 |

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Lesson
33
MODIFICATIONS
IN MILLAR MODIGLIANI CAPITAL STRUCTURE
THEORY
Learning
Objectives:
After
going through this lecture,
you would be able to have an
understanding of the following
topic:
�
Modifications
in Miller Modigliani Capital Structure
Theory
Modified
MM -
With
Taxes:
In
order to apply it in the real
world for its use,
Miller-Modigliani and some other
economists made
some
modifications. In order to make this
theory applicable in the real
world and to account for
the
effects
of corporate and personal taxes on investment
decision and on firm, the effect of
taxes was
included
in it.
�
Modigliani-Miller
(With Corporate
Tax)
In most countries, a Firm's
Interest Payments to Bond
Holders are NOT Taxed.
But
Dividend
Payments to Equity Holders
are taxed. This was
conclusion after study
of
different
countries. Most of the firms prefer
debt rather than
equity.
Based on CORPORATE TAXES,
FIRMS should prefer to raise
Capital using DEBT
Financing
rather than equity as there is saving
associated with capital
raised through
this
source.
From
firms point of view interest
payments are source of tax
savings.
�
Modigliani
-Miller (With Personal
Tax)
In most countries, INVESTORS
(bondholders and shareholders) pay a
higher Personal
Income
Tax on Interest Income from
Bonds than on Dividend Income
from Equity (or
Stocks).
Based on PERSONAL TAXES,
INVESTORS should prefer to
invest in STOCKS (or
Equity).
Uncertain
Conclusion:
Difficult to determine Net
Effect of taxes on optimal
capital structure. Effects
of
corporate taxes and personal taxes are
contradictory. But, practically speaking,
Corporate Tax Effect
is
generally stronger so Based on Taxes
alone, Firms should prefer
Debt.
Modified
MM - With Bankruptcy
Cost:
The
second major change in
MM-theory was to incorporate the
effect of bankruptcy costs. In
the
real
world companies face cash
problems, their sales might
drop, they face more
competition, the
interest
rate might go up, their debt
servicing charges might go
up, they start incurring
losses, making
operational
cash outflows and this may
lead the company to close down or go
bankrupt.
�
Bankruptcy: when a Firm is
forced to close down because
of continual Losses and Net
Cash
Outflows
or Default on Interest
Payments.
�
Bankruptcy Costs Real Money -
Companies Do Not Die in
Peace! There are costs
associated
with
bankruptcy companies have to pay.
Fees paid to Lawyers and
Accountants, possible
penalties
and Legal Claims by Suppliers,
Buyers, & Partner Firms, and Loss on
Sale of Assets
because
Firm is forced to quickly
Liquidate its Assets and
repay the Debt Holders (such
as
Banks)
first.
�
Even before bankruptcy the
THREAT or RUMOR of Bankruptcy
can create problems for
a
Firm.
Suppliers refuse to supply
raw materials and cancel
Trade Credit facilities. Banks
demand
higher
Interest Rates. Customers
cancel Purchase Orders so
sales fall.
�
If Firm is EXCESSIVELY LEVERAGED
(or has a Lot of Debt)
then there is a HIGHER
Chance
of Bankruptcy.
�
For Certain Types of Firms,
Debt is More Likely to Cause
Bankruptcy:
Firms with High Operating
Leverage or high Fixed
Costs
Firms with Non-Liquid
Assets that are difficult to
sell quickly for
cash
Firms whose EBIT (or
Earnings) Fluctuate a
Lot
Tradeoff
Theory of Capital Structure With
Tax & Bankruptcy:
Now
let us discuss trade off
theory. It mixes a couple of changes in
pure MM-theory by taking
into
consideration
both bankruptcy costs and
taxes. We will start with a
firm of 100% equity capital
and see
what
happens when a firm starts
taking debt and gradually
increases the percentage of debt in
its capital
143
Financial
Management MGT201
VU
structure.
See the following graph to determine the
effect of increasing leverage on the
value of firm
measured
by its stock value to make trade
off theory concepts
clear:
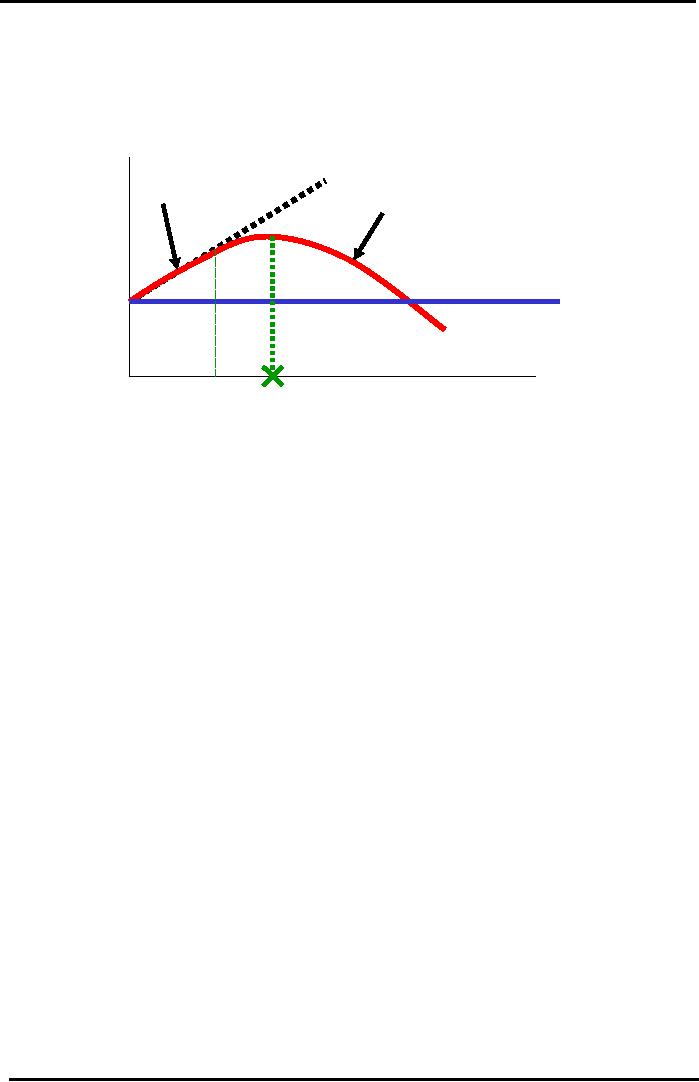
Tradeoff
Theory Graph
Leverage
& Optimal Capital
Structure
Slightly
Leveraged Firm:
Interest Tax
Shield
Benefit. Total Return to
Investors
Excessively
Leveraged Firm:
Rises
so Stock Value Rises.
Total
Return
Threat
of Bankruptcy has Real
=
Net Income (paid to
Shareholders) +
Value
of
Costs.
Less Investor
Interest
(paid to Debt
Holders)
Firm
or
Confidence
and Lower Share
Price.
Price
of
Stock
Firm
Remains 100%
Equity
(Un-Levered)
Financial
Leverage =
OPTIMAL
Capital
Debt
/ Assets =
Structure
- MAXIMUM
D/(D+E)
VALUE
& MINIMUM
WACC
Keep
in mind,
Value
of Firm = Price of One Share x
Number of Shares
Outstanding
On
the Y-axis we have the Value of Firm or
Price of Stock and on X-axis the
Financial Leverage =
Debt
/
Assets = Debt/ (Debt +
Equity) in percentage. In the graph
1.0 shows 100% capital is
from debt at that
point.
Horizontal line represents the
case when a firm is 100%
equity. It is un levered firm.
Here firm
has
no debt so its stock value is
not sensitive to financial leverage.
Now let us take the case of
the same
firm
if it gradually adds debt to its
capital structure.
�
When 100% Equity Firm
adds a Small Amount of Debt,
the Value of its Stock Goes
Up at first
because
Total Return
Increases.
Total
Return
=
Net Income (paid to Equity
Holders) + Interest (paid to
Debt Holders).
The
line therefore rises
initially but then it
reaches a maximum point
which is the optimal
capital
structure. At this point value of
firm will be at its maximum.
This is the best debt
to
equity
ratio for this firm at
which WACC will be at
minimum. After this point
firms' debt gets
high
and it starts facing high interest
costs, chances of loosing creditors and
buyers and threats
of
bankruptcy. Investors' loose confidence
on the share of the firm and the
Chances of
Bankruptcy
will offset the Initial
Benefit and the Stock Value
will Fall.
�
Decision regarding how
much Debt (or Financial
Leverage) to take is based on
Tradeoff
between
the Advantage of Debt & Disadvantage of
Debt.
Advantage of Debt over
Equity: Interest Payments
are Not Taxed. Known as
Interest
Tax
Saving or Tax Shield or Tax
Shelter
Disadvantage of Too Much Debt:
Firm becomes more Risky so Lenders
and Banks
Charge
Higher Interest Rates and
Greater Chance of Bankruptcy
�
Trade theory tells there is
some optimal capital structure or there
is some percentage of debt
in
capital
structure for a firm at a particular
date. But it does not
give us the exact figure for
that. A
range
for the Optimal Capital Structure or
Debt/Equity Mix can be calculated in
theory. This is
where
the Firm has Maximum Value
and Minimum WACC.
Practically speaking it varies
across
industries and companies. Optimal
D/E can range from 20/80 to
70/30 and keeps
changing
with time depending on the
firm's financial health and
growth strategy.
Signaling
Theory of Capital Structure- An
Improvement on Tradeoff
Theory:
This
is another modification of the theory of
Miller Modigliani Capital
Structure.
144

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
�
This
theory takes into account
the practical fact of the world
that NOT all Investors have
equal
amount
of information. All investors are not
rational. A Firm's Owners &
Managers (Insiders)
know
more about it than Ordinary outside
Investors.
�
Signaling Theory: "Insiders
(Managers & Owners) Know
Better"
When Firm's Future
genuinely looks Good (i.e.
High forecasted Cash Flows,
Earnings,
NI,
and ROE) then Managers will
choose to raise financing
through Debt (or Bonds
or
Loan)
because they do not want to
share the Financial Gain
with More Shareholders.
Rather
They Prefer to Take on Debt
and pay a small interest to the
Debt Holders. There
is
almost no risk of Default.
When Firm's Outlook
looks bad, then Managers
will choose to raise capital
by Issuing
Equity
(or Stock) to be able to
share the Likely Losses
amongst more Shareholders
(Owners).
If they took Debt and
couldn't repay it, they
might Default and be forced
to
go
Bankrupt.
So
mangers are in a better
position to decide about the
firm.
Signaling
Theory Conclusions:
�
Practically speaking, Firms should
maintain LESS Leverage than
the Optimal Level
from
Tradeoff
Theory.
�
Firms Should Save Some
Reserve Debt Financing
Capacity in case they find a
Great Project or
Investment
Opportunity. They should
finance the Project using
Debt for 2 reasons:
they don't have to share the
Financial Gains with more
shareholders and
they give the Right
Signal to the Market of Investors
about the good health of
their
Firm
!
Debt Financing brings
Financial Discipline and tighter
cash control on some
Managers
that
waste Shareholders'
money
�
News of New Equity
Financing Signals bad news: It indicates
shortfall in cash flows
through
profit,
Investors will sell stock and
Market Price (Po) of Stock
will fall. Therefore,
Required
ROR
(r = DIV/ (Po + g)) will Rise
and WACC will Increase.
Now more difficult for
Projects
and
Investments to meet this Firm's
Capital Budgeting Criterion by
showing positive NPV
(=
Sum
of Cash Flows / (1+r) t).
145
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Corporate Financing & Capital Structure,
- OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, FINANCIAL ASSETS AND FINANCIAL MARKETS:Real Assets, Bond
- ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Basic Financial Statements, Profit & Loss account or Income Statement
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Discounting & Net Present Value (NPV), Interest Theory
- FINANCIAL FORECASTING AND FINANCIAL PLANNING:Planning Documents, Drawback of Percent of Sales Method
- PRESENT VALUE AND DISCOUNTING:Interest Rates for Discounting Calculations
- DISCOUNTING CASH FLOW ANALYSIS, ANNUITIES AND PERPETUITIES:Multiple Compounding
- CAPITAL BUDGETING AND CAPITAL BUDGETING TECHNIQUES:Techniques of capital budgeting, Pay back period
- NET PRESENT VALUE (NPV) AND INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR):RANKING TWO DIFFERENT INVESTMENTS
- PROJECT CASH FLOWS, PROJECT TIMING, COMPARING PROJECTS, AND MODIFIED INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (MIRR)
- SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING:SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING, SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING
- CAPITAL RATIONING AND INTERPRETATION OF IRR AND NPV WITH LIMITED CAPITAL.:Types of Problems in Capital Rationing
- BONDS AND CLASSIFICATION OF BONDS:Textile Weaving Factory Case Study, Characteristics of bonds, Convertible Bonds
- BONDS’ VALUATION:Long Bond - Risk Theory, Bond Portfolio Theory, Interest Rate Tradeoff
- BONDS VALUATION AND YIELD ON BONDS:Present Value formula for the bond
- INTRODUCTION TO STOCKS AND STOCK VALUATION:Share Concept, Finite Investment
- COMMON STOCK PRICING AND DIVIDEND GROWTH MODELS:Preferred Stock, Perpetual Investment
- COMMON STOCKS – RATE OF RETURN AND EPS PRICING MODEL:Earnings per Share (EPS) Pricing Model
- INTRODUCTION TO RISK, RISK AND RETURN FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT:Diversifiable Risk, Diversification
- RISK FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT, PROBABILITY GRAPHS AND COEFFICIENT OF VARIATION
- 2- STOCK PORTFOLIO THEORY, RISK AND EXPECTED RETURN:Diversification, Definition of Terms
- PORTFOLIO RISK ANALYSIS AND EFFICIENT PORTFOLIO MAPS
- EFFICIENT PORTFOLIOS, MARKET RISK AND CAPITAL MARKET LINE (CML):Market Risk & Portfolio Theory
- STOCK BETA, PORTFOLIO BETA AND INTRODUCTION TO SECURITY MARKET LINE:MARKET, Calculating Portfolio Beta
- STOCK BETAS &RISK, SML& RETURN AND STOCK PRICES IN EFFICIENT MARKS:Interpretation of Result
- SML GRAPH AND CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL:NPV Calculations & Capital Budgeting
- RISK AND PORTFOLIO THEORY, CAPM, CRITICISM OF CAPM AND APPLICATION OF RISK THEORY:Think Out of the Box
- INTRODUCTION TO DEBT, EFFICIENT MARKETS AND COST OF CAPITAL:Real Assets Markets, Debt vs. Equity
- WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL (WACC):Summary of Formulas
- BUSINESS RISK FACED BY FIRM, OPERATING LEVERAGE, BREAK EVEN POINT& RETURN ON EQUITY
- OPERATING LEVERAGE, FINANCIAL LEVERAGE, ROE, BREAK EVEN POINT AND BUSINESS RISK
- FINANCIAL LEVERAGE AND CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Capital Structure Theory
- MODIFICATIONS IN MILLAR MODIGLIANI CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORY:Modified MM - With Bankruptcy Cost
- APPLICATION OF MILLER MODIGLIANI AND OTHER CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES:Problem of the theory
- NET INCOME AND TAX SHIELD APPROACHES TO WACC:Traditionalists -Real Markets Example
- MANAGEMENT OF CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Practical Capital Structure Management
- DIVIDEND PAYOUT:Other Factors Affecting Dividend Policy, Residual Dividend Model
- APPLICATION OF RESIDUAL DIVIDEND MODEL:Dividend Payout Procedure, Dividend Schemes for Optimizing Share Price
- WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT:Impact of working capital on Firm Value, Monthly Cash Budget
- CASH MANAGEMENT AND WORKING CAPITAL FINANCING:Inventory Management, Accounts Receivables Management:
- SHORT TERM FINANCING, LONG TERM FINANCING AND LEASE FINANCING:
- LEASE FINANCING AND TYPES OF LEASE FINANCING:Sale & Lease-Back, Lease Analyses & Calculations
- MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS:Leveraged Buy-Outs (LBO’s), Mergers - Good or Bad?
- INTERNATIONAL FINANCE (MULTINATIONAL FINANCE):Major Issues Faced by Multinationals
- FINAL REVIEW OF ENTIRE COURSE ON FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Financial Statements and Ratios