 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
03
CLASSICAL
SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS I
At the
end of the lecture the students
will be able to
understand:-
The
work of Classical
school
Scientific
management concepts like
efficiency
The
concept of Weber's
bureaucracy
Henri
Fayol's General Principles of
Management
The
concepts in Human Relation
Approach
As
mentioned early the main contributors to the
classical thought
are:-
Woodrow
Wilson
�
Leonard
D. White
�
W.
F. Willoughby
�
Fredrick
Winslow Taylor
�
Henry
L. Gantt
�
Frank
and Lillian Gilbreth
�
Max
Weber
�
Henri
Fayol
�
The
work of Max Weber, Henry L.
Gantt, Frank and Lillian
Gilbreth and Henry Fayol
will be
discussed.
In
the last lecture we made
effort to understand Taylor's scientific
management and the
underlying
assumptions.
We also tried to see the Results of
his experiment.
Henry
L GANTT
Gantt
also belongs to the classical
school, because he was also
trying to focus on efficiency
and
maximization
of output. He emphasized the need
for developing mutuality of
interests between
management
and labour, which mean a
"harmonious cooperation," between
both. He asserted:
That
in all problems of management the
human element is the most
important."
The
importance of time, as well as cost, in
planning and controlling
work
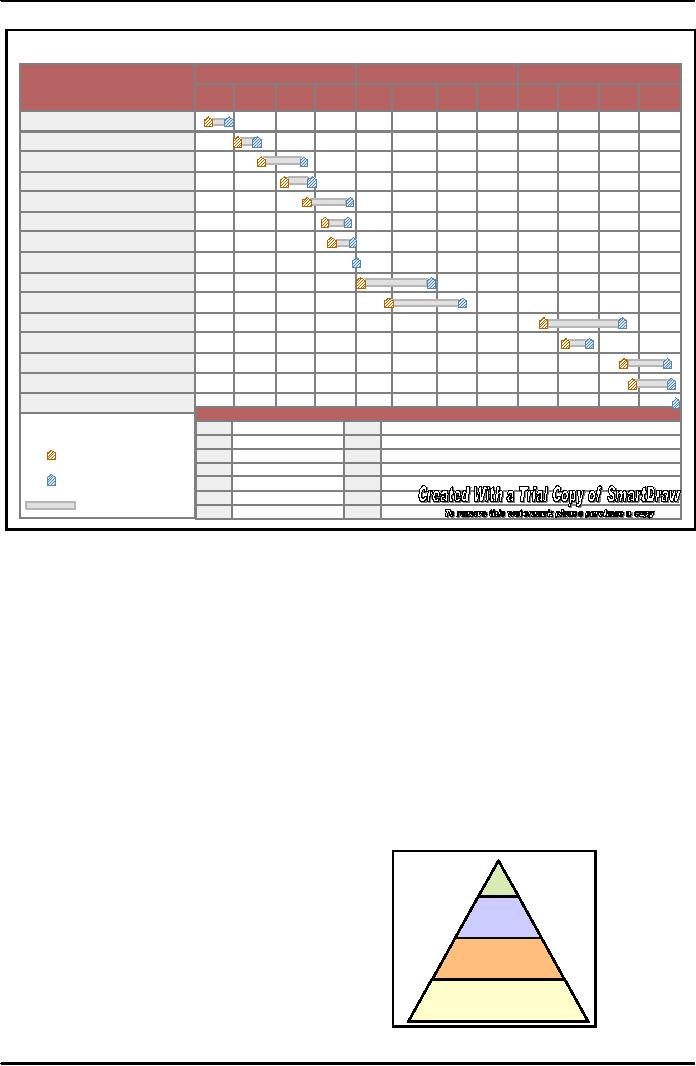
This
led eventually to the famous Gantt chart,
(Figure below) which is basis of such
modern
techniques
as the Program Evaluation and
Review Technique (PERT).
This
chart enables managers to
break work in task and
then determine to how much
time and
resources
will be required to complete each
task.
9
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Gantt
chart
GANTT
CHART - 3 MONTH TIME LINE
January
Fe
bruary
March
Tas
ks
Week
Week
1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4
Week 1
Week
2 We ek 3 Week 4
Week
2 Wee k 3 Week 4
1
Form
BPM team
Identify
problem
Map
process
Identify
causes
Analyze
causes
Develop
improvement plan
Set
budget
Get
approval
Collect
data
Analyze
data
Develop
improved process
Get
approval
Implement
process
Document
improved process
Train
staff
Key
Dates
KE
Y
1/7
Form team
2/14
All
data collected
1/9
Identify problem
2/21
All
data analyzed
Milestone
marker - start
1/14
Map process
3/7
Mapped
improved process
1/20
Identify causes
3/12
New
process map approved
Milestone
marker - end
1/27
Develop improvement
plant
3/21
New
process implemented
1/29
Set budget
3/28
Staff
trained
Gantt
bar
1/30
Budget and plan
approved
Frank
and Lillian Gilbreth
Frank
and Lillian Gilbreth strongly supported
the ideas of Taylor. (Frank and
Lillian were husband
and
wife). Gilbreth became interested in
wasted motions in work. He observed the
work of bricklayers
and
said
that it can be reduced from
18 to 5 movements. He met Taylor in
1907 and combined his ideas
with
Taylor
to improve productivity of workers.
Frank and Lillian Gilberth
emphasized the following:-
�
Application
of scientific-management principles (time and
motion study)
�
The
need to understand workers
personalities and
needs
Theory
of Bureaucracy
Max
Weber (1864-1920)
Max
Weber was a lawyer who
got interested in the social
aspects of organizations. During
his time
markets
were booming and his
life long work on the study
of organizations led to believe that
specific kind
of
organizations called "bureau"
(desk), will help in the
growth of markets. He gave
following main
characteristics
of the bureaucracy.
General
Characteristics
�
Hierarchy
of authority
�
Impersonality
�
Written
rules and documents
Middle
�
Promotion
based on achievement
�
Specialized
division of labor
Bottom
�
Efficiency
Figure
10

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Hierarchy
of Authority
�
Hierarchy
is the various levels in the
Organization.
Authority
Authority
is the ability to exercise influence over
a group of people. As shown in the
figure a
hierarchical
organization looks like
Pyramid.
Weber
distinguished three main
types of authority:
1.
Traditional Authority: The
authority that one inherits,
e.g. the son of king will be
the future king. In
traditional
societies the authority is
transmitted.
2.
Charismatic: It is the authority that
one possesses because of
one's personal traits and abilities.
E.g.
TV
artist, sports stars.
3.
Rational-legal Authority: It is the
authority that is acquired as a
result of a position. E.g.
Policeman
has
authority because of the
position.
One
may posses a mix of these
above authorities.
Impersonality
The
official is provided all equipment to
carry out his duties; he
does not own the "means
of
administration."
Activities are completed impersonally,
which means that the `self'
of individual is not
involved
in the work.
Written
Rules and Documents
Bureaucracy
demands that the written
rules of the organization be strictly followed
and that the
officials
remain loyal. All the work in
organization is written. Compliance is to the
written instructions.
Promotion
Based on Achievement
Bureaucracy
requires the tasks assigned to an
official performed and
completed in an efficient
and
effective
manner, and promotion is
based on the level of skill and
ability of the official.
Specialization/
Division of Labour
Each
person should perform a given and
assigned task
Example:
1.
A person assigned the task of
typing should only perform
that task. He should not be
asked to do
other
task. If he/she continues to
perform the task he/she will
develop competence in that
area.
2.
Pin making: Another example
is of pin making given by Adam Smith. If
the pin is made by
one
person
he will take longer. But if
the wire is straightened by one person,
the other person cuts
the
wire
and the third person rounds the
head of the pin, then the
output can be increased due
to
specialization.
Henri
Fayol
Henri
Fayol is called the father of modern
management theory. He was a
French Industrialist.
His
book
on `General Administration' appeared in
1916. It was written in
French. Fayol found that activities
of
industrial
undertaking could be grouped in 6
parts
1.
Production
2.
Commercial
3.
Financial
4.
Security (protection of
property)
5.
Accounting
6.
Managerial
General
Principles of Management
He
gave following 14 general principles of
management:
1.
Division of work
2.
Authority & Responsibility
3.
Discipline: respect for
agreement
4.
Unity of command: receive
order from one superior
only
11

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
The
figure below shows senior
manager supervising the work of 3
Assistants. All 3 receive
order
from
one superior.
Senior
Manager
Assistant
Assistant
Assistant
Unity
of direction: each group of activities
with same objectives must
have one head and
one plan.
5.
Subordination
of individual interests to the general
interest: The mangers should
work in the
interests
of organization.
6.
Remuneration:
methods of payment should be fair
and give maximum satisfaction to
employee and
employer
7.
Centralization:
The extent to which the authority is
concentrated in one person or
dispersed in the
organization
8.
Scalar
chain (line of authority) or
chain of command
9.
Order:
a place for everything and
every thing in its
place
10.
Equity:
justice and fairness on the
part of managers
11.
Stability
of tenure of personnel
12.
Initiative:
keenness to work
13.
Esprit
de corps: union is strength
(teamwork)
Main
Feature of Classical
School
The
main focus of the classical
school was as
follows:-
1.
The task of administration is not
political but technical,
i.e. only carry out the
will of the political
authority.
2.
Its emphasizes is on material
and methods instead of human
element in the organization
3.
It treated people as `cogs in the
machines' people in the organization were
like other machines
and
tools.
4.
Focus was to increase
productivity.
It
improves organizational efficiency and ensures
high productivity due to
economic incentives to
workers.
Human
Relation Approach
This
approach started as a reaction to the
classical approach.
It
was initiated in 1930's with
the "Human Relation Movement".
Research
and Theory development in the 1950s
and 1960s provided further
conceptual grounding
to
this school of thought.
Research
and Theory development in the 1950s
and 1960s provided further
conceptual grounding
to
this school of thought.
12

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Concepts
Productivity:
increasing
output per worker
Division
of work/specialization: assign
work clearly to one person
so that he improves the skills
Authority:
ability
to influence others
Impersonality:
"self"
on individual is not involved in the
work.
Hierarchy:
various
levels or tiers in the
organization
Time
& motion study:
to
study the movements of workers
and eliminate unnecessary
and
inefficient movements
13
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management