 |
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
33
MOTIVATION
AND LEADERSHIP
After
the lecture students should be able to
examine:
-
Remaining
theories of motivation;
-
Relation
of motivation to leadership;
-
Defining
leader and leadership
and
-
Importance
of leadership;
Expectancy
Theory
Another
important theory of motivation is
expectancy theory that helps
us understand human
behaviour
and people in organization can be
motivated.
According
to expectancy theory, people choose
how to behave from among
alternative courses of
action,
based on their expectations of what
there is to gain from each
action. There are four
assumptions
about
behaviour in organizations on which the
expectancy approach is based.
These assumptions
are:
1.
Behavior
is determined by a combination of factors in the
individual and factors in
the
environment.
Individual's behaviour is not
simple. It is complex as many factors
are affecting
person.
2
Individuals
make conscious decisions
about their behavior in the organization.
Individuals
know
how they have to behave in organization
because they can judge their
actions and
response.
3.
Individuals
have different needs,
desires, and goals.
4.
Individuals
decide between alternative behaviors on
the basis of their expectations
that a
given
behavior will lead to a
desired outcome. For example
individuals know that if
they
disobey
or do not comply they will be fired
from the job.
These
assumptions become the basis
for the
expectancy
model, which has three
major
components:
1.
Performance-0utcome
expectancy: Individuals
expect certain consequences of
their
behavior.
These expectations, in turn, affect
their decisions on how to
behave. For
example,
a student who is thinking
about getting good marks may
expect praise if he
gets
good
marks or an employee who has
achieved the desired results
expects that he/she
will
be
rewarded.
2.
Valence:
The
outcome of a particular behavior has a
specific valence, or power to
motivate,
which varies from individual
to individual. For example, to a
manager who values
money
and achievement, a transfer to a higher
paying position in another city may
have
high
valence. Valence can be expressed in
mathematical term from the example given
to
you.
If transfer (T) has high
value or valence and where
transfer brings "money".
The
individual
will give high value or
preference or valence to transfer.
3.
Effort-performance
expectancy: People's
expectations of how difficult it
will be to
perform
successfully, affect their decisions
about behavior. If the task is
difficult and
complex,
employee will assess the
effort involved in doing or completing
the job.
Accordingly
he will put his effort
commensurate with reward.
The employee will ask
what
I
will get in return in doing
such a difficult job.
4.
These
three components of Expectancy
Theory can be summarized in
three questions.
These
questions
are:
a.
If
I do this, what will be the
outcome?
b.
Is
the outcome worth the effort to
me?
c.
What
are my chances of achieving an
outcome that will be
worthwhile for me?
118
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Thus,
according to expectancy theory,
individuals are motivated when they
see a favourable
combination
of what is important to them and what they
expect as a reward for their
efforts, and they
behave
accordingly.
Reinforcement
Theory
Reinforcement
theory is associated with the
psychologist B.F. Skinner and
other contemporary. He
has
shown through the experiment that
how the consequences of past
behavior affect future actions in
a
cyclical
learning process. He conducted an experiment on a
dog. What he did was
that he brought food
in
front
of a dog. When the food came
in front of dog his mouth
started to salivate. Every time the
food
came
the mouth salivated. Now, in
his experiment he introduced another
element. The food was
presented
and
as soon as food was
presented the dog was given electric
shock. The sequence of event
was:
Food
→
salivation→ shock.
This
experiment was repeated number of times.
After sometime it was
observed that the dog
stopped
salivating whenever the food was
presented.
The
results of the experiment were that
behaviour can be modified. This
process may be
expressed
as
follows:
Stimulus
→
Response
→
Consequences
→
Future
Response.
(Food)
(Salivation)
(Electric
Shock)
(no
salivation).
We
see that behind the Reinforcement Theory
is the concept of punishment and reward.
The
application
of this theory is seen when
animals are trained to perform
certain actions. You might
have seen
monkeys
being asked to dance by monkey-man and
when monkey performs an act he is given
something to
eat.
Reinforcement Theory is useful in understanding
human behaviour as well. Human
behaviour can also
be
modified through reward and
punishment.
If
in organizations we want to encourage people to
come on time, then those who
come on time
have
to be encouraged. Now encouragement is a
kind of reward. We have to
remember that rewards
have
many
forms and dimensions. Rewards
are not only in money
form. Even a nice word
can be reward. In
organization
sometimes certificates, badges,
mugs etc can be used as
rewards for good
behaviour.
Similarly
punishment has many dimensions in
organization. The severe being thrown
out of job
and
a mild punishment could be to use
word of censure for
behaviour that is not
desirable.
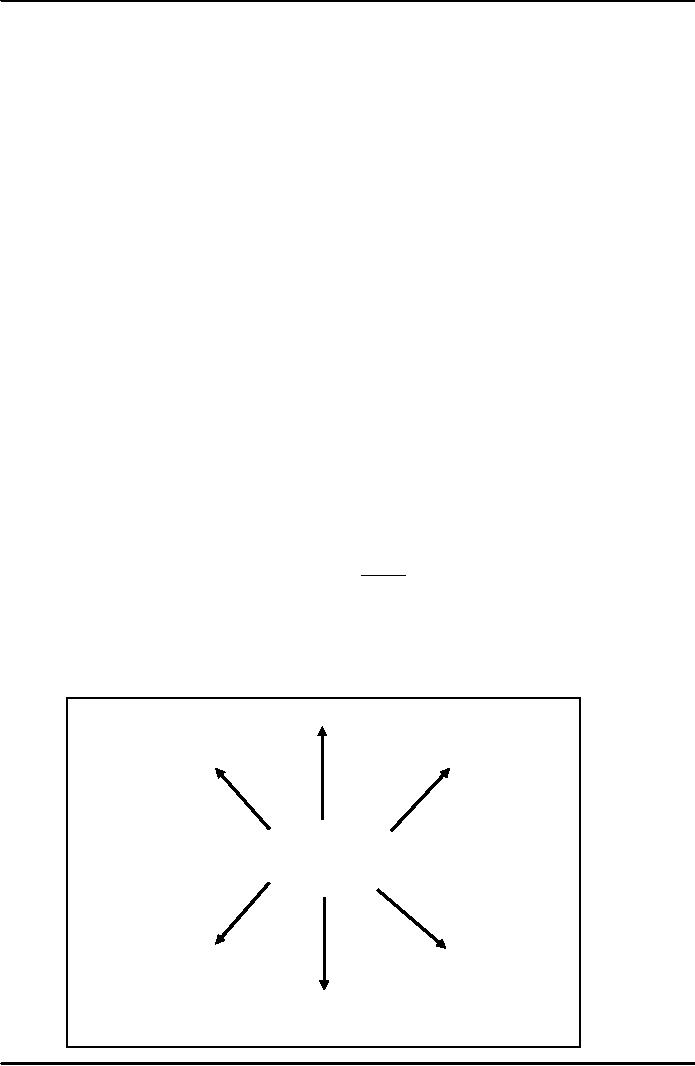
Figure
1
Team
Building/Work
Coping
Change
Leadership
MOTIVATION
Environment
Feel
Good about Yourself
(Non-complaining,
non-cynical)
Personal
Charisma
Behaviour
119
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Figure
1 presents the importance and relationship of
motivation to other dimensions of
life in
general
and organizational life as well. A
motivated person in general is a
good person because he/she
has
positive
and pleasant affect on environment. A
motivated employee or manager or superior
can lead and
makes
other feel good about
themselves. Motivation is required also
to build team and make
teams work.
Motivation
also helps that environment
are non complaining environment.
All of this is manifestation of
positive
behaviour; which is essential for a
good manger.
Leadership
Leader
and leadership are two
different concepts. A leader is a
person who leads a group
of
individuals.
Leadership on the other hand defines the
characteristics of the person who
leads. Thus
Leadership
is the software that makes a
leader.
Managerial
Leadership
Leader
and leadership are often
thought of in the larger context
like, political leader,
reformers,
prophets,
thinkers, philosophers etc. But in the
discussion of leadership that
will follow the emphasis is
on
Managerial
leadership. Managerial leadership is the
leadership that managers
exercise in organizational
situation
to achieve its goals.
Defining
Leadership
There
are almost as many different
definitions of leadership as there
are persons who
have
attempted
to define the concept. We will define
managerial leadership as the process of
directing and
influencing
the task-related activities of group
members. There are four
important implications of our
definition
of managerial leadership. This is
discussed below:
1.
First,
leadership involves other
people-employees or followers. By their
willingness to accept
directions
from the leader, group
members help define the
leader's status and make
the
leadership
process possible; without people to
lead, all the leadership
qualities of a manager
would
be irrelevant.
Second,
leadership involves an Unequal
distribution of power between leaders
and group
2.
members.
Group members are not
powerless; they can and do
shape group activities in a
number
of ways. Still the leader
will usually have more
power. Where does a
manager's power
come
from? The five bases of a
manager's power are:
a.
Reward
power;
b.
Coercive
power;
c.
Legitimate
power;
d.
Referent
power and
e.
Expert
power.
The
Trait Approach
There
is a believe that leaders
are born and that people
are born with certain traits
or characteristics
that
are peculiar to leaders.
Others who are not
born with those traits cannot be
leaders
3.
The
third aspect of leadership is the
ability to use the different forms of
power to influence
followers'
behaviours in a number of ways.
4.
The
fourth aspect combines the
first three and acknowledges
that leadership is about
values.
Moral
leadership concerns values
and requires that followers
be given enough knowledge of
alternatives
to make intelligent
choices.
The
first systematic effort by
psychologists and other
researchers to understand leadership
was the
attempt
to identify the personal characteristics
of leaders. This approach assumed
that leaders share
certain
inborn
personality traits. This view
that leaders are born
and not made is still
popular among
laypersons,
though
not among professional
researchers.
What
are the traits? Following
are some of the traits that
leaders possess:
1.
Confidence.
2.
Sense
of direction (clear
goals)
3.
Human
insight
120

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
4.
Discipline
5.
clarity
of tasks
6.
Consistency
7.
Hard
work
8.
Motivate
9.
Good
communication skills
10.
Integrity
11.
Honesty
In
searching for measurable
leadership traits, researchers
have taken two
approaches:
(1)
Comparing
the traits of those who have
emerged as leadership with the traits of
those who
have
not; and
(2)
Comparing
the traits of effective leaders with
those of ineffective
leaders.
Leaders
and Non-leaders
It
is true that leaders as a group
have been found to be
brighter, more extroverted, and
more self-
confident
than non leaders. So some of
the traits identified may be the results
of leadership experience
rather
than of leadership ability i.e., people
who get more opportunity to
interact may acquire some of
the
traits
of leaders.
Effective
& Ineffective Leaders
Comparing
the characteristics of effective and
ineffective leaders are more
recent studies. One
study
did find that intelligence,
initiative, and self-assurance
was associated with high
managerial
performance.
The study also found
that manager's supervisory
ability for better performance
was most
important.
Concepts
Expectancy
theory:
The
theory explains that people
try to assess the response of
their
actions
and expect something in
return.
Leader:
A
person who leads.
Leadership:
It
is a quality or a trait that
leaders possess that makes
them unique.
Managerial
leadership:
It
is the leadership that managers
exercise in organization to
achieve
goals.
121
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management