 |
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
30
ADMINISTRATIVE
CONTROL
At the
end of the lecture student
will be able to:
-
Understand
the concept of Administrative
Accountability and
Control
-
Understand
the types of internal accountability and
external accountability
Administrative
Accountability
According
to Leonard D. White accountability is `the
sum total of constitutional,
statutory,
administrative
and judicial rules and
precedents and the established
practices by means of which
public
officials
may be held accountable for
their official actions'. It
refers to the formal and
specific location of
responsibility
vested in a person. While responsibility
has a personal and moral connotations
and is not
necessarily
related to formal status and
power. Accountability is also
defined as the answerability of a
person
in
organization.
The
Meaning of Control
Accountability
is a kind of management Control.
Control is the process of ensuring
that actual
activities
conform to established standards
and laid done procedures.
Control helps managers to
monitor
the
effectiveness of managers
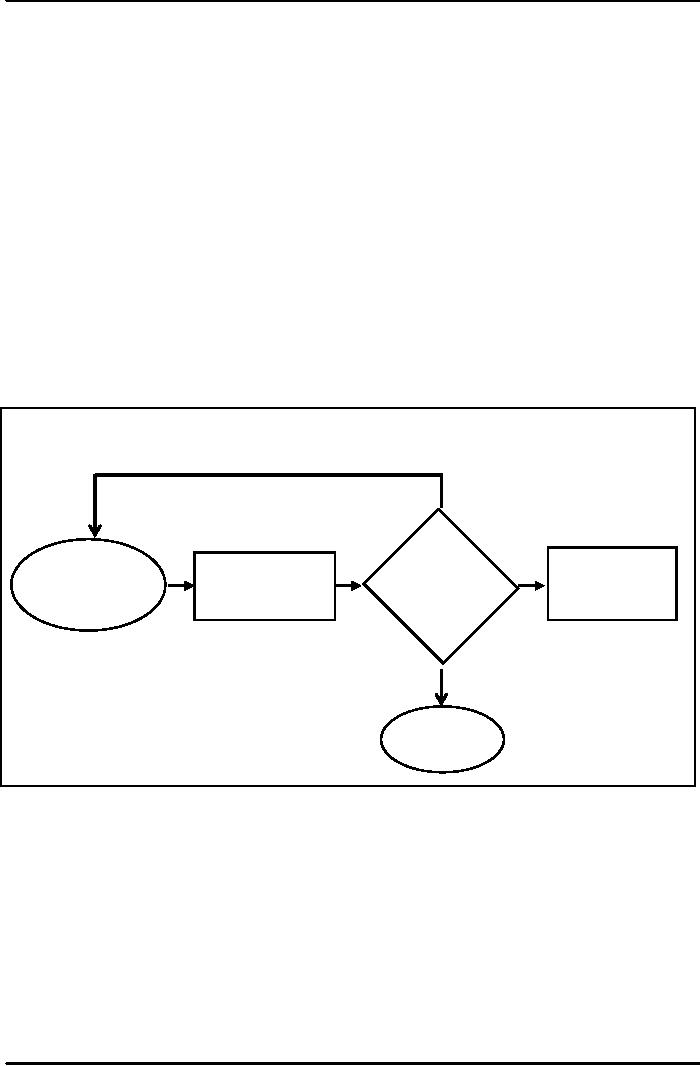
Figure
1
Basic
steps in Control
Process
No
Does
Establish
Take
corrective
Measure
Performance
Standards
&
action
Performance
Match
Standards
Methods
Yes
Do
nothing
Figure
1 shows the basic control
process. This process is
essential to accountability. As shown
in
figure
before control process is initiated
standard and methods are
established against which
performance is
measured.
Then it is measured or assessed if the
performance matches the laid
down standard. If it
matches
then
it is satisfactory performance. But if it
does not match corrective
actions are taken. Now, this
is a
general
process of control and accountability.
These general steps can be
adapted to any work
situation.
Types
of Accountability
There
are two types of accountability
mechanism that make
organizations to continue to
achieve
goals.
These are discussed
below:
1.
Internal
Control: is exercised either by superior
over the subordinates within the
chain of
hierarchy
or by other parallel agencies in the
executive branch of government. It
consists
of
directing, regulating, supervising, advising,
inspecting and evaluating. It should
be
108

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
continuously
done; without being felt.
This mechanism of accountability has
positive
results
also.
2.
External
control, is fitted outside the
administrative machinery and works
within the
general
constitutional framework of the system. It is
exercised by the external bodies
such
as
legislature and
judiciary.
(A)
Internal
Control:
In
internal control mechanisms
follows methods are
used:
i)
Administrative
process:- In a
parliamentary system, cabinet
stands at the apex of the
executive.
Prime minister directs the ministers;
who are in-charge of their
respective
department
and are responsible for the
efficient working to the cabinet
and prime minister.
The
whole working of the departments
are reviewed by the Prime
Minister and his
Cabinet.
ii)
Hierarchical
order:- Every
administrative department is arranged on scalar
pattern and
executives
are organized in hierarchical
order. The executives are
linked with superior-
subordinate-relationship
with clear authority and
responsibility. They are accountable
to
their
respective superiors for
their actions and dealings.
Thus hierarchy itself a
powerful
instrument
for monitoring subordinates
behavior and for enforcing
accountability.
iii)
Annual
confidential Reports:-The
superior officers prepare annual
confidential reports
(ACRs)
of their subordinates every
year. The work of whole
year of each public servant
is
assessed.
iv)
Budgetary
control:- A budget is
not only a complete policy
statement of the total
activities
of the government but it also reflects
the aspiration of the people. The
Ministry
of
Finance prepares budget, and
operations of the budgetary sanctions and
appropriations.
v)
Administrative
leadership:- It is another
means of internal control.
Leadership
motivates,
and inspires the employees
for efficiency. Thus the morale
and motivation of
employees
depends upon the leadership.
The effective leader set
examples of high
standards
of integrity and performance
for his followers. He inspires them
for work and
instills
in them a pride in work. A good
leader is objective oriented and
always tries his
subordinates
to achieve that objective.
(B)
External
Control:-
Following
mechanism is in place as external
methods
1.
Legislative
Control: The
major instrument of public accountability is the
authority of the
legislature
to empower, limit, investigate and
censure the executive branch.
The legislature
enacts
Laws, authorizes administrators to
engage in quasi-legislative and
quasi-judicial
activities,
appropriates funds for all administrative
programmes, and determines the
general
outlines
of administrative organization and
procedure.
2.
Questions:-
The
first hour of every day
sitting of legislature is known as the
question-
hour.
This time is allotted for asking
and answering questions.
Every legislators, after
giving
due notice, are entitled to
put questions and
supplementary questions to the
ministers
about the state of public administration.
The ministers are bound to
answer these
questions.
The purpose of questions is to
elicit information on the working
of
administrative
departments.
3.
Resolutions
and Motions:- Resolutions
and motions are of two kinds
i.e. firstly, those
whose
object is to censure a particular minister or government as a
whole, secondly those,
which
recommend some course of action to be
adopted. The former leads to
dismissal of
the
government or ministry. The later is
recommendatory, hence it may or
may not be
accepted
by the government. Members of parliament are
entitled to pass resolutions on
matter
of general public
interest.
4.
Debates
and Discussions:- Debates
or discussions in the House constitute another
important
means for controlling the
executive. Houses perpetually go on debating
one
thing
or other. Discussions, take
place over every point of a
bill or budget. Every
motion
comes
under discussion in the house. The
inaugural address of the President, the
budget
speech,
introduction of bill for
amendment, introduction of new law, or
introduction of
motion
or resolution provide opportunity
for debates and
discussions.
109

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
5.
Committees
of Legislature:- Legislatures
are unwieldy bodies and
can not meet for
the
whole
of year. Hence, they appoint
committees of their own
members, who are
specialists
in
their sphere of activity and
keep constant watch over
administration. Public Accounts
Committee,
Committee on Subordinate legislation, petitions
Committee, Committee on
Public
Service. These committees
gather a lot of material,
hear expert evidences and
frame
conclusions.
Such conclusions, which are
formed in the form of recommendations,
which
correct
the tone of administration, by improving efficiency
and quality of work civil
service
responds
immediately to the recommendations of such
committees, because they
know
that
their opinions are of
experts and backed by the
full house.
Methods
of Executive Control
The
executive exercises control
over administration through the following
methods:-
i.
Policy-Making:-
The
chief executive along with his
cabinet, control the
administration
through
policy-making. All important
policy-decisions are taken by the
cabinet in every
country.
The departments carry on
their day to day business,
within the policies laid
down
by
cabinet.
ii.
Budgetary
System: It is the
main responsibility of the chief executive to
prepare budget
and
to present it to the legislature. After
the approval by legislature, the chief
executive
implements
it through the allocation of funds among
various departments, and controls
it
by
proper utilization of funds.
iii.
Recruitment
system:- The
third system of executive
control works through
recruitments
of
public personnel. This is usually
placed in the hands of an independent
recruiting agency
like
Public Service Commission.
Judicial
Control
Judiciary
is one of the important external agency,
which exercises control over
administration. By
judicial
control means the power of courts to
keep the decisions and acts,
of administrative officials within
the
bounds of law. L.D. White explains the
importance of judicial control and
says, "The system of
formal
external
control officials and their
acts which fall primarily
into two divisions that
exercised by the
legislative
bodies and that imposed by
the courts.
The
main purpose of judicial
control is to determine the
constitutionality and legality of
administrative
acts of public administrators,
and thus to protect the rights
and liberty of citizens from
the
wrongful
acts of government officials.
Types
of Remedies
There
are two systems of legal
remedies against the unlawful
acts of government officials. One is
called
the Rule of law and the
other Administrative law or
Driot Administrative; the former
system prevails
in
USA, England and Common
Wealth countries including
Pakistan, while the latter prevails
chiefly in
France,
and Germany and Sweden.
Brief description of each is given
below:-
(a)
Rule
of law System:- Theoretically it
means that every body
high or low, and official or
private is
subject
to the same law. The public administrator
is not above the law, while
performing official
duties.
Ordinarily the aggrieved party to shall
have all those legal
remedies against the
offending
officials;
which are known as prerogative
writs,
Concepts
Control:
a
process of ensuring the actual activities
conform to established
standards.
Legislative
control:
the
control exercised by legislature,
through system of question
hours,
resolution
and motions, debates and
discussion.
Hierarchical
order:
type
of internal control in which
individuals are supervised
by
superiors.
110
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management