 |
COOPERATIVE SOCIETY:ADVANTAGES OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY |
| << WINDING UP OF COMPANY:VOLUNTARY WIDNIGN UP, KINDS OF SHARE CAPITAL |
| WHO ARE MANAGERS?:THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS, BASIC MANAGEMENT SKILLS >> |
Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
LESSON
12
COOPERATIVE
SOCIETY
COOPERATIVE
SOCIETY
A
cooperative society is formed by
the people of limited means
for self help through
mutual
help.
It is set up to protect economically
the poor sections of the
society. It is set up
for
cooperation,
not for competition. The
motto of a society is self
help, without dependence
on
other
business units.
DEFINITION
1.
According
to Herrik,
"Cooperation
is an action of persons voluntarily
united for utilizing
reciprocally their
own
forces,
resources or both under
mutual management for their
common profit or
loss."
2.
According
to Mr. Plunket,
"The
cooperation is self help
made effective by
organization."
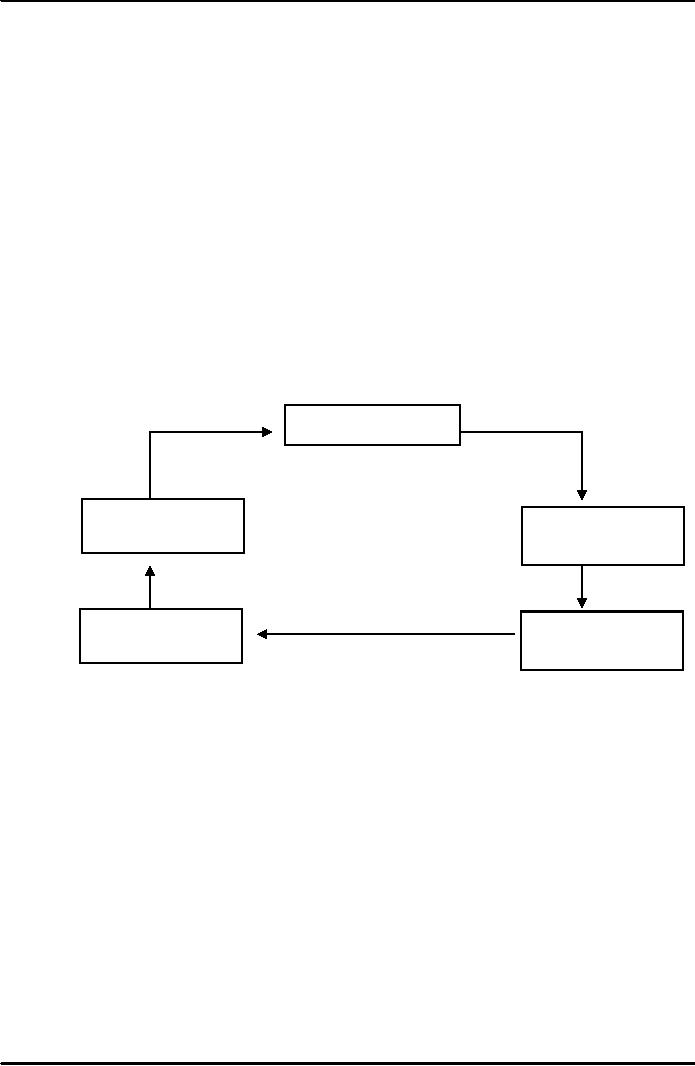
Cooperative
Society
Diagram
Welfare
Number
of persons
Business
Pool
Resources
ADVANTAGES
OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
Following
are the important advantages
or merits of cooperative
society:
1.
Advantage for
Farmers
Farmers
can get fertilizers and
seeds at low prices from
such cooperative societies.
Farmers
can
also self their production
at high rate or prices
through cooperative
societies.
2.
Easy Formation
the
formation of cooperative society is
very easy. the formalities
for registration are
simple
and
formation expenses are also
normal. The registration of a
society is not compulsory
but it
is
desirable to have its
registration.
3.
Equal Rights
All
members of cooperative society
enjoy equal right of vote
and ownership.
Each
shareholder
has only one vote in
the management of cooperative
societies.
4.
Equal Distribution of
Wealth
The
profit of middlemen is also
distributed among the
workers. These societies
remove the
unequal
distribution of wealth.
69

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
5.
Economic Democracy
Cooperative
society is a domestic form of
organization. Every member is
allowed to
participate
in the management of the
business. Each member has
the right to cast vote.
The
decision
of majority is honored.
6.
Elimination of Middlemen
Cooperative
society eliminates the
profit of middlemen. These
societies purchases
goods
directly
from the producers for
members and provide them on
wholesale rate to
society
members.
7.
Financial Assistance
These
societies also provide
financial assistance to its
members. In case of house
building
cooperatives
housing society provides
loan for the purchase of
inputs.
8.
Friendly Relations
A
cooperative society is a mean of
developing friendly relations
among the members. A
society
provides a platform for the
introduction of members with
each other.
9.
Improve the Standard of
Living
Such
societies provide the goods
and services to the members
of the society at low
prices.
Due
to this, the purchasing
power of the people
increases and their standard
of living
improves.
10.
Increase in Employment
The
cooperative societies also
increase the employment
opportunities for people.
Thousands
of
people are engaged in
different types of cooperative
societies.
11.
Limited Liability
The
liability of each member in
cooperative society is limited to
the share capital, which
he
invested.
His remain safe.
12.
Mutual Cooperation
It
is worthwhile to mention here
that cooperative society is
very useful for creating
the spirit of
friendship
and brotherhood among the
members. Cooperative society is
the basic need of
human
being in modern era.
13.
No Monopoly
A
start of the society is the
end of monopoly. The
monopoly eliminates the
competition and
controls
the market and prices.
The society tries to
restore competition and to
eliminate
control
over market and
prices.
14.
Open Membership
The
membership of a cooperative society is
open for all people
living in the same area. It
is a
voluntary
association of persons of any
caste, colour and
creed.
15.
Protection of Mutual
Interest
In
cooperative societies its
members take an advantage of
mutual interest and
cooperate with
each
other achieve the common
interest.
16.
Responsibility
A
society is a training centre
for the members to feel
their responsibility. A cooperative
society
is
an ideal place for building
up the moral character and
development of personal qualities
of
the
members.
70

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
17.
Supply according to
Demand
Such
societies purchase the goods
according to the demand of
members. The question
of
surplus
does not arise.
18.
Stable Life
The
cooperative societies, as compared to
other business organization
like sole-proprietorship
or
partnership, exists for a
longer period. It has a
fairly stable life.
19.
Saving in Expenditure
In
cooperative societies, most of
offices bearers work
voluntarily. So, there are
no heavy
expenditures
on management. It also reduces
the cost of
production.
20.
Tax Concession
Government
provides certain concessions to
cooperative societies, i.e.
exemption from stamp
duty,
super tax, income tax
and registration fee
etc.
DISADVANTAGES
OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
Following
are the disadvantages of
cooperative societies:
1.
Lack of Capital
Generally
the members of cooperative
societies are related to
poor group and they
cannot
provide
the capital on large scale.
External financial resources
are also limited.
So,
cooperative
society faces the shortage
of capital, which is a handicap to
their development.
2.
Untrained Supervision
The
government has sufficient
control over the movement of
these societies. These
societies
cannot
prosper because the staff
appointed for supervision is
mostly untrained.
3.
Defective Organization
The
organizations of cooperative societies
are defective and these
cannot operate efficiently
to
fulfill
their objectives.
4.
Illiterate and
Ignorant
In
our country, the villagers
are generally illiterate and
ignorant. So, they are
not familiar with
the
basic concept of the
cooperative societies.
5.
Lack of Experience
The
members of societies have
less experience of business.
Due to lack of capital,
they
cannot
hire the services of
experts.
6.
Lack of Discipline
Every
member of the cooperative
society considers himself as
the owner of the business.
Due
to
lack of discipline, business
suffers a loss.
7.
Lack of Sincere
Management
It
is our common observation
that the management of
society remains in the hands
of selfish
and
dishonest persons or members
who obtains undue advantage
form their powers.
So,
business
suffers a loss.
8.
Lack of Profit
Incentive
It
is not a profit earning
institution.
Due
to absence of profit incentive,
the progress of
cooperative
society is very poor.
9.
Lack of Secrecy
There
is no secrecy in the business of
cooperative societies.
71

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
10.
Lack of Knowledge
The
members of cooperative society do
not know the principles
and rules of society. So,
they
create
great problem for
society.
11.
Lack of Unity
In
the absence of proper
education and training, it is
useless to think about
unity. The lack of
unity
leads towards the
destruction of the
business.
12.
No use of New
Technology
The
cooperative societies cannot
use the latest technology in
production. As a result of
this,
demand
and profit remains
low.
13.
No Public Confidence
A
cooperative society is not
bound to publish annual
financial statements for the
information of
general
public. Due to this public
shows less confidence in
them.
14.
Delay in Decision
The
main cause of failure of
cooperative societies is delayed in
decisions.
15.
Government Control
The
cooperative department of the
provincial government supervises
the work of all
cooperative
societies. The business of a
society is not free like
other forms of business, so
it
cannot
earn maximum profit.
72
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:CONCEPT OF BUSINESS, KINDS OF INDSTRY, TYPES OF TRADE
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:THE ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATION:Sole Proprietorship, Joint Stock Company, Combination
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):KINDS OF PARTNERS, PARTNERSHIP AT WILL
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):PARTNESHIP AGREEMENT, CONCLUSION, DUTIES OF PARTNERS
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:ETHICS IN THE WORKPLACE, SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
- JOINT STOCK COMPANY:PRIVATE COMPANY, PROMOTION STAGE, INCORPORATION STAGE
- LEGAL DOCUMENTS ISSUED BY A COMPANY:MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION, CONTENTS OF ARTICLES
- WINDING UP OF COMPANY:VOLUNTARY WIDNIGN UP, KINDS OF SHARE CAPITAL
- COOPERATIVE SOCIETY:ADVANTAGES OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
- WHO ARE MANAGERS?:THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS, BASIC MANAGEMENT SKILLS
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT:Human Resource Planning
- STAFFING:STAFFING THE ORGANIZATION
- STAFF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT:Typical Topics of Employee Training, Training Methods
- BUSINESS MANAGER’S RESPONSIBILITY PROFILE:Accountability, Specific responsibilities
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS:THE LEGAL CONTEXT OF HR MANAGEMENT, DEALING WITH ORGANIZED LABOR
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS (Continued):MOTIVATION IN THE WORKPLACE
- STRATEGIES FOR ENHANCING JOB SATISFACTION AND MORALE
- MANAGERIAL STYLES AND LEADERSHIP:Changing Patterns of Leadership
- MARKETING:What Is Marketing?, Marketing: Providing Value and Satisfaction
- THE MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:THE MARKETING MIX, Product differentiation
- MARKET RESEARCH:Market information, Market Segmentation, Market Trends
- MARKET RESEARCH PROCESS:Select the research design, Collecting and analyzing data
- MARKETING RESEARCH:Data Warehousing and Data Mining
- LEARNING EXPERIENCES OF STUDENTS EARNING LOWER LEVEL CREDIT:Discussion Topics, Market Segmentation
- UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR:The Consumer Buying Process
- THE DISTRIBUTION MIX:Intermediaries and Distribution Channels, Distribution of Business Products
- PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION:Transportation Operations, Distribution as a Marketing Strategy
- PROMOTION:Information and Exchange Values, Promotional Strategies
- ADVERTISING PROMOTION:Advertising Strategies, Advertising Media
- PERSONAL SELLING:Personal Selling Situations, The Personal Selling Process
- SALES PROMOTIONS:Publicity and Public Relations, Promotional Practices in Small Business
- THE PRODUCTIVITY:Responding to the Productivity Challenge, Domestic Productivity
- THE PLANNING PROCESS:Strengths, Weaknesses, Threats
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Planning for Quality, Controlling for Quality
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Tools for Total Quality Management
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Process Re-engineering, Emphasizing Quality of Work Life
- BUSINESS IN DIGITAL AGE:Types of Information Systems, Telecommunications and Networks
- NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION MODES:Body Movement, Facial Expressions
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS:Organization as a System
- ACCOUNTING:Accounting Information System, Financial versus Managerial Accounting
- TOOLS OF THE ACCOUNTING TRADE:Double-Entry Accounting, Assets
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:The Role of the Financial Manager, Short-Term (Operating) Expenditures