 |
Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
Lesson
05
PARTNERSHIP AND
ITS CHARACTERISTICS
PARTNERSHIP
Partnership
is the second stage in the
evolution of forms of business
organization. It means
the
association of two or more
persons to carry on as co-owners,
i.e. a business for profit.
The
persons
who constitute this
organization are individually
termed as partners and
collectively
known
as firm; and the name
under which their business
is conducted is called "The
Firm
Name".
In
ordinary business the number
of partners should not
exceed 20, but in case of
banking
business
it must nor exceed 10.
This type of business
organization is very popular
in
Pakistan.
DEFINITION
1.
According to
Section 4 of Partnership Act,
1932
"Partnership
is the relation between
persons who have agreed to
share the profits of
a
business
carried on by all or any of
them acting for
all."
2.
According to
Mr. Kent
"A
contract of two or more
competent persons to place
their money, efforts, labour
and skills,
some
or all of them, in a lawful
commerce or business and to
divide the profits and
bear the
losses
in certain proportion."
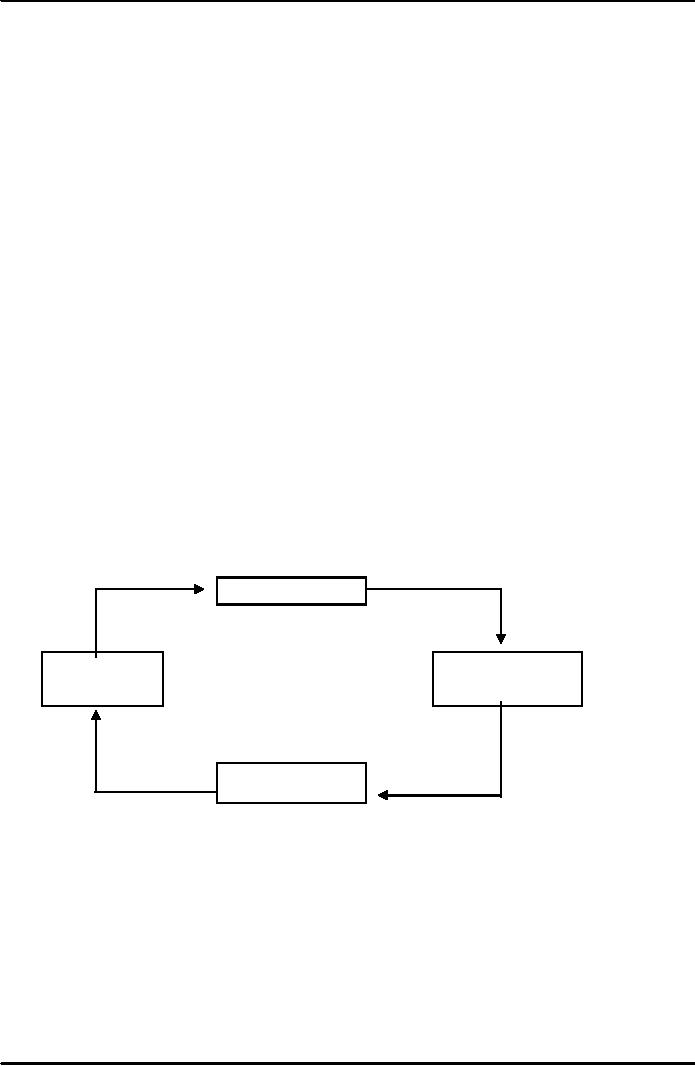
Structural
Diagram:
Association
Profit
& Loss
Money,
Labour
PARTNERSHIP
And
Other Skills
Lawful
Business
CHARACTERISTICS
The
main characteristics of partnership
may be narrated as
under:
1.
Agreement
Agreement
is necessary for partnership.
Partnership agreement may be
written or oral. It is
better
that the agreement is in
written form to settle the
disputes.
2.
Audit
If
partnership is not registered, it
has no legal entity. So
there is no restriction for
the audit of
accounts.
23

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
3.
Agent
In
partnership every partner
acts as an agent of another
partner.
4.
Business
Partnership
is a business unit and a
business is always for
profit. It must not include
club or
charitable
trusts, set up for
welfare.
5.
Cooperation
In
partnership mutual cooperation
and mutual confidence is an
important factor.
Partnership
cannot
take place with
cooperation.
6.
Dissolution
Partnership
is a temporary form of
business.
It
is dissolved if a partner leaves,
dies or
declared
bankrupt.
7.
Legal Entity
If
partnership is not registered, it
has no legal entity.
Moreover, partnership has no
separate
legal
entity from its members
and vice versa.
8.
Management
In
partnership all the partners
can take part or participate
in the activities of
business
management.
Sometimes, only a few
persons are allowed to
manage the business
affairs.
9.
Number of Partners
In
partnership there should be at
least two partners. But in
ordinary business the
partners
must
not exceed 20 and in case of
banking business it should
not exceed 10.
10.
Object
Only
that business is considered as
partnership, which is established to
earn profit.
11.
Partnership Act
In
Pakistan, all partnership
businesses are running under
Partnership Act,
1932.
12.
Payment of Tax
In
partnership, every partner
pays the tax on his
share of profit, personally or
individually.
13.
Profit and Loss
Distribution
The
distribution of profit and
loss among the partners is
done according to their
agreement.
14.
Registration
Many
problems are created in case
of unregistered firm.
So,
to avoid these
problems
partnership
firm must be
registered.
15.
Relationship
Partnership
business can be carried on by
all partners or any of them
can do the business
for
all.
16.
Share in Capital
According
to the agreement, every
partner contributes his
share of capital. Some
partners
provide
only skills and ability to
become a partner of business
and earn profit.
17.
Transfer of Rights
In
partnership no partner can
transfer his shares or
rights to another person,
without the
consent
of all partners.
24

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
18.
Unlimited Liability
In
partnership the liability of
each partner is unlimited. In
case of loss, the private
property of
the
partners is also used up to
pay the business
debts.
ADVANTAGES
AND DISADVANTAGES OF
PARTNERSHIP
ADVANTAGES
OF PARTNERSHIP
Following
are the advantages of
partnership:
1.
Simplicity in Formation
This
type of business of organization
can be formed easily without
any complex legal
formalities.
Two or more persons can
start the business at any
time. Its registration is
also
very
easy.
2.
Simplicity in Dissolution
Partnership
Business can be dissolved at
any time because of no legal
restrictions.
Its
dissolution
is easy as compared to Joint
Stock Company.
3.
Sufficient Capital
Partnership
can collect more capital in
the business by the joint
efforts of the partners
as
compared
to sole proprietorship.
4.
Skilled Workers
As
there is sufficient capital so a
firm is in a better position to
hire the services of
qualified and
skilled
workers.
5.
Sense of Responsibility
As
there is unlimited liability in
case of partnership, so every
partner performs his
duty
honestly.
6.
Satisfaction of Partners
In
this type of business
organization each partner is
satisfied with the business
because he
can
take part in the management
of the business.
7.
Secrecy
In
partnership it is not compulsory to
publish the accounts. So,
the business secrecy
remains
within
partners. This factor is
very helpful for successful
operation of the
business.
8.
Social Benefit
Two
or more partners with their
resources can build a strong
business. This factor is
very
helpful
in solving social problems
like unemployment.
9.
Expansion of Business
In
this type of business
organization, it is very easy to
expand business volume by
admitting
new
partners and can borrow
money easily.
10.
Flexibility
It
is flexible business and
partners can change their
business policies with the
mutual
consultation
at any time.
11.
Tax Facility
Every
partner pays tax
individually. So, a firm is in a
better position as compared to
Joint
Stock
Company.
25
Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
12.
Public Factor
Public
shows more confidence in
partnership as compared to sole
proprietorship. If a firm is
registered,
people feel no risk in
creating relations with such
business.
13.
Prime Credit
Standing
The
liabilities of partners are
unlimited, so the banks and
other financial institutions
provide
them
credit easily.
14.
Minority Protection
In
partnership all policy
matters are decided with
consent of each
partner.
This
gives
protection
to minority partners.
15.
Moral Promotion
Partnership
is the best business for
small investors. It promotes
moral courage of
partners.
16.
Distribution of Work
There
is distribution of work among
the partners according to
their ability and
experience. This
increases
the efficiency of a
firm.
17.
Combined Abilities
Every
partner possesses different
ability, which helps in
running the business
effectively, when
combined
together.
18.
Absence of Fraud
In
partnership each partner can
look after the business
activities. He can check the
accounts.
So,
there is no risk of
fraud.
DISADVANTAGES
OF PARTNERSHIP
The
disadvantages of partnership are
enumerated one by one as
under:
1.
Unlimited Liability
It
is the main disadvantage of
partnership. It means in case of
loss, personal property of
the
partners
can be sold to pay off
the firm's debts.
2.
Limited Life of
Firm
The
life of this type of
business organization is very
limited. It may come to an
end if any
partner
dies or new partner enters
into business.
3.
Limited Capital
No
doubt, in partnership, capital, is
greater as compared to sole
proprietorship, but it is
small
as
compared to Joint Stock
Company. So, a business
cannot be expanded on a large
scale.
4.
Limited Abilities
As
financial resources of partnership
are limited as compared to
Joint Stock Company, so it
is
not
possible to engage the
services of higher technical
and qualified persons. This
causes the
failure
of business, sooner or
later.
5.
Limited number of
Partners
In
partnership, the number of
partners is limited, so the
resources are also limited.
That is why
business
cannot expand on large
scale.
6.
Legal Defects
There
are no effective rules and
regulations to control the
partnership activities. So, it
cannot
handle
large-scale production.
26

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
7.
Lack of Interest
Partners
do not take interest in the
business activities due to
limited share in profit and
limited
chances
of growth of business.
8.
Lack of Public
Confidence
As
there is no need by law to
publish accounts in partnership, so
people lose confidence
and
avoid
dealing and entering into
contract with such
firm.
9.
Lack of Prompt
Decision
In
partnership all decisions
are made by mutual
consultation. Sometimes, delay in
decisions
becomes
the cause of loss.
10.
Lack of Secrecy
In
case of misunderstandings and
disputes among the partners,
business secrets can
be
revealed.
11.
Chances of Dispute among
Partners
In
partnership there are much
chances of dispute among the
partners because all the
partners
are
not of equal mind.
12.
Expansion Problem
Partnership
business may not be expanded
due to limited number of
partners, limited
capital
and
unlimited liability.
13.
Frozen Investment
It
is easy to invest money in
partnership but very
difficult to withdraw
it.
14.
Risk of Loss
There
is a risk of loss due to
less qualified and less
experienced people.
15.
Transfer of Rights
In
partnership no partner can
transfer his share without
the consent of all other
partners.
CONCLUSION
From
the above-mentioned findings, we
come to this point that
despite the above
disadvantages,
partnership is an important from of
business organization. This is
because its
formation
is very easy and due to
unlimited liabilities, partners
take great interest in
business,
because
in case of loss they are
personally responsible.
27
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:CONCEPT OF BUSINESS, KINDS OF INDSTRY, TYPES OF TRADE
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:THE ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATION:Sole Proprietorship, Joint Stock Company, Combination
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):KINDS OF PARTNERS, PARTNERSHIP AT WILL
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):PARTNESHIP AGREEMENT, CONCLUSION, DUTIES OF PARTNERS
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:ETHICS IN THE WORKPLACE, SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
- JOINT STOCK COMPANY:PRIVATE COMPANY, PROMOTION STAGE, INCORPORATION STAGE
- LEGAL DOCUMENTS ISSUED BY A COMPANY:MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION, CONTENTS OF ARTICLES
- WINDING UP OF COMPANY:VOLUNTARY WIDNIGN UP, KINDS OF SHARE CAPITAL
- COOPERATIVE SOCIETY:ADVANTAGES OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
- WHO ARE MANAGERS?:THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS, BASIC MANAGEMENT SKILLS
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT:Human Resource Planning
- STAFFING:STAFFING THE ORGANIZATION
- STAFF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT:Typical Topics of Employee Training, Training Methods
- BUSINESS MANAGER’S RESPONSIBILITY PROFILE:Accountability, Specific responsibilities
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS:THE LEGAL CONTEXT OF HR MANAGEMENT, DEALING WITH ORGANIZED LABOR
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS (Continued):MOTIVATION IN THE WORKPLACE
- STRATEGIES FOR ENHANCING JOB SATISFACTION AND MORALE
- MANAGERIAL STYLES AND LEADERSHIP:Changing Patterns of Leadership
- MARKETING:What Is Marketing?, Marketing: Providing Value and Satisfaction
- THE MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:THE MARKETING MIX, Product differentiation
- MARKET RESEARCH:Market information, Market Segmentation, Market Trends
- MARKET RESEARCH PROCESS:Select the research design, Collecting and analyzing data
- MARKETING RESEARCH:Data Warehousing and Data Mining
- LEARNING EXPERIENCES OF STUDENTS EARNING LOWER LEVEL CREDIT:Discussion Topics, Market Segmentation
- UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR:The Consumer Buying Process
- THE DISTRIBUTION MIX:Intermediaries and Distribution Channels, Distribution of Business Products
- PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION:Transportation Operations, Distribution as a Marketing Strategy
- PROMOTION:Information and Exchange Values, Promotional Strategies
- ADVERTISING PROMOTION:Advertising Strategies, Advertising Media
- PERSONAL SELLING:Personal Selling Situations, The Personal Selling Process
- SALES PROMOTIONS:Publicity and Public Relations, Promotional Practices in Small Business
- THE PRODUCTIVITY:Responding to the Productivity Challenge, Domestic Productivity
- THE PLANNING PROCESS:Strengths, Weaknesses, Threats
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Planning for Quality, Controlling for Quality
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Tools for Total Quality Management
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Process Re-engineering, Emphasizing Quality of Work Life
- BUSINESS IN DIGITAL AGE:Types of Information Systems, Telecommunications and Networks
- NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION MODES:Body Movement, Facial Expressions
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS:Organization as a System
- ACCOUNTING:Accounting Information System, Financial versus Managerial Accounting
- TOOLS OF THE ACCOUNTING TRADE:Double-Entry Accounting, Assets
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:The Role of the Financial Manager, Short-Term (Operating) Expenditures