 |

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Lesson
16
INTRODUCTION
TO STOCKS AND STOCK VALUATION
Learning
Objectives:
After
going through this lecture,
you would be able to have an
understanding of the following
topics
�
Introduction
to Stocks
�
Stock
Valuation
In
previous lectures, we have discussed
about one kind of direct
claim security which is
bonds.
Bonds
are long term debt
instruments. Now, we will take in
detail about another kind of
security which
is
known as Stocks or
Shares.
Stocks:
These
are equity paper representing ownership.
Shareholders are part owners of the
company. If
you
look at the balance sheet
when the company issues shares to
raise money such shares
should be
shown
on the liability side of the balance
sheet of the company. Shareholders are
called owners of the
company
these are shown under the
equity section .However, the shares
that are purchased by
the
company
are shown on the asset side of the
company under the head of marketable
securities .Generally,
when
we are talking about the
issuance of the shares we refer to
shares as liability. Basically, the
share
is
a legal contractual piece of paper it
shows the name of the company. It
shows the par or face value
of
the
share and it also assures
that the shareholder is the part owner of
the company.
Remember
that Shares
are distinguished from the
bonds because shares
represent the
ownership
whereas the bond is a debt
instrument. Another thing
about the shares is to remember
that par
value
is the value when they are
issued the market value of the
shares changes with
investor's
perception
about the company's future
and supply and demand
situation. So, do not
confuse the par
value
with the Market value of the
shares .par value is printed on
that share certificate. As we
have
studied
that Value of Direct
Claim Security
is directly tied to the value of the
underlying Real Asset.
Why
raise money through Equity
(i.e. Shares or Stocks) rather
than Debt (i.e. Bonds or
Loan)?
What
are the advantages of raising
money through equity?
Equity
financing gives the flexibility
that you do not have to made
regular payments. In case of debt
or
bond
you have under taken a promise to
pay a fixed rate of return
.but in case of shares o
fixed rate of
interest
is paid only dividend is
paid on net income according to the
decisions of the board of directors
and
management. You have no obligations to
pay fixed dividend to common
shareholders. But, if the
Company
raises money using Bonds,
then it will have to pay a
fixed amount of interest (or
mark-up)
regularly
for 2 Years. If the Company
does NOT pay on time,
you are declared Defaulter and
your
business
can be closed and the Lenders
(Bondholders) can sell the
company's assets to recover
their
money.
The
value of direct claim
security because derived
from underlying real asset.
It can be thought
of
as a piece of paper that generates a
certain cash flow over the
period of time. Share
certificate is a
piece
of paper that represents
some other real assets and
it generates future cash
flows.
1.
Dividend you are received as
shareholder.
2.
Capital gain
For
example, if there is a textile company
which need to raise the amount of
Rs1 million to
invest
in looms. Company can raise
this amount either by equity or
bonds.
In
case the company decides to raise it
through equity. Then it
issues the share certificate
amounting to
Rs
1 million and sells them to various
interested investors and receives the capital in the
form of equity.
Why
do these share certificates
carry value?
This
investment for the share holders
will generate the cash flow
in form of income and the
cash
flows
in the form of capital gains .These
cash flows are generated
through the under lying
real
assets
.what are these real
assets .the real assets in
this example are the textile
weaving looms and fabric
prepared
by these looms. The cash
flows are generated from the
sale of this fabric. From
these cash
flows
the company is paying dividend (See
diagram)
74
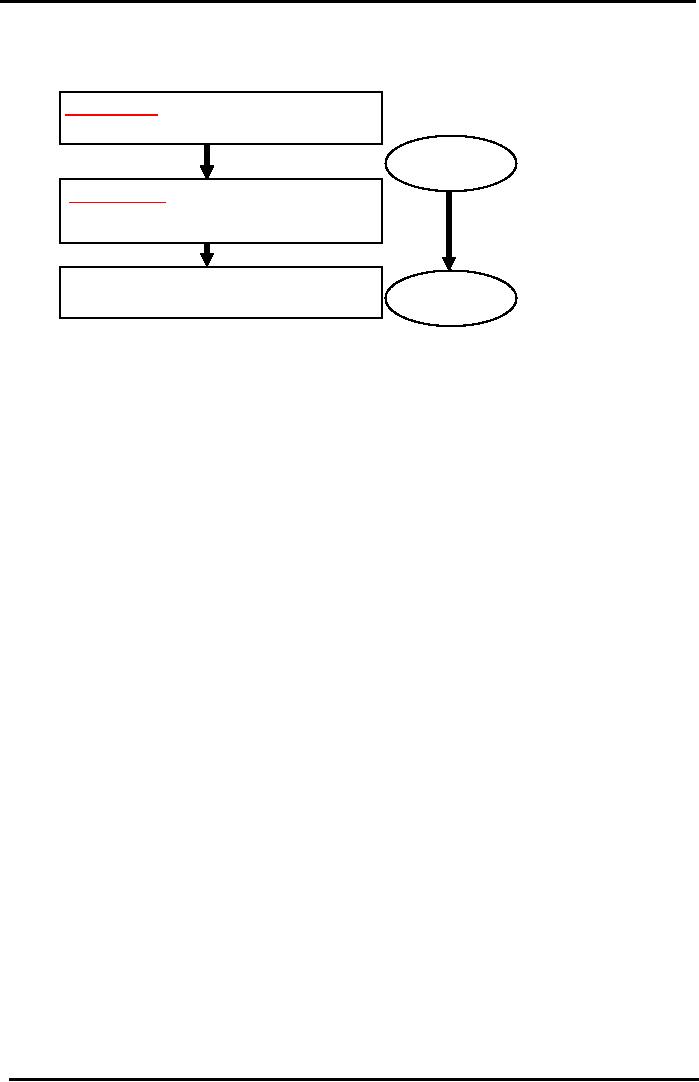
Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Share
Value & Cash
Flows
from
Underlying Real Assets
COMPANY'S
REAL
WORKING ASSETS
that
has issued the Share
ie: Weaving Looms
Capital
Budgeting
NPV
Criteria
COMPANY'S
OPERATING
CASH FLOWS
&
INCOME ie. Revenue from
sale of Fabric
(Company
Value)
DIVIDEND
& CAPITAL GAIN CASHFLOWS
Securities
Valuation
i.e.
Cash pay out to Shareholders
(Share Value)
or
Share Pricing
Share
Concept:
A
Limited Company can raise
money by Issuing (or
selling) Equity in the form of
Shares. In
Pakistan,
the Par Value (or Face
Value) of each share is
generally Rs 10. But by in
large public listed
companies'
issues shares with par value
of Rs.10each .keep in mind that par
value of the share is
value
when
it was issued when it has
gone into market it has
different value. The Life of
a Share is considered
Perpetual
(or never-ending "going
concern") unless of course the company
closes down or goes
bankrupt.
As
the financial health (cash
flows and income) of the company changes
with time, the Market
Value
(or Price) of the Share changes
(even though it's Par
Value is fixed). Market
Prices also change
depending
on the Supply-Demand for the share and
also speculation or satta.
Shares
of Listed Public Limited Companies
are traded in the Stock Exchange like
KSE (Karachi
Stock
Exchange), LSE (Lahore), ISE
(Islamabad). You can buy /
sell shares over the phone
&/or
computer
through your Broker whose
agents / Jobbers are trading
at the exchange. You make payments
to
your Broker through a
Brokerage Account at one of the banks in
the Stock Exchange or through
cash
soon
after the trade is made.
Shares
of Private Limited Companies
(which are not listed)
can also be bought and
sold
privately
and the Corporate Law Authority and
Registrar Joint Stock Companies
need to be informed.
Types
of Equity:
There
are two types of
equity
1.
Common Stock
2.
Preferred Stock
Common
Stock:
It
is the most common kind of equity as
compared to preferred stock. Common Shareholders
are
Owners
who have Voting Rights in
management decisions. Common Shareholders are owners
who
receive
a Dividend (share of the Profit or
Net Income proportionate to
their shareholding) which
varies
depending
on the Net Income for that
year and the decision of the Board of
Directors regarding
how
much
to Retain and Reinvest. Cash
flows associated with common
shares will be used to calculate
the
expected
price of share then we
compare it market value of stock.
There are 2 kinds of cash
flow
associated
with the stocks
1.
Dividend you received as shareholder: In
case of common stocks, these
are unpredictable
and
changing as to bond valuation where the
coupon receipts are generally
constant and
regular
in time interval. Therefore we
can use annuity formula.
But when we are
talking
about
common shares dividends are
not fixed. That's make the
valuation of common stock
different
from bond valuation
2.
Capital gains
Preferred
Stock:
This
kind of Equity is rare. Preferred Shareholders get a
preference (or priority) over
the
Common
Shareholders in recovering their money if
the company goes bankrupt.
Although
Preferred
Shareholders are owners, they may
not get voting rights. It is
also known as Hybrid
75

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Equity.
As it is a Mix of Bond and Share. Preferred
Shareholders receive a Fixed
Regular
Dividend
(similar to the Coupon for a
Bondholder).
Share
Price Valuation - Preferred
Stock:
Perpetual
Investment with Fixed Regular
Dividends:
Perpetual
Investment means you are
considering buying this
Stock and keeping it
forever!
PV
= Po* = DIV 1 / r PE
Where
r PE = Minimum Required Rate of
Return on Preferred Stock Equity
for the individual
investor,
PV
= Present Market Value (or
Estimated Present Price) which depends on
DIV 1 = Forecasted Future
Dividend
in the next period (ie. Year
1 and all other years
since DIV 1=DIV2= DIV3=...)
Basically, it
is
a Perpetuity Formula.
Finite
Investment:
Finite
Investment means you plan to
buy this Stock and
then sell it in a few days
or years (n). Formula
similar
to Bond.
PV
= Po* =
DIVt
/ (1+ rPE) t + Pn /
(1+
rPE) n .
t=year.
Sum from t = 1 to n. Pn = Final
Expected Selling Price
PV
(Share Price) = Dividend Value + Capital
Gain /Loss.
The
Dividend Value derived from
Dividend Cash Stream and
Capital Gain /Loss from
Difference
between
Buying & Selling Price.
Example:
Company
ABC Preferred Stock is traded in the
Lahore Stock Exchange and
has a Market Price of
Rs
13. The Company has
fixed the Dividend to be Rs 2 per share.
The Par Value of each
share is
Rs
10. You expect the Price to be Rs 13 after 2
years. As the investor, you expect a
Minimum
Required
Return of 10% because you
can earn that much
from a bank deposit account
almost risk
free.
BUT, Stocks are generally
more risky investments than bank
deposits SO you will only
invest
in
risky stock IF the expected return is
higher than 10% - lets say
15%. Calculate the Fair
(or
Expected)
Price of the Preferred Stock.
NOTE:
We will discuss RISK in detail
later in course
Perpetual
Investment in Preferred Stock
PV
= DIV 1 / r PE = Rs 2 /
15% = 2 / 0.15 = Rs
13.33
The
Fair (or Intrinsic Value) of
the Share to You is Rs 13.33. The
Market Value is Rs 13. So,
the Share
is
worth more to You than its
price in the market. It is undervalued
and you will gain value by
buying it.
Finite
Investment in Preferred Stock:
PV
=
DIVt
/ (1+ rPE) t + Pn /
(1+
rPE) n. n = 2
years
=
2 / (1.15) + 2 / (1.15)2
+ 13 /
(1.15)2
=
Rs
13.08
In
this example, Perpetual Investment in
Preferred Stock is worth more than
Finite Investment in
Preferred
Stock because Present Value
of the Infinite Stream of Rs 2 Dividends
is more than the
Present
Value
of the expected future Selling Price (Rs
13).
Share
Price Valuation - Common
Stock
Finite
(Limited Life) Investment in Common
Stock
It
is more common. Need to account for
Cash Flows from Variable
Dividends and Estimated
Selling
Price (Pn).
Note
that Pn depends on DIVn+1. Price at
any point in time will
always depend on Dividend in the
following
year! Formula is similar to
Bond Valuation
Equation.
Perpetual
Investment in Common Stock:
PV
= DIV1/(1+rCE)
+DIV2/(1+rCE)2
+..+
DIVn/(1+rCE)n
+
Pn/(1+rCE)n
PV
= Po* = Expected or Fair Price = Present
Value of Share, DIV1=
Forecasted Future Dividend
at
end
of Year 1, DIV 2 = Expected Future
Dividend at end of Year 2, ..., Pn = Expected
Future Selling
Price,
rCE = Minimum Required Rate
of Return for Investment in the Common
Stock for you
(the
investor).
Note that Dividends are
uncertain and n = infinity
PV
(Share Price) = Dividend Value + Capital
Gain.
Dividend
Value is derived from
Dividend Cash Stream and
Capital Gain / Loss from
Difference
between
Buying & Selling Price.
Perpetual
Investment in Common Stock:
It
is an idealized Case. The
Final Cash Flow term
(containing Pn) in the equation takes
place at
Year
n = infinity The last term (containing
Pn) has a Present Value almost
equal to Zero because
the
76

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Discount
Factor (1+rE)n in the
denominator becomes very
large when n=infinity. So,
you can ignore
the
Last Cash Flow terms
taking place at Year n.
Simplified
Formula (Pn term
removed from the equation
for large investment
durations i.e. n =
infinity):
PV
= DIV1/ (1+rE) +
DIV2/ (1+rE)
2
+ ...
DIVn/(1+rE)n
=
DIVt
/ (1+ rE) t. t =
year. Sum from t =1 to
n
This
Equation is still impractical
because need to forecast
Dividends for every year
forever!!
Example:
The
Common Stock of Company ABC
is being traded in the Islamabad Stock
Market. Its
Market
Price is Rs.13. You study Company
ABC's Annual Report, Balance
Sheet, Income Statement,
and
Cash Flow Statement and you
forecast the future Dividends to be Rs 2
in the first year and Rs 4 in
the
second year. You forecast the
Market Price to be Rs 13 after 2 years.
The Par Value of each
share is
Rs
10. The Risk Free
Return is 10% pa. Your
expected Minimum Required Return
from the high-risk
Common
Stock of ABC is 20%.
Calculate
the Fair (or Expected) Price of the
Common Stock
Common
Stock Valuation (Risky
Investment: rCE=
20%)
1st year will be Rs.2 and
dividend in 2nd
year
will be Rs.4 assume risk
free rate of return is 10%
and high
rate
of return to be required is 20%again
this 20% is higher than
10% in a country .and this
20%
minimum
required rate of return is higher
than the preferred stock required by
that company is
15
% .this is because common stock is considered more
risky than preferred stock and
bank deposit in a
country
.let's calculate the value of common stock
for company ABC we will use
our old present
value
formula
for finite investment
:
PV=2/12+4/(1.2)2+1.3/(1.2)2
Finite
Investment for 2 Years: PV =
2/1.2
+ 4 /
(1.2)2
+ 13 /
(1.2)2
= Rs
13.47
This
is estimated price for
2nd year investment based on
forecasted dividend let's
see the long term
investment
use present value formula
about which we talked
earlier on
Perpetual
Investment: PV =??
We
can not determine it because
we don't have Dividend forecast
data for every year
forever!! We need
to
use Models for approximating
future Dividends Cash Flow
Stream:
Zero
Growth Model
Constant
Growth Model
We
will discuss about these in
the next lecture.
77
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Corporate Financing & Capital Structure,
- OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, FINANCIAL ASSETS AND FINANCIAL MARKETS:Real Assets, Bond
- ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Basic Financial Statements, Profit & Loss account or Income Statement
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Discounting & Net Present Value (NPV), Interest Theory
- FINANCIAL FORECASTING AND FINANCIAL PLANNING:Planning Documents, Drawback of Percent of Sales Method
- PRESENT VALUE AND DISCOUNTING:Interest Rates for Discounting Calculations
- DISCOUNTING CASH FLOW ANALYSIS, ANNUITIES AND PERPETUITIES:Multiple Compounding
- CAPITAL BUDGETING AND CAPITAL BUDGETING TECHNIQUES:Techniques of capital budgeting, Pay back period
- NET PRESENT VALUE (NPV) AND INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR):RANKING TWO DIFFERENT INVESTMENTS
- PROJECT CASH FLOWS, PROJECT TIMING, COMPARING PROJECTS, AND MODIFIED INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (MIRR)
- SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING:SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING, SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING
- CAPITAL RATIONING AND INTERPRETATION OF IRR AND NPV WITH LIMITED CAPITAL.:Types of Problems in Capital Rationing
- BONDS AND CLASSIFICATION OF BONDS:Textile Weaving Factory Case Study, Characteristics of bonds, Convertible Bonds
- BONDS’ VALUATION:Long Bond - Risk Theory, Bond Portfolio Theory, Interest Rate Tradeoff
- BONDS VALUATION AND YIELD ON BONDS:Present Value formula for the bond
- INTRODUCTION TO STOCKS AND STOCK VALUATION:Share Concept, Finite Investment
- COMMON STOCK PRICING AND DIVIDEND GROWTH MODELS:Preferred Stock, Perpetual Investment
- COMMON STOCKS – RATE OF RETURN AND EPS PRICING MODEL:Earnings per Share (EPS) Pricing Model
- INTRODUCTION TO RISK, RISK AND RETURN FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT:Diversifiable Risk, Diversification
- RISK FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT, PROBABILITY GRAPHS AND COEFFICIENT OF VARIATION
- 2- STOCK PORTFOLIO THEORY, RISK AND EXPECTED RETURN:Diversification, Definition of Terms
- PORTFOLIO RISK ANALYSIS AND EFFICIENT PORTFOLIO MAPS
- EFFICIENT PORTFOLIOS, MARKET RISK AND CAPITAL MARKET LINE (CML):Market Risk & Portfolio Theory
- STOCK BETA, PORTFOLIO BETA AND INTRODUCTION TO SECURITY MARKET LINE:MARKET, Calculating Portfolio Beta
- STOCK BETAS &RISK, SML& RETURN AND STOCK PRICES IN EFFICIENT MARKS:Interpretation of Result
- SML GRAPH AND CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL:NPV Calculations & Capital Budgeting
- RISK AND PORTFOLIO THEORY, CAPM, CRITICISM OF CAPM AND APPLICATION OF RISK THEORY:Think Out of the Box
- INTRODUCTION TO DEBT, EFFICIENT MARKETS AND COST OF CAPITAL:Real Assets Markets, Debt vs. Equity
- WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL (WACC):Summary of Formulas
- BUSINESS RISK FACED BY FIRM, OPERATING LEVERAGE, BREAK EVEN POINT& RETURN ON EQUITY
- OPERATING LEVERAGE, FINANCIAL LEVERAGE, ROE, BREAK EVEN POINT AND BUSINESS RISK
- FINANCIAL LEVERAGE AND CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Capital Structure Theory
- MODIFICATIONS IN MILLAR MODIGLIANI CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORY:Modified MM - With Bankruptcy Cost
- APPLICATION OF MILLER MODIGLIANI AND OTHER CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES:Problem of the theory
- NET INCOME AND TAX SHIELD APPROACHES TO WACC:Traditionalists -Real Markets Example
- MANAGEMENT OF CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Practical Capital Structure Management
- DIVIDEND PAYOUT:Other Factors Affecting Dividend Policy, Residual Dividend Model
- APPLICATION OF RESIDUAL DIVIDEND MODEL:Dividend Payout Procedure, Dividend Schemes for Optimizing Share Price
- WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT:Impact of working capital on Firm Value, Monthly Cash Budget
- CASH MANAGEMENT AND WORKING CAPITAL FINANCING:Inventory Management, Accounts Receivables Management:
- SHORT TERM FINANCING, LONG TERM FINANCING AND LEASE FINANCING:
- LEASE FINANCING AND TYPES OF LEASE FINANCING:Sale & Lease-Back, Lease Analyses & Calculations
- MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS:Leveraged Buy-Outs (LBO’s), Mergers - Good or Bad?
- INTERNATIONAL FINANCE (MULTINATIONAL FINANCE):Major Issues Faced by Multinationals
- FINAL REVIEW OF ENTIRE COURSE ON FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Financial Statements and Ratios