 |
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
27
BUDGET
At the
end of the lecture students
will:
-
Understand
the concept of budget
-
Examine
the Revenue raising of the government
(taxes Vs. Fee)
-
Examine
the purpose, quality of good
taxation, types of taxation, impact of
taxation and
objectives
and impact of public
spending
First
of we will see and try to
explain the budget as a concept. A budget is a
statement of income
and
expenditure. By normal standards the expenditure should
equal expenditure, so that the economic
unit
(house-hold,
government, firm etc.) stays in
its mean. We will look at
the example below to understand
the
concepts
involved in budget.
Example
In
this example we have taken a household
whose income is Rs. 7000
per month and its
family
members
are four. Let us see
their budget for one month.
This is given below
Expenditure
Income
Salary
5000
Food
3000
Rent
on
Education
3000
Property
1000
Health
1000
Overtime
1000
Loan
Repayment
2000
Installment
2000
Other
2000
Total
7000
Total
13000
What
we see here is that the expenditure
exceeds income. When
expenditures exceed income in
a
given
period of time, the budget is in deficit.
What we observe in the example is
that household has
borrowed
money and loan is repaid
every month. This loan was
taken for creating asset,
like a house, or a
piece
of land, or motorbike etc. Another
form of loan for which
Rs.2000 installment is paid was also
taken
to
create another asset.
Expenditures
are usually incurred to create
assets or maintain assets like
for education, health
etc.
On
the other hand an income is either the
wages for labour or rent on
property or return on assets.
From
budget
we can analyze where to
reduce expenditure or increase
income.
Why
Organizations Need Budget
A
household is a small economy, which
uses inputs and gives output
in the form of services that
it
provides.
Likewise organizations use inputs and
process inputs to give outputs. Organizations need
to
control
the use of resources to ensure
that these are utilized
for the purpose of achieving the
goals of
organization.
Budgets also indicate what the
organizations plan to do in
future.
Budget
For
any organization financial resources
are an important input to the
running of organization.
Organization
generates resources to make
expenditures to produce goods &
services. Private
organization
price their product or
services on the basis of value of the
product or service and cost
in
producing
product and in this way
generate income. But
organizations also create
assets to produce
output
which
are source of income.
Definition
of Budget
Budget
is an instrument of financial control and
management. It is summary of
intended
expenditures
along with proposals for how
to meet this expenditure.
97

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
It
is also detailed plan of
income and expenses expected
over a period of time. It provides
guidelines
for managing future investment
and expenses.
Components
of Public Income
Just
as households have income,
governments also have source
of income. The source of
income
for
the government is taxes. Taxes are of
various types. Besides taxes
government have non tax
receipts.
Following
are the component of government
income:
Tax
Receipt: can be divided into
direct and indirect taxes.
Direct tax is levied on income.
Indirect
tax
is not directly on income but is paid
through a product or service being
consumed by user. You
might
have
purchased a bottle of Coca
Cola or some other drink on
which the rice is written
plus sales tax.
The
sales
tax is indirect tax.
Non
Tax Receipt: Non tax
receipts comprise Income
from Property & Investment
and Receipt
from
civil administration.
Use
of Taxes
During
the Moghul period and later
British period government pursued the
policy of laissez-faire
(leave
alone) which
meant that government chooses
not to interfere with the
economy or society. The
taxes
that
were collected were for the
purpose of defence or law
and order and the welfare
concept was non
existent
Principle
purpose of taxation
The
governments of today have many
sources of income but taxes
remain an important source
of
income.
Today government's expenditures
have also increased
manifold. The main expenditure
purpose is:
1.
Redistribution of income (from
rich to poor) or help
finance welfare activities
and
2.
To achieve economic objectives
such as control of inflation,
economic growth, employment
and
reduction
of balance of payment
deficit.
Principles
of good Taxation
Since
the foundation of modern economy was
laid, there has been many
changing ideas and
philosophy
on the role of government. Along side the
idea and principle of good
taxation has also
evolved.
Adam
Smith the economist who
wrote Wealth
of Nation in
1776 said that a good tax
has following four
principles:
1.
A
good tax should be equal: an individual
should be called upon to pay tax
according to his/
her
ability to pay tax. This is
called progressive taxation, where the
rich pay the higher
percentage
of taxation then
poor;
2.
A
good tax should be certain: people are
certain about how the tax
works and how
much
has
to be paid as well as when to
pay;
3.
A
good tax should be convenient: People should be
able to pay without any
inconvenience.
The
Pay as You Earn (PAYE)
system of income tax complies
with this principles and
4.
A
good tax should be economical: the cost
of collecting and administering should not
exceed
revenues
There
are several other principles of modern
taxation. These are:
a.
Tax
should be impartial, two citizen who earn
equal income and have
same size of family
should
be taxed the same;
b.
It
should not be disincentive to hard work
and therefore should not penalize
for hard work
i.e.
that those who work hard
and earn income should not
be heavily taxed.
c.
The
tax should be consistent with government
policy. If for example the government
is
trying
to reduce inflation, it should not
pursue the policy of taxation
which increases
demand
too
much in the economy
98

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Types
of Taxation
Taxes
tend to fall in two
categories: direct and indirect
taxation. Direct taxation is a tax
levied
directly
on individual's income. Whereas
indirect taxation is levied on consumers'
expenditure or outlay.
Following
are the types of taxation:
1.
Direct
Taxes
Income
Tax
Wealth
Tax
Workers
Welfare Tax
Capital
tax
2.
Indirect
Taxes
Custom
Duty
Sales
tax
Excise
Duty
3.
Non-
tax Revenue
Income
from Property and Enterprise
Profit
from Railways
Profit
from PTCL
Profit
from Post office
Miscellaneous:
Foreign travel, passport fee,
airport tax, sale proceed on
oil and tax etc.
The
government of Pakistan levies all the
above type of taxes.
Advantages
of Direct Taxes
Direct
taxes tend to be progressive.
People in the higher income groups
pay greater taxes than
poor
people,
i.e. income tax is graduated so
that high income earner
pays a larger tax. Also
projected wealth tax
would
apply to those owing more
than a certain level of wealth
It
is cheap and easy to
collect. Consider for
example PAYE system which is
used to collect
income
tax
from wages and salary
earner
Impact
of Taxation
Taxes
have variety of impact of
following:
On
income: Higher
taxes reduce disposable
income (what people have to spend after
taxation). Direct
taxes
by directly reduce the
income.
On
savings and investment:
Higher
direct taxes reduce individuals'
and firms' ability to save
and invest.
To
a certain extent it depends on how
much of the increase in taxes is financed
from savings and
how
much
from consumption.
On
prices: Higher
direct taxes have deflationary effect on
prices by reducing demand.
However trade
unions
may ask for higher wages to
compensate for higher taxes
and effect of this will be
inflationary.
99
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
On
economy: Higher
taxation will, other things being
equal, reduce demand in the
economy which will
have
deflationary effect on the
economy.
P
D
S
S
a
a
S
S
a
a
Output
The
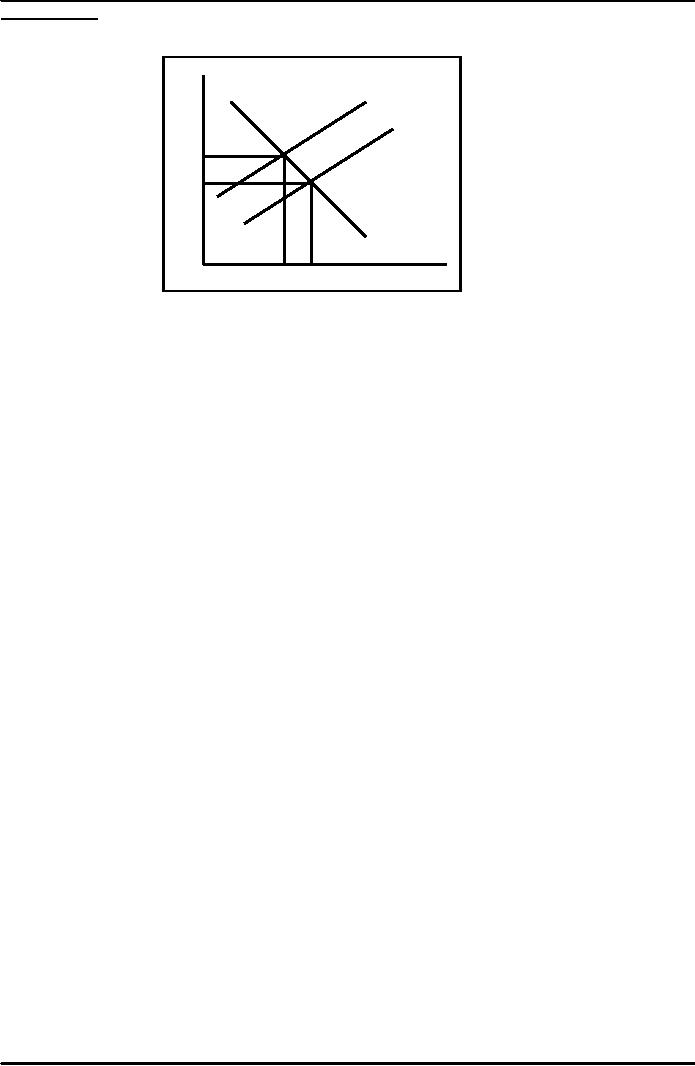
affect of taxes is shown in figure 1
below. On the vertical axis is shown
price and on
horizontal
axis
is shown output. With price
`a' the demand for output is
`b'. When demand decreases
the output will
also
decrease. So the tax increases price
and reduce demand which
reduces out put and
which reduces
investment.
Concepts
Budget:
a
document showing income and expenditure
in case of
household;
and an instrument of financial control
and future
plans
in case of organization.
Taxes:
levies
charged by government as its source of
income.
Non
tax
Revenue:
fee,
penalties, user charge etc.,
which constitute the income of
government
100
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management