 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
02
EVOLUTION
OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION
At the
end of the lecture students should be
able to understand:
Relationship
between public administration, democracy
and rights (Constitution of
Islamic
Republic
of Pakistan 1973)
Evolution
of Public administration/ management
and
The
work of the contributors of the Classical
School
In
the last lecture we talked about
democracy and democratic
values. Why did we mention
these
two
concepts in the context of public
administration/management? The mention
was made because we
would
like to know about the rights of
citizens and the response of government
toward democratic
values.
These
values and how people should
respond to the work of public
organizations is important. But
we
know
people differ over the degree to
which they influence day-to-day operation of
public agencies
because
they
do not know their rights and
the procedures of government agencies.
The 1973 Constitution
contains
Fundamental
Rights and Principles of
Policies which give basic rights to
citizens. Some of the
articles
pertaining
to human dignity and respect
given in constitution are as
follows:-
(1)
Security
of persons: No
person shall be deprived of life or
liberty saves in accordance
with law.
(2)
Safeguards
as to arrest and detention: No
person who is arrested shall
be detained in custody
without
being informed, as soon as many
are not, of the grounds for
such arrest, nor shall he
be
denied
the right to consult and be
defended by a legal practitioner of
his choice.
(3)
Slavery,
forced labor, etc.,
prohibited:
slavery is non-existent and forbidden
and no law shall
permit
or facilitate its introduction into
Pakistan in any form.
(4)
Inviolability
of dignity of man, etc.: The
dignity of man and, subject
to law, the privacy of home,
shall
be inviolable.
(5)
Freedom
of movement, etc.: Every
citizen shall have the right to
remain in, and subject to
any
reasonable
restriction imposed by law in the public
interest, enter and move
freely throughout
Pakistan
and to reside and settle in
any part thereof.
(6)
Freedom
of assembly:
Every citizen shall have the
right to assemble peacefully
and without arms,
subject
to any reasonable restrictions
imposed by law in the interest of
public order.
(7)
Freedom
of association:
Every citizen shall have the
right to form associations or unions,
subject
to
any reasonable restrictions
imposed by law in the interest of
(sovereignty or integrity of
Pakistan,
public
order or morality.)
(8)
Freedom
of trade, business or
profession:
Subject to such qualifications, if any,
as may be
prescribed
by law, every citizen shall have the
right to enter upon any
lawful profession or
occupation,
and to conduct any lawful
trade or business:
(9)
Freedom
of speech, etc Every
citizen shall have the right to freedom
of speech and
expression,
and
there shall be freedom to the Press,
subject to any reasonable
restrictions imposed by law in
the
interest
of the glory of Islam or the integrity,
security or defense or Pakistan or
any part thereof,
friendly
relations with foreign States,
public order, decency or
morality, or in relation to
contempt
of
Court, (commission of) or incitement to
an offence.
(10)
Freedom
to profess religion and to manage religious
institution: Subject
to law, public order
and
morality:-
(a)
every
citizen shall have the right to
profess, practice and
propagate his religion;
and
(b)
Every
religious denomination and every
sect thereof shall have the
right to establish,
maintain
and manage its religious
institutions.
(11)
Safeguard
against taxation for purposes of any
particular religion: No.
person shall be
compelled
to pay any special tax the
proceeds of which are to be
spent on the propagation or
maintenance
of any religion other than
his own.
(12)
Safeguard
as to educational institution in respect of religion,
etc.: No
person attending any
educational
institution shall be required to receive
religious instruction, or take part in
any religious
ceremony,
or attend religious worship, if such instruction,
ceremony of worship relates to a
religion
other
than his own.
5
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
(13)
Equality
of citizens: (1)
All citizens are equal
before law and are entitled
to equal protection of
law.
(2) There shall be no discrimination
based on sex alone. (3)
Nothing in this Article
shall
prevent
the State from making any
special provision for the
protection of women and
children.
(14)
Non-discrimination
in respect of access to public
places: (1) In
respect of access to places
of
public
entertainment or resort, not intended for
religious purposes only, there
shall be no
discrimination
against any citizen on the ground
only of race, religion,
caste, sex, residence or
place
of
birth.
The
way democracy functions in the
political tradition of a country
have important influence on the
working
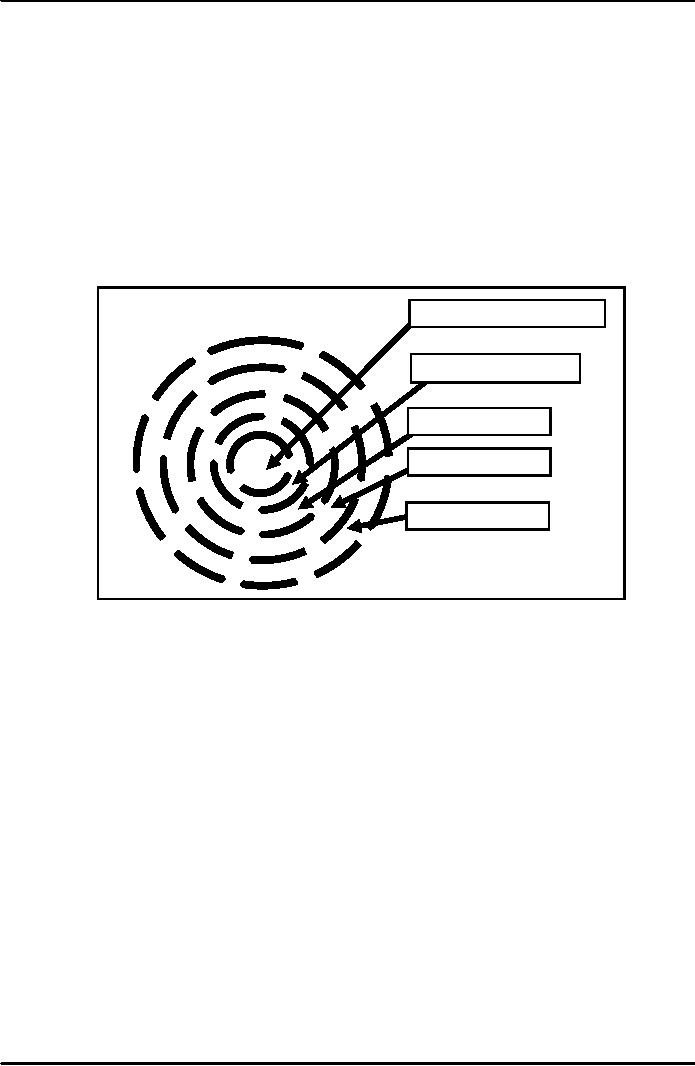
of public organization. This is illustrated in Figure
which shows the international,
social, economic,
political
system influence on public administration.
The figure shows public
administration in the centre and
all
other systems influencing
it. Thus public administration
exists and functions under
these influences and
is
driven by these
systems.
Factors
Affecting Public
Agencies
Public
administration
Political
System
Social
Economic
International
Evolution
of Public Administration
One
of the definitions of Public Administration is
that public administration is about
management
of
public programmes. As we have learnt
that during the period of
Indus Valley civilization
cities were well
constructed
and planned and that the
practice of public administration is old.
But as a subject it is new. We
would
now see the development of this practice
as a subject.
The
evolution of public administration/
management is discussed in following
paragraphs. The
study
of public administration is divided in
following Schools:
1.
The Classical School
2.
Human Relations
School
3.
Behavioural School
4.
System School
5.
Management Science
School
6.
Power and Politics
School
Classical
School
We
will examine the work of
Classical School and see the
theory presented by this school. We
will
review
the work of the main contributors of this
school. The main
contributors of this school
are:
�
Woodrow Wilson
�
Leonard D. White
�
W. F. Willoughby
6

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
�
Fredrick Winslow Taylor
�
Henry L. Gantt
�
Frank and Lillian
Gilbreth
�
Max Weber
�
Henri Fayol
The
growth of public administration has to do
with the growth of markets
and the fall out of
market
imperfection. Example of market
imperfection is pollution, i.e.,
markets produce goods and
the
markets
would not care if in the
production of goods, they pollute
environment. For example
a
manufacturer
who emits smoke will
pollute the environment. Environment if
gets polluted will effect
the
health
of people. Who is responsible for this
situation? Governments intervene to correct
market
imperfection
and may tax the
polluter.
The
institutions of government therefore should be effective to
control market imperfections.
Similarly
if private schools charge
more fees then government should open
schools for those who
cannot
pay
high fee. How to make
government institutions effective?
To
answer this question we need to look at
the works of those who contributed to the
efficient
working
of organizations. Those studying work in
the organization developed theories and
concepts for
increasing
the efficiency and effectiveness of
organization
In
USA the study of government began in
late 19th century. The first
Essay was on `The Study
of
`Administration'
1887 written by Woodrow Wilson (American
Scholar and late President
of USA) His essay
was
of very practical nature. In his
essay he pointed out
following things:-
It
addressed the inefficiency and
corruption in USA government in late
1880's
He
said that political
scientist had given little
attention to how government
operates
He
was impressed by the business, industry
and technology
He
believed that the work of government should be
accomplished with the efficiency of
private
sector.
He
believed that there should be separation
of politics from administration
Another
article that appeared was on
`Introduction to the Study of Public
Administration' (1926) by
Leonard
D. White. In his paper:
He
commented that government should function
in the context of democratic values
(role of states
in
human affairs). According to
him there are 2 concerns in
public administration:
1.
Efficiency: to improve the functioning of
organization.
2.
Democratic values: that the organizations
should keep in view the democratic
values when
providing
services.
W.
F Willoughby in his article
`Principles of Public Administration'
(1927) emphasized the idea
of
`value
free' science of management. By value
free service he meant that
those executing public
programmes
should
be neutral unbiased and provide
services without discrimination.
F.
W Taylor
Fredrick
Winslow Taylor is called the `father of
scientific management'. He worked as
machine
operator
in Midvale Steel Company in
USA. He observed the workers
using shovels for unloading
coal and
iron
ore what he observed was
that when workers shovel
rice coal they can lift
3.75 lbs. And when
they
shoveled
iron ore they could lift 38
lbs.
His
question was which is the right
load?
In
order to find the answer he
thought that he should inquire
and he thought should ask
people.
But
then he thought he should conduct experiment to
find the right answer. He
thought the experiment will
give
the right output.
7

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
The
Shovelling Experiment
In
order to conduct the experiment he selected 2
best shovelers and told them
that they will be paid
double
wages if they did what was
told to them. The two
selected men were the best
in the company. They
had
reputation of working hard and honestly.
The two men shovelled the
whole day, in two different
places
until
they were tired but not
over-tired (a good day's
work). Their supervisor
noted down the
following:
1.
What was the number of shovelful in a
day by each worker?
2.
Weight of load in shovel (38-39 lbs) by
each worker
His
experiment gave him results
that if different kinds of shovels
were used, the shoveller can
lift
load
between 21.5 lbs to 38 lbs.
But this was possible if the
worker was well trained and
worked
consistently.
Results
of the Experiment
o
There is
scientific way of doing things and he
called it `one best
way'
o
Replace
rule of thumb with
science
o
Obtain
harmony in group action rather than
discord
o
Achieving
cooperation of human beings rather than
chaotic individualism
o
Working
for maximum output rather
than restricted output
(productivity)
o
Developing
all workers to the fullest extent for
their own and company's
prosperity
o
Workers
should be carefully selected
We
must remember that the time
period of Taylor was mid
19th century, and the impact
of
industrial
revolution on organizations were
imminent. The organizations
were demanding more
output
from
labour. This demand led to
dissatisfaction in the labour because the
labour thought that if they
gave
more
output more will be
expected.
Concepts
Classical
School of Management:
They
believe the efficiency of organizations
can be
increased
by
following
standards
(scientific
management).
Value
free:
without
bias.
Theory:
set
of assumptions based on observation or
experiment
which
explain phenomenon or situation.
8
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management