 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
31
AUDIT
At the
end of lecture the students
will be able to:
-
Understand
the concept of audit and
audit in government
-
Understand
the concept of Performance
Audit
-
Understand
Audit as control tool
Audit
is a specialized area of financial
management and control.
Their instruments of control
are
governments
rules, regulations and
procedures which must
adhered to when making financial
transactions.
Definitions
of Audit
Following
are some of the definitions of
audit:
It
is an examination and verification of a
company's financial and accounting
records and
supporting
documents by a professional,
It
is a formal examination of an organization's accounts
or financial situation. An audit may
also
include
examination of compliance with applicable
award terms, laws,
regulations and policies
after
transactions
are made.
It
is the examination of some or all of the
following items: documents,
records, reports, systems
of
internal
control, accounting procedures,
and other evidence, for
one or more of the
following
purposes:
An
examination and verification of a
company's financial and accounting
records and
supporting
documents
by a professional
A
formal examination of an organization's individual
accounts or financial situation. An audit
may
also
include examination of compliance with
applicable award terms,
laws, regulations and
policies.
The
examination of some or all of the
following items: documents,
records, reports, systems
of
internal
control, accounting procedures,
and other evidence, for
one or more of the
following
purposes:
(a) determining the propriety, legality,
and mathematical accuracy of
proposed or
consummated
transactions; (b) ascertaining whether
all transactions have been
recorded; and (c)
determining
whether transactions are accurately
reflected in the accounts and in the
statements
drawn
there from in accordance
with accepted accounting
principles.
Article
169 of the Constitution gives the
functions of the Auditor General, who
heads the Audit &
Accounts
organization of Government of Pakistan. This
organization, under the Audit & Accounts
Order
1973
ensures that the public
money is spent and
transactions are made in
accordance with the financial
rules.
The
accounts of federation and of provinces
will be kept according to the principles
and methods
given
by the Audit & Accounts Order and
rules and procedures. All
the accounts will have to be
submitted
to
the President in the case of federation
and to the Governors in case of the
Provinces who will put
before
the
respective assemblies.
Use
of Public Money
Public
money is the money from tax
and non tax revenue and
borrowed money. This money
has to
be
spent according to the laid
down procedures (Drawing and
disbursing Handbook). The
fundamental
principle
of spending public money is to
spend public money in a
manner as one would spend
ones own
money.
Definition
of Performance Audit and Value
for Money
While
audit is like a "post
mortem", after the event or financial transaction
has taken place it
verifies
whether rules were adhered
to. In performance audit the
whole working of the organization
is
analyzed.
111

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Performance
audits are value for
money audit and the use of
resources by public
sector
organizations
in relation to its achievement of
goals. Although performance
audit can be very wide-ranging,
in
broad terms, it can be applied
to:
-
Those
activities involving a considerable level of
resources
-
Projects
that are at risk of failing in
their objectives
-
Issues
which are of concern to Parliament or the
Public Accounts Committee, (Public
Accounts
Committee is a committee of parliament which reviews
the accounts of all
government
organization every year).
The
term "value for money"
refers to the way in which
resources (financial, human or
physical)
have
been allocated and utilized
by the entity (organization).
Following
definition has been used
for performance audit:
"A
performance audit "is an objective
and systematic examination of a
public
sector organization's programme,
activity, function or
management
systems
and procedures to provide an
assessment of whether the entity,
in
the
pursuit of predetermined goals, has
achieved economy, efficiency
and
effectiveness
in the utilization of its
resources".
Performance
audit, therefore, involves an independent assessment
of whether economy, efficiency
and
effectiveness have been
achieved by organization. Now let us
see each of the word used in
definition to
have
better understanding of performance audit.
Economy
Economy
is concerned with minimizing the
cost of resources used (staff,
materials and equipment)
for
an activity in the pursuit of its
objectives and whether they are in
accordance with sound
administrative
principles
and practices and management
policies. An economical organization
acquires its input
resources,
of
the appropriate quality and quantity, at
the lowest cost. In summary,
economy means minimizing the
cost
of
resources used for an
activity, having regard to quality
i.e. spending economically, whilst
maintaining
quality.
Example:
Where standard items such as
school or hospital supplies of a given
quality are purchased at
the
best
possible price.
Example:
Cost of a vehicle in comparison with
another model of similar quality.
Efficiency
Efficiency
is concerned with the relationship
between goods and services
produced (the outputs)
and
the resources used to produce them (the
inputs). An efficient entity produces the
maximum output
from
any given set of inputs. Alternatively,
it may require minimum input. This
will be reflected in
increased
productivity
and lower unit costs. In
summary, efficiency means ensuring
that maximum output of
goods
and
services has been gained
from the resources used in
their production i.e.
spending well.
Example:
Efficiency has improved when
the unit cost of teaching
children or providing hospital
treatment
has
been reduced over time; or
where more children have
been taught or hospital beds
provided,
without
additional resources.
Example:
Reduction in repairs and maintenance
cost of equipment, for example,
vehicles, computers or
photocopiers,
is a measure of efficiency
Effectiveness
Effectiveness
is concerned with achieving predetermined
objectives (specific planned
achievements)
or goals and with actual
impact (the output achieved)
compared with the intended
impact
(the
objectives). Using a range of performance
measures and indicators, it is possible
to assess an entity's
effectiveness.
In summary, effectiveness means
ensuring that the desired
results, objectives, targets
or
policies
have been successfully
achieved i.e. spending
wisely.
112
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Example:
Where there has been an
improvement in school examination results
or where sickness rates
have
fallen
as a result of medical
care.
Example:
Whether the purchased item or service
provided was "fit for
purpose".
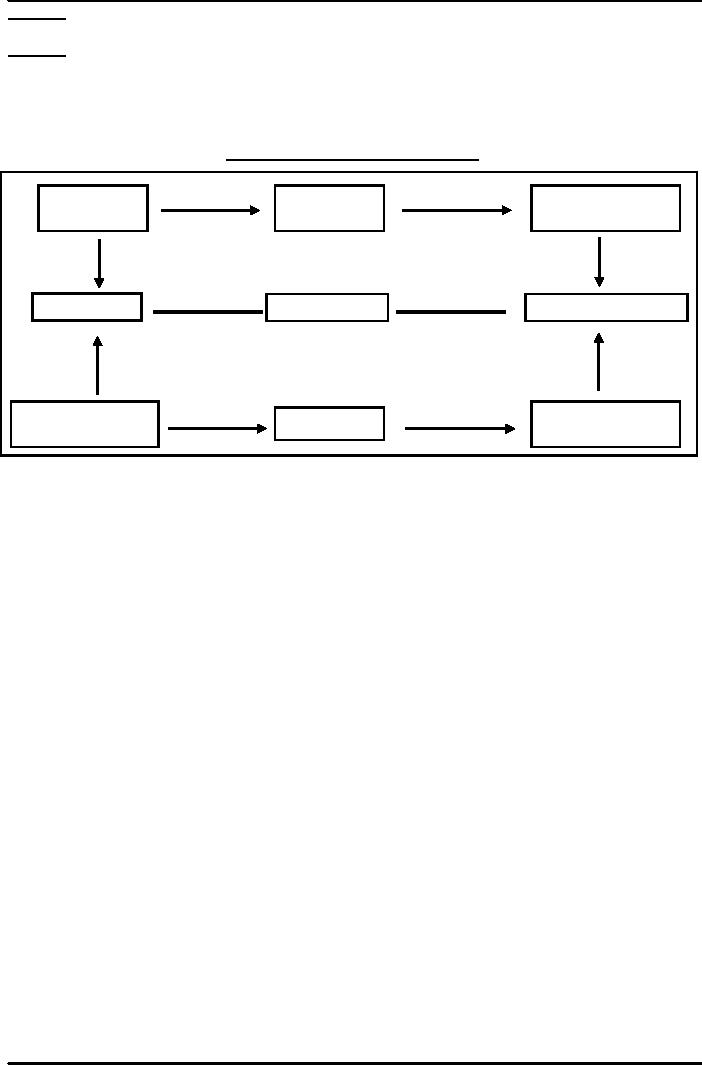
The
following model presented in Figure 1,
illustrates the relationships between inputs,
processes
and
outputs and between economy, efficiency
and effectiveness:
Figure
1
Economy,
Efficiency and
Effectiveness
Planned
Planned
Planned
Inputs
Inputs
Inputs
(Policy
Objectives)
Economy
Efficiency
Effectiveness
Actual
Inputs
Actual
Outputs
Process
(Resources
Used)
(Output
Achieved)
The
figure 1 illustrates that
economy is related to plan inputs
and actual input use
which is
processed
and it is what the actual outputs are. So
there should be economy in use of
resources, these
resources
should be efficiently processed and
should also be able to achieve/realize outputs,
which will
show
effectiveness in use of
resources.
In
practice, the boundaries between
economy, efficiency and effectiveness
are seldom clear-cut.
Examinations
of Value For Money (VFM),
therefore, normally pursue these
various aspects of
performance
simultaneously
as part of the same
exercise.
Objectives
of Performance Audit
The
primary objective of performance audit is to
provide parliament with independent
information,
assurance
and opinion about economy,
efficiency and effectiveness in major fields of
revenue, expenditure
and
the management of resources.
A
secondary objective of performance audit
is to identify ways of improving
value for money
and
to
encourage and assist audit
bodies to take the necessary action to
improve systems and controls.
Areas of
Performance
Audit are that Performance
reviews can be used to cover
all types of management
activities,
which
must be audited for better use of
resources.
Concepts
Audit:
it
is the examination of financial records of an organization
after
transactions
have taken place at the end
of financial year. It
reviews
whether the rules of accounts were
applied or not.
Performance
audit:
it
is the examination and analysis of all
the activities of the
organization
and it is seen that the
money used has been
able to
achieve
objectives/goals economically, efficiently and
effectively.
113
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management