 |
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
12
STRUCTURE
OF GOVERNMENT
At the
end of the lecture the students
will be able to
understand:
1.
The Concept of Rules of
Business
2.
The structure of government which
comprise ministries, divisions, attached
department
3.
What are functions? An example of
one of the ministry/division will be
given explain functions of
a
ministry:
In
the last lecture the structure of
government was explained as per article
91(1) of the constitution.
The
cabinet is headed by the Prime
Minister who is the Executive head of the
government. It has been
stated
that the president is the Head of the
State and the prime minister helps
him in decision making and
it
is
the Prime Minister who is
responsible for running of government.
Thus, the structure of government
can
be
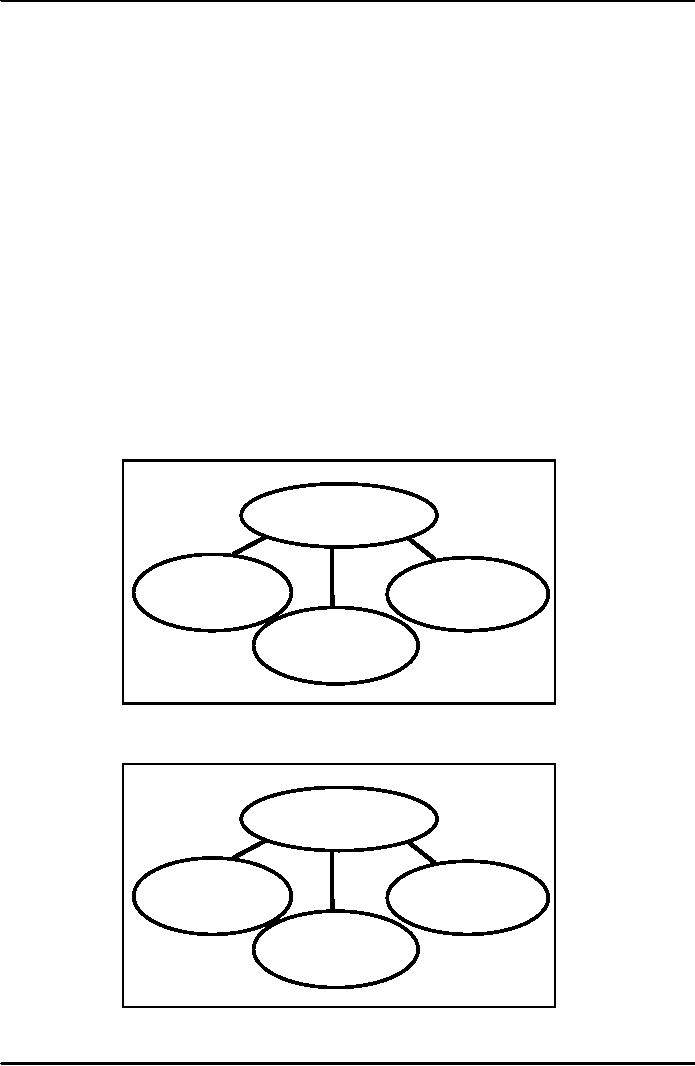
understood from Figure A and Figure B. Figure A
shows the relationship of the Constitution
with the
legislature
which comprise the National
and Provincial assemblies
and the Senate. That is the
Constitution
gives
the structure, formations, functioning
and methods of these
institutions. Then, as shown in
figure B
the
constitution also provides for the
structure, functions and operations of
the three branches of
government
i.e. legislature, judiciary and
executive. It is mentioned here that
while the Constitution provides
broad
framework of government, the operational level functioning
are regulated by the specific Acts
which
have
to be placed before the legislature and
approved.
Structure
of Government
Figure
A
Constitution
National
Provincial
Assembly
Assembly
Senate
Figure
B
Constitution
National/Provincial
The
Executive
Assemblies
Courts
42
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Organization
Chart of Government
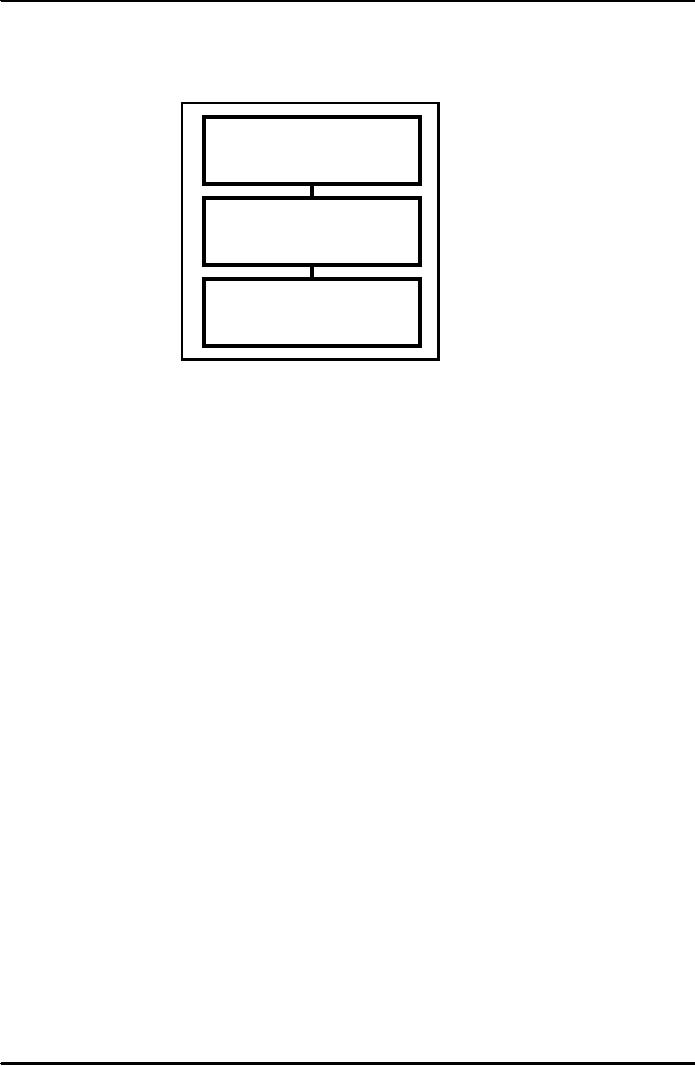
As
mentioned earlier that the president is
the head of the State and
Prime Minister (PM) is the
head
of
Executive is shown in the Figure. The PM
heads the Cabinet and the Cabinet
comprises ministers.
The
number
of Ministers keeps varying. Some time it
is 29; sometime 16 and
sometimes 39. These
ministers
head
the ministries.
President
Head
of the State
Prime
Minister
Chief
Executive
Cabinet
Comprising
Ministers (39)
Rules
of Business
The
question that can arise is,
how ministries work. The
Constitution of the country under
Article
90-99
states the formulation of `Rules of
Business'. This means that
Rules have to be framed for
the
working
of the ministries and divisions. What is
Business? `Business' means
all work done by the
Federal
Government,
and the Federal Government
means all the ministries, divisions
and attached departments
and
autonomous
bodies etc. Thus Rules of
Business explain the responsibilities of the
Secretary who heads
the
division.
It also delineates the ministries
and the division/department under each
ministry. Just as there
are
Rules
of Business for the Federal government,
there are Rules of Business
for the provincial
governments
Ministries
of Federal Government
(39)
Although
it has be stated that in
2004 there are 39
ministries, but only the
list of few selected
ministries
is given below:
1.
Cabinet
Secretariat
2.
Ministry
of Commerce
3.
Ministry
of Culture, Sports & Youth
Affairs
4.
Ministry
of Communication
5.
Ministry
of Defence Production
6.
Ministry
of Finance & Revenue
7.
Ministry
of Information & Technology
8.
Ministry
of Interior
9.
Ministry
of Housing and Works
The
Cabinet Secretariat, is the Secretariat of the
Cabinet, which maintain all its
paper work.
Ministries
cited above are indicative of the
kind of work that government
do.
Structure
of Ministry
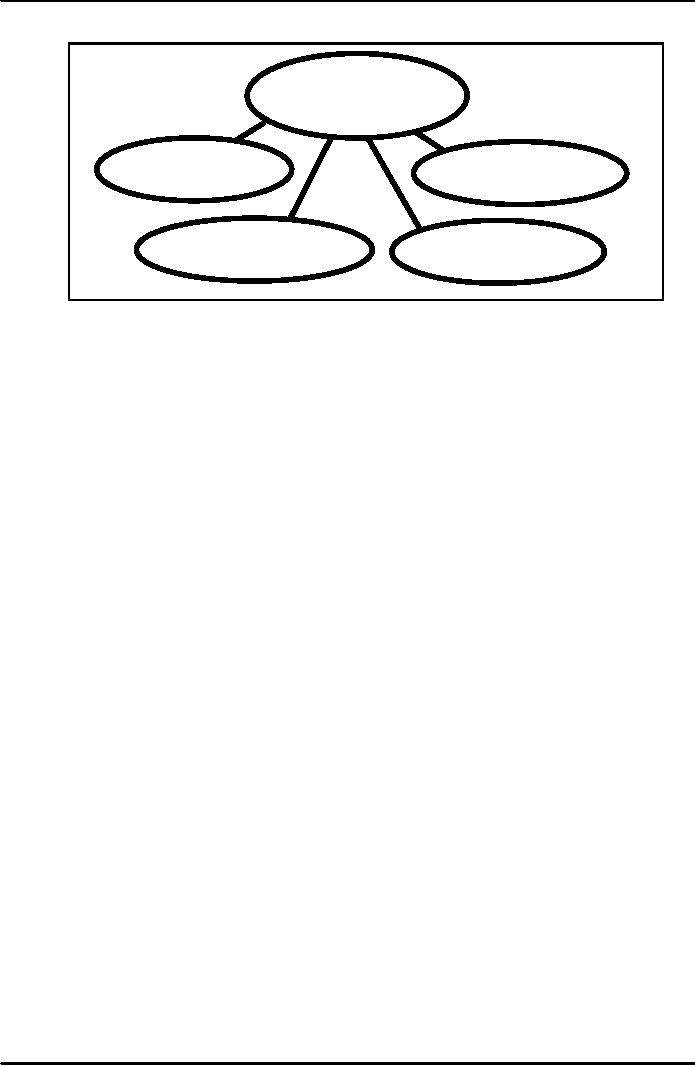
It
would be in the fitness of things to
first define ministry A Ministry is
Division or Group of
Division.
The Division is entrusted
with one task: For
example: Ministry of Finance
has divisions. The
division
are shown in the Figure are
Finance Division, Economic Affairs
Division, statistics Division
and
Revenue
Division.
43
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Figure
Ministry
of Finance
Finance
Division
Revenue
Division
Economic
Division
Statistics
Division
The
Ministry of Finance oversees the
work of all these Divisions.
To further understand the
responsibilities
of these Divisions, for the
purpose of illustration we look at the
functions of Finance
division
and Economic Affairs
Division.
Main
Functions of Finance Division:
The
main functions of the Finance
Division are as
follows:
1.
Finances of Federal government and
financial matters affecting the whole of the
country
2.
The Annual Budget Statement
& supplementary/excess Budget to be placed before
the National
Assembly
3.
Allocation of shares of proceeds
from the taxes collected by the
Federal Government
4.
Public debt of the Federation both
internal and external
5.
Currency, coinage, and legal
tender Pakistan Security Printing
Corporation and Pakistan
Mint
6.
Regulatory functions pertaining to
Banking sector, Stock exchanges,
foreign currency,
etc.
Main
Functions of the Economic Affairs
Division
The
main functions of the Economic Affairs
division are as
follows:
1.
Negotiations with the foreign
governments and organizations
pertaining to economic
assistance,
requirement
2.
Matters relating to technical assistance to
foreign countries
3.
Review and appraisal of
international and regional economic
trends and its impact on
national
economy
Organization
of Finance Division
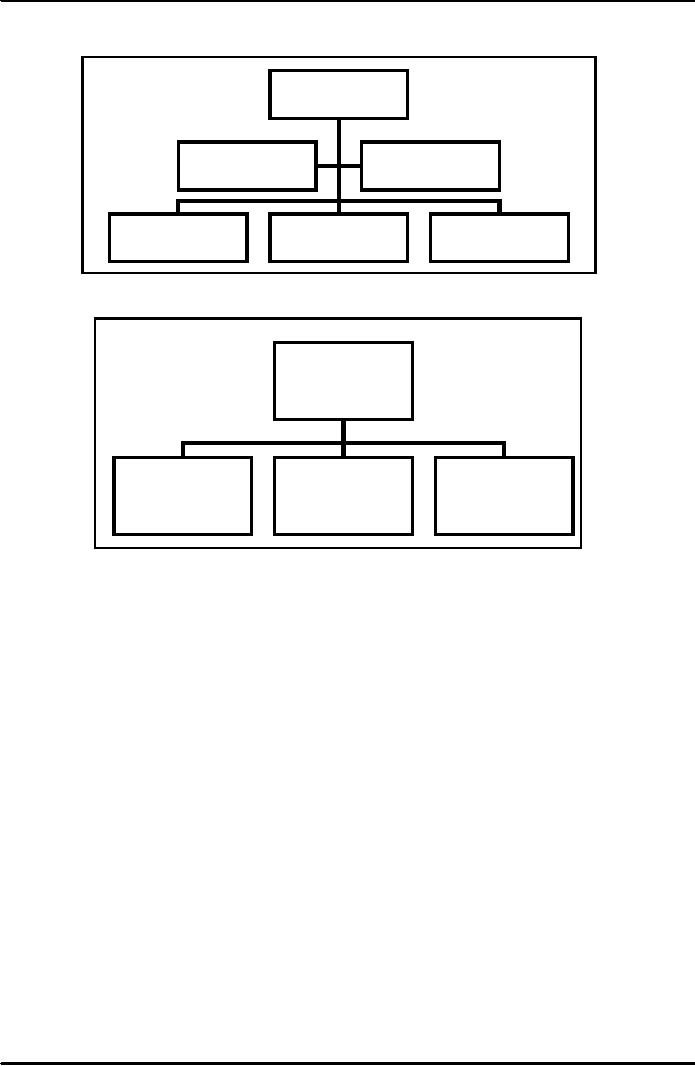
How
is Division structured? Or who
Heads the Division. As we know a
ministry may have
more
then
one Division, so the Minister is the
political head (usually a
politician) he/she provides
policy
guidelines
to the Ministry. The division is
headed by Secretary, who is a
career civil servant (Figure
1).
Figure
2 gives the simplified structure of
Finance. Secretary Finance
head of the Division and
Joint
Secretary
(JS) (expenditure & Administration), JS
(Budget) and JS (Finance)
help the Secretary in day to
day
working.
44
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Figure
1
Minister
for
Finance
Special
Advisor
Assistant
Secretary
Secretary
Secretary
Finance
Revenue
Division
Economic
Affairs
Figure
2
Secretary
Finance
Joint
Secretary
Joint
Secretary
Joint
Secretary
(Exp
& Adm.)
(Budget)
(Finance)
Attached
Departments
Secretary
Finance sits in Islamabad,
but the Ministry of Finance
has its offices all over
Pakistan. For
example
finance division military would be in
Rawalpindi. The Central Directorate of Savings
has its office
all
over the country.
An
attached department is administratively under the
control of Ministry of Finance.
Some of the
attached
departments are as
follows:
-
Finance Division
Military
-
Office of the Controller General of
Pakistan
-
Auditor General of Pakistan
-
Central Directorate of Savings
Autonomous
Bodies under Ministry of
Finance
Following
are the Autonomous Bodies of
Ministry of Finance:
�
Monopoly Control
Authority
�
Nationalized Commercial
Banks
�
Pakistan Security Printing
Corporation
Autonomous
bodies are not administratively
controlled by the ministry. These
bodies have their
own
Board of Governors. In this way they do
not receive directives from
the ministry
45

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Conclusion
By
now structure for government should be
fairly clear. The Federal
executive branch comprises
of
ministers
who head 39 ministries. The
Federal Secretaries of the ministries
assist the ministers in
formulation
of policies, execute the policy,
write proposal for legislation to be submitted to the
cabinet, and
keep
the minister informed. The Minister is
responsible for the working of the
Division and in the question
answer
sessions of the National Assembly he
answers the questions raised on the
working of the Ministry
in
the
Assembly.
Concepts
Cabinet:
A
group of ministers working under the
guidance of
Prime
Minister
Rules
of Business:
Rules
that explain the working of
government
Ministry:
A
group of more than one
Division.
Division:
A
unit assigned with a task
e.g. Finance Division
Functions:
Work
to be performed by the Division
Autonomous
Body:
An
organization that has its
own Board of governors
that
sets
policy for it. Autonomous
Bodies are more
independent
in decision making.
46
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management