characteristics
and expectations of employee
and decide to have a
leadership style accordingly.
4.
Organizational
culture and policies: Organizations have
their culture and every organization
has its
own
policies; therefore, managerial leader
should also keep in view
these factors before
adopting
leadership
style.
123
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Hersey
& Blanchard's Contingency
Model
Main
contingency approach to leadership is given by
Paul Hersey and Kenneth H.
Blanchard's
Contingency
leadership model. It says that the
most effective leadership style
varies with the "readiness" of
employees.
Hersey and Blanchard define
`readiness' as desire for
achievement, willingness to
accept
responsibility,
task-related ability, skill,
and experience of employees.
Also the goals and knowledge
of
followers
are important variables in determining
effective leadership style.
In
other words the situational leadership
says that leadership style
will vary from situation to
situation.
Personal
Characteristics of Employees
The
personal characteristics of employees
will partially determine leadership
style. Hersey and
Blanchard
believe that the relationship between a
manager and follower
(employee) moves through
four
phases
as employees develop, and managers
need to vary their leadership
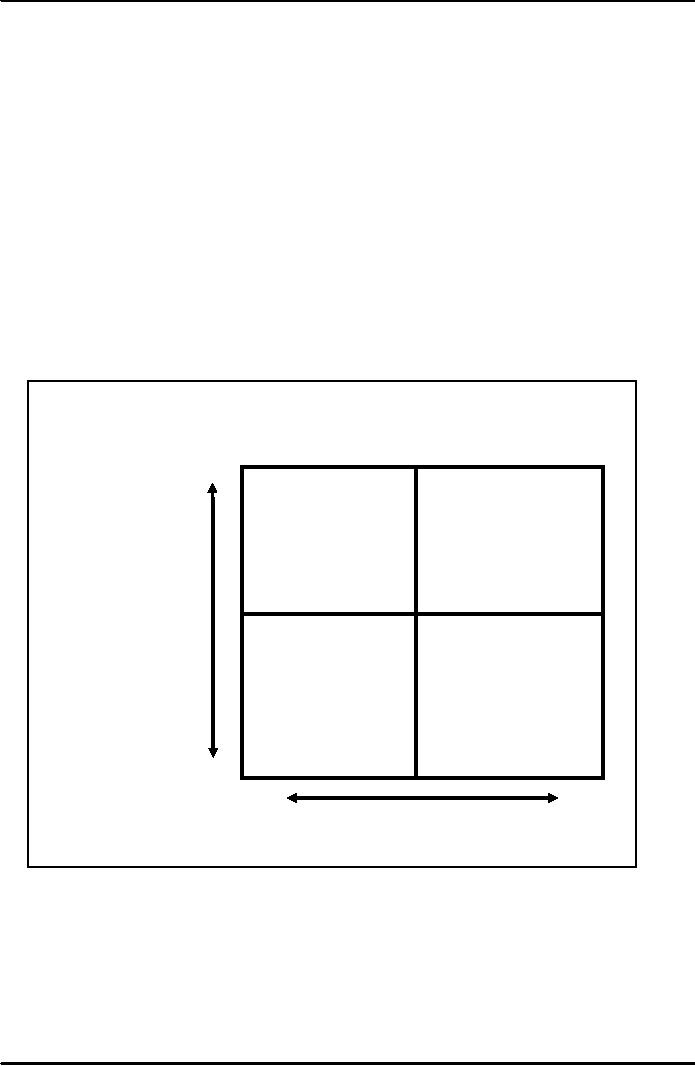
style (Figure 2). In the initial
phase
of
readiness high amounts of
task behavior by the manager is
most appropriate (box 1). In this
situation
employees
must be instructed, and
managers will have low level
of relationship behaviour and high level
of
guidance.
In box 2 there is high task
and high relationship as employees
have understood the job
and
manager's
guidance is little and there
is shift on relationship. In box 3
employees have understood job
well,
now
there is high relationship and
low task emphasis.
Figure
2
Situational
Model of Leadership
Leader
Behavior
(High)
High
Task And
High
Relationship
High
Relationship
And
Low Task
Relationship
Behavior
2
3
(Providing
Supportive
Behavior)
High
Task and
Low
Relationship
Low
Relationship
And
Low Task
4
1
(Low)
(Low)
(High)
Leader
Behavior
(Providing
Guidance)
There
are two other types of
leader. These are discussed
below
1.
Transformational or
Charismatic
One
area of growing interest is the
study of individuals who
have an exceptional impact on
their
organizations.
These individuals may be
called transformational leaders. Through
their personal vision
and
energy
they inspire followers and have a major
impact on their
organizations.
2.
Transactional Leaders
124

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Leaders
who determine what subordinates
need to do to achieve objectives,
classify those
requirements,
and help subordinates become
confident. They do routine
work of the organization and
are
also
called bureaucratic
leader.
Managerial
Leadership and Team
As
it was said in the beginning of the
lecture on leadership that a
leader needs followers
and
without
followers leader has no
significance. In managerial leadership it
is the existence of team which
is
important.
Besides, people get the organizational
work done through people. Therefore
must know the
dynamics
of team
Concepts
Leadership
functions:
Two
important leadership functions
that manager has to
perform
(task-related and social
functions).
Employee
centered style:
This
style of leadership is more
concerned with
employee
characteristics
and accordingly adopting a
leadership style.
Situational
leadership style:
This
style of leadership is the style
that depends on situation.
125
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management