 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
14
ORGANIZATION
At the
end of the lecture the students
will be able to
understand:
1.
The concept of organization
roles;
2.
The concept of organizing;
3.
What are the types of
organization?
4.
The concept of organization
Organizational
Roles
Organizational
roles are the part or
position that a person is
assigned in the organization, for
example
the role of manager sales or
your role as a student.
People will cooperate
effectively in
organizations
if they know the part they have to play
in the organizations i.e. if they know
their roles in the
organization
Following
are the requirement of organizational
goals:
1.
Clear objectives; People
must know the objectives
that they have to achieve
clearly, student must
know
their objectives.
2.
Clear idea of duties or
activities: People must know
their duties and activities
that they must
perform.
E.g., student duties are to
study, be disciplined
3.
Clear area of authority: In organization
people must know the extent of authority
that they have.
What
is Organizing
Organizing
means that there should be
clear line of authority and
all should know who reports
to
whom.
Following are the main steps
in organizing:
1)
Classification of activities: First all
activities in organization must be
classified i.e. activities
similar
in
nature should be identified
separately.
2)
Grouping of activities to achieve
objectives: Similar activities should be
grouped.
3)
Assigning a manager to each group of
activities: A manager should be
assigned
4)
Coordination of group of activities both
horizontally and vertically:
Coordination
means the interrelationship among
activities.
Organization
Now
we have talked about concepts of
`roles' and `organizing', we
will connect these two
concepts
with
the concept of organization. Organization means a
formalized intentional structure of roles
and
positions.
Here we refer to organization as a structure in
which people work. E.g.,
school is organization.
Types
of Organization
Organizations
can be categorized into
following types:
1.
Formal Organizations
2.
Informal Organizations
Formal
Organizations
Formal
organizations mean the intentional
structure of roles in a formally
organized enterprise.
The
structures
are created by people to achieve
certain defined goals. The
formal organizations could be
hospitals,
schools, Water and Power
Development authority
(WAPDA).
Informal
Organizations
A
network of personal and
social relations not established or
required by the formal organization
but
arising spontaneously as people associate
with each other is called
informal organization. The
example
of
informal organization is friendship
within the organization amongst people
working at various
levels.
50
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
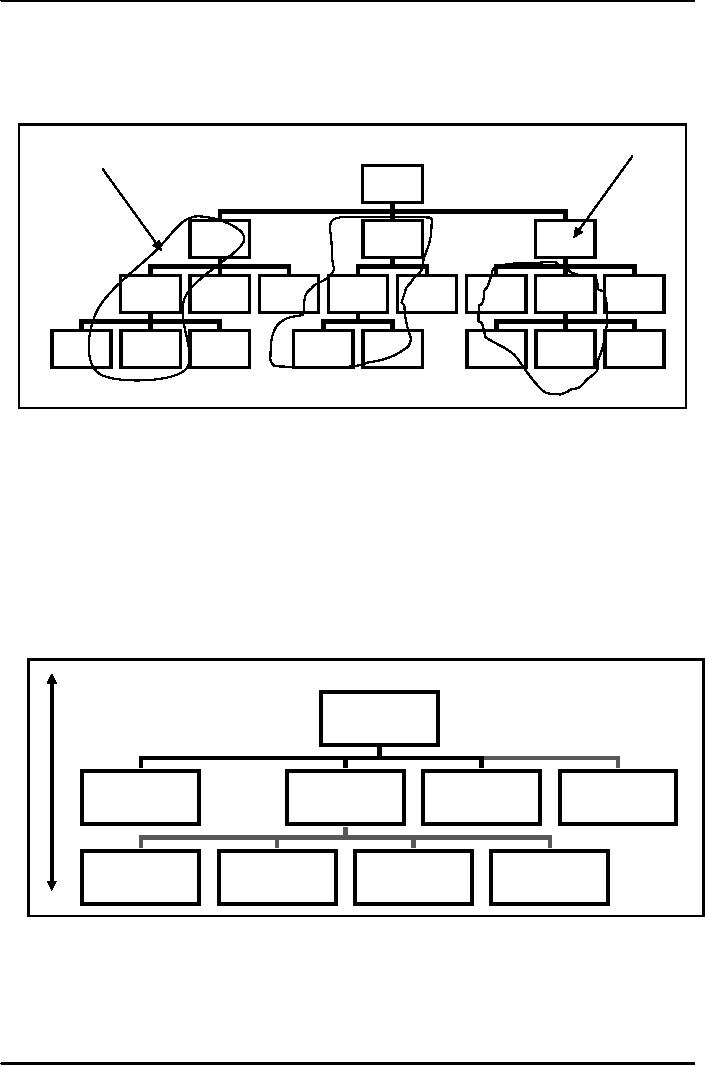
The
figure below illustrates the
concept of formal and
informal organization. While the formal
organization
is
the people working who are
assigned roles and given a
position in a box. There are
four levels in an
organization
and the straight lines show
formal structure. However the irregular
lines show informal
relationship
or informal structure.
Figure-1
Formal
Org.
Informal
Org.
Title
Name
Title
Title
Title
Name
Name
Name
Organizational
Levels and Span of
Management
Organizational
levels exist because there
is a limit to the number of persons a
manager can
supervise
effectively, even though this
limit varies depending on situations.
Organizational span, therefore,
means
the number of people a manager can
supervise. It is generally believed that
a number of people that a
manager
can effectively supervise
are between 7 and 10.
But this is a not a
principle.
While
span refers to number of people a person
can supervise organizational level refers
to "ties"
or
level. In the figure-2 horizontal arrow indicate
span and vertical arrow shows the
organizational level. In
figure-1
the organizational level are shown by
numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Figure-2
Organizational
Span
Principle
of Span of Control
There
is a limit to the number of subordinates a
manager can effectively
supervise, but the
exact
number
will depend on the impact of the
following:
51

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Factors
Determining an Effective
Span
Training
of subordinates: The more trained
and experience the employees, the
less supervision they
require,
and therefore, the manager can
supervise more
employees.
Clear
delegation of authority: Delegation of authority
means to give part of authority
to
subordinate.
Thus, if managers can
delegate authority clear to
each subordinate being supervised;
more
employees can be brought under
supervision.
Clarity
of plans: When the plans are
clearly understood by the employees, the
manager can
supervise
more people.
Use
of objective standards to determine whether
employees are following
plans
Rate
of change
Communication
techniques
Amount
of personal contact Needed
Variation
by organization level
Personal
abilities of managers
Need
for balance
Department
One
way of grouping activities is
establishing `department'. A department is a distinct
area, division,
or
branch of organization over which
manager has authority for
performance of specified
activities.
Departmentalization
Grouping
activities and people into departments
makes it possible to expand
organizations to an
indefinite
degree.
Types
of Departmentalization
By
Number
By
Time
By
Function
By
Geography
By
Production
By
Customer
Concepts:
Organization:
a
formalized institutional structure
that shows
relationship
amongst "organization
role"
Organizational
roles:
the
position that each person is
assigned in the
organization,
for example a peon, manager
sales, deputy
secretary
training etc. Each role
has specific task to
perform.
Formal
organization:
the
structure of the organization as is indicated in
figure
1.
But the formal structure is the
relationship between
straight
lines.
Informal
organization:
it
can be organization of informal relationship
that
people
in organization have beyond the
formal
relationship.
This is shown in figure1 in irregular
line.
Span
of organization:
is
the number of people a manager can
supervise.
Organizational
level:
it
refers to levels in the organization and
relates to
hierarchy.
52
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management