 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
11
1973
CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN
At the
end of the lecture the students
will be able to understand
the:
1.
The
constitutional provisions relating to the government
structure
2.
Preamble
of the Constitution (1973) of Islamic Republic of
Pakistan
3.
Territories
of the State of Pakistan
4.
Constitutional
bodies of decisions making
The
Constitutional Framework of Government of
Pakistan
Overview
of 1973 Constitution
We
will start with the Preamble
of the Constitution. A Preamble is the
`Preface' or `introduction'
which
tells us the main focus of the
document. According to the Preamble the
entire control of universe
belongs
to Allah. The constitution
reads as follows:
Preamble
"Whereas
Sovereignty over the entire universe
belongs to Allah alone, and
the authority to be
exercised
by the people of Pakistan within limits
prescribed by Him is a sacred
trust;......."
The
Republic of Pakistan
The
Constitution explains Republic
as:
"Pakistan
shall be a Federal Republic to be known
as the Islamic Republic of Pakistan." Federal
Republic
means that the country has
provinces and these together constitute
the federation. Besides we call
ourselves
Islamic Republic, because we are
ideological state, as the basis of
independence of this country
was
Islam.
The
Territories
According
to the Constitution the territories of the state
are:
a.
The
Province of Balochistan, the North-West
Frontier, the Punjab and Sindh
b.
The
Islamabad Capital territory, Hereinafter
referred to as the Federal
Capital.
c.
The
Federally Administered Tribal
Areas; and
d.
Such
states and territories as are or
may be included in Pakistan, whether by
accession or otherwise.
So
there are 4 Provinces, the
capital territory and the
Federally Administered Tribal
Areas (FATA)
and
section (d) above sees the inclusion of
Kashmir in Pakistan as and when the
decision about it
takes
place.
State
Religion
Article
2 of the Constitution provide for the
Islam as the State Religion: "Islam shall
be the State
Religion
of Pakistan".
Definition
of the State
Article
7 of the Constitution gives definition of
the state which is as
follows:
"State
means the Federal Government,
Parliament, a Provincial Government, a
Provincial Assembly,
and
such
Local or other Authorities in Pakistan as
are by Law empowered to
impose any Tax"
So
the state comprises of all Governments
i.e. Federal, Provincial and
the Assemblies and the local
or
other authorities. It means it comprise
of all these institutions
which are permanent.
37
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
What
does Government
Comprise?
It
is appropriate to differentiable between government
and state. But is must be
stated that the two
are
used interchangeably. We have attempted
to explain this term before. But now we
relate to the
explanation
with the definition given in the
Constitution. The basic difference is
that state institutions
are
fixed
but people who occupy the positions in
the institutions may come
and go, thus government will
come
after
every 5 years through
elections as given in the Constitution
and go after five years. It
means people
have
fixed period in which they
work so Government (in
generic) comprise:
-
Elected Representatives (Politicians:
members of Political
Parties)
-
Judiciary
-
Executive (career civil
servants).
Now
the government sector and private
sector touch each other
boundaries
Figure
Government
Private
Sector
(Public)
Sector
Therefore,
these influence each
other.
The
Federation of Pakistan
The
Federation is the Unity of all the constituent units
and article 41 of the constitution
defines
President
as the symbol of unity. It
says:
"There
shall be President of Pakistan
who shall be the Head of State
and shall represent the
unity of
State."
The
Parliament
Article
50 of the Constitution explains the
Parliament. It states:
There
shall be a Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament) of
Pakistan consisting of the President
and two
houses
to be known respectively as
1.
The National Assembly
2.
The Senate
The
National Assembly
Article
51 explains that:
"The
National Assembly shall
consist of three hundred and
thirty two Muslim Members to
be
elected
by direct and free vote in
accordance with Law."
Besides
there shall be 10 non Muslim
members and the total
members in National Assembly
shall
be
342. The National Assembly
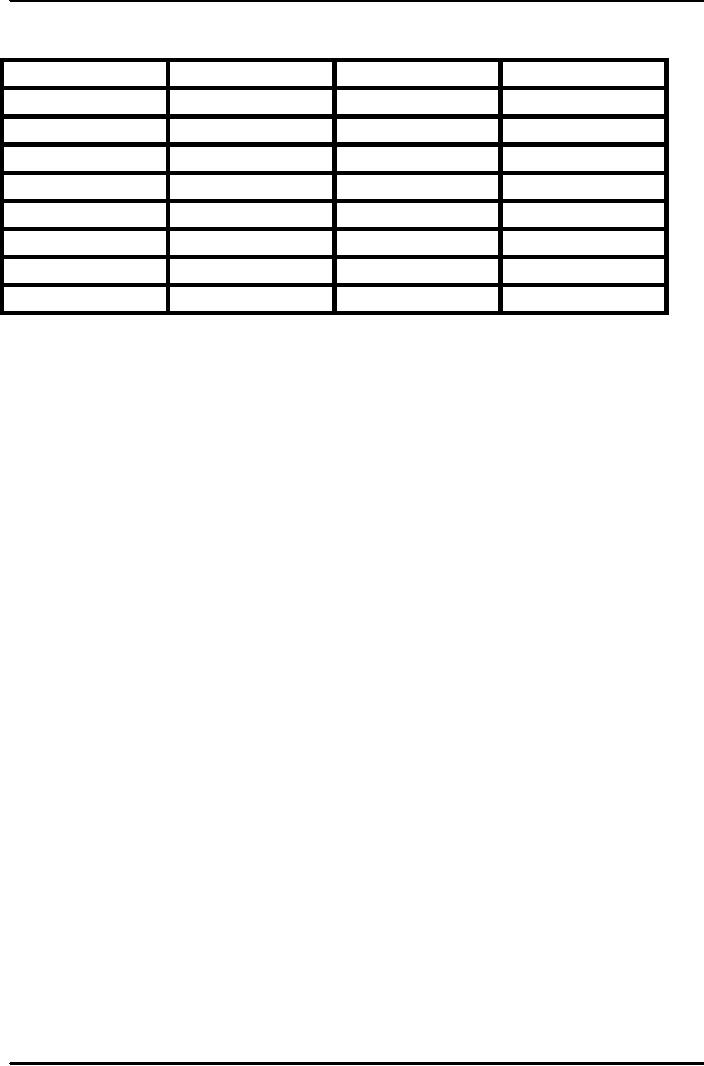
is also called the `Lower House'. The
table below shows the
provincial
distribution
of seats:
38
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Table
Seats
in the National
Assembly
General
seats
Women
Total
Balochistan
14
3
17
The
NWFP
35
8
43
The
Punjab
148
35
183
Sindh
61
14
75
The
FATA
12
-
12
Capita
2
-
2
Total
272
60
332
Non-
Muslims
10
-
The
Senate
The
Senate is `Upper House' and
according to Article 59 (1) of the
constitution:
The
Senate shall consist of one
hundred members, of whom,
a.
Fourteen shall be elected by
members of each Provincial
Assembly (56)
b.
Eight shall be elected from
FATA. (8)
c.
Two on general seats,
and one women and
one technocrat.....(4)
d.
Four women shall be elected
by the members of each Provincial
Assembly (16)
e.
Four technocrats including
ulema shall be elected by the
members of each Provincial
Assembly (16)
The
total of all the above seats
comes to 100.
Federal
Government
Article
90 of the Constitution provides for the
exercise of executive authority by the
President.
"The
Executive Authority of the federation shall
vest in the President and
shall be exercised by
him,
either directly or through officers subordinate to
him."
The
Cabinet
A
cabinet according to the Constitution
Article 91 (1) of the Constitution
comprises of Ministers
and
the prime minister heads the
Cabinet:
"There
shall be a Cabinet of Ministers, with the
Prime Minister as its head,
to aid and advise the
President
in the exercise of his
Functions."
So,
the Prime Minister is the functional
head and he helps the
President in fulfilling his
duties.
Constitutional
Bodies
There
are other constitutional
bodies which have the
functions defined by the constitution.
These
are:
National
Economic Council, National Finance
Commission, The Supreme
Court, High Court
and
Public
Service Commission. These
bodies regulate and make
policy decisions which have
long term impact.
National
Economic Council
(NEC)
Article
156 (1) of the constitution
states that:
"The
President shall constitute a National
Economic Council consisting of Prime
Minister, who
shall
be its Chairman, and such
other members as the President
may determine."
2)
NEC shall review the overall
economic condition of the country
and shall, formulate plans
in
respect
of financial, commercial, social and
economic policies.
39

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Thus
NEC is the highest body in the
that it provides framework for the
economic and financial
and
social
policies. In this way it is an important
body.
National
Finance Commission (NFC)
Article
160 provides for the
NFC:
"The
President shall constitute a National
Finance Commission consisting of the
Minister of
finance
of Federal Government, Ministers of
Finance of the Provincial Governments
etc."
The
NFC is a body that decides
every five years that
from the taxes collected by the
government,
how
much should be given to provinces and
how much to the federal government. It
also gives the criteria
on
the basis of which resources
are allocated among
provinces.
The
Courts
Article
175 of the constitution provides:
"There
shall be a Supreme Court of
Pakistan, a High Court for
each Province and such
other
courts
as may be established by
law."
Article
176 provides for the Supreme
Court:
The
Supreme Court of Pakistan
shall consist of a Chief
Justice and so any other
Judges as may be
determined
by Act of Majlis-e-Shoora or, as ay be
fixed by the President."
The
High Court
Article
192 provides for the high
court:
"A
High Court shall consist of
a Chief Justice and so many
other Judges as may be determined
by
the
law or, until so determined,
as may be fixed by the President."
Courts
are bodies which interpret
law i.e. give decisions on
cases brought before the courts
e.g. A
case
was brought before the Court by the
affected party against legislation passed
by the provincial assembly
banning
serving of food on marriage.
The court after reviewing the case, up
held the legislation.
Provisions
of the Services
The
Constitution Article 240
also provides for the service
condition of the civil
service:
The
appointments to and the conditions of
services of persons in the service of
Pakistan shall be
determined:-
a)
In the case of the Services of the Federation,
Posts in connection with the Affairs of
the Federation
and
All-Pakistan services, by and under the
act of Parliament,
and
b)
In the case of the services of a Province
and posts in connection with the
affairs of the Province,
by
or under Act of the Provincial
Assembly."
The
Act of parliament referred to in the above
article is the Civil Service
Act 1973.
Public
Service Commission
The
Public Service Commission, Article
242, gives provision of a
body which is the recruiting
agency
for the Federal and
Provincial Governments:
"Parliament
in relation to the affairs of the Federation,
and the Provincial Assembly of a
Province
in
relation to affairs of a Province, may,
by law, provide for the Establishment of
a Public Service
Commission."
40

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Conclusions
The
Constitution provides the framework for the
government. It gives provision of the
bodies that
will
make policies for the government. In
fact, if we look at all the provisions
studied we will find that
it
gives
the structure for the three
branches of the government i.e.
executive, legislative and
judiciary. It also
provides
for bodies like NEC
and NFC, both of which
are important bodies for
making decision of
national
significance.
Concepts
National
Economic Council:
This
body makes financial, commercial,
social and
economic
decisions for the
country.
Federation:
It
is the unity of diverse constituent units. It is
also the
unity
of the provinces and territories of a
country.
Parliament:
It
is also called legislature. It
comprises National
Assembly,
Provincial Assemblies and the
Senate.
National
Finance Commission (NFC): NFC is
constituted every five years.
This body decides
the
criteria on which the resources will be
distributed
between
the Federal Government and
Provincial
Government
and amongst
provinces.
41
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management