 |
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Corporate Financing & Capital Structure, |
| OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, FINANCIAL ASSETS AND FINANCIAL MARKETS:Real Assets, Bond >> |

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Lesson
01
INTRODUCTION
TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Learning
objectives:
The
purpose of this lecture is to
provide you with an overview
of financial management.
After
finishing
this lecture, you would be
able to have a better understanding of
the following.
�
Definition
of financial management
�
Significance
of financial management for
non-finance students and
professionals
�
Important
concepts and areas in financial
management
�
The
position of financial managers in
organizational hierarchy and
their respective work
domains.
�
Different
business legal entities,
their advantages and
limitations.
�
The
external and internal business
environments and their relevance to
financial management.
�
Different
types of financial and real
assets markets.
What
is FM?
FM
is the management of financial resources
how to best find and
use investments and
financing
opportunities in an ever-changing and
increasingly complex
environment.
Why
should CS majors study
FM?
First
of all, financial management is a
core life skill; almost
every one needs to understand
some
concepts
of finance to manage his/her
business & personal finances.
It
is generally and quite rightfully said,
"Money makes the world go
round". Finance is like a
life-blood
for a company. Even the
best of the companies and
CEOs go out of the business
because of
poor
financial management
policies.
Management
Information Systems (MIS) and
Information Technology (IT)
are just a part of
the
overall
corporate strategy which runs on finances, the
major resource. So the computer
sciences
professionals
need to have an understanding of the
financial concepts to understand and
contribute to
the
overall corporate strategy.
Financial
Engineering is an upcoming field
that requires people with
CS, math/science, and
finance
background. Financial engineering is the
application of engineering methods to
finance. One
important
area of study is the design, analysis,
and construction of financial
contracts to meet the
needs
of
enterprises. This field is
experiencing an increased demand
for professionals, especially those
who
are
trained in both the underlying
mathematics/computer technologies and
finance.
Definitions
Finance:
Finance
is the science of managing financial
resources in an optimal pattern
i.e. the best use of
available
financial sources. Finance consists of
three interrelated areas:
1)
Money & Capital markets, which
deals with securities markets &
financial institutions.
2)
Investments, which focuses on the decisions of
both individual and
institutional investors as
they
choose assets for their
investment portfolios.
3)
Financial Management, or business
finance which involves the actual
management of firms.
Major
Areas & Concepts of Financial
Management
Following
are some of the important
areas and concepts of
financial management, which
would
be
discussed in detail in the lectures to
come.
Analysis
of Financial Statements:
Analysis
of financial statement is one of the
most common techniques of financial analysis,
in
which
the financial performance and financial
health of a company are analyzed based on
its past
performance.`
The
following financial statements
are used in the analysis
process.
�
Profit
& Loss Statement or Income
Statement
Income
statement reflects the operating
efficiency or profitability of a company as a
result
of
its operations along with the net
profit available to the shareholders
for a given year
(usually
one accounting period). This
statement provides the analyst
with some insight
into
the
financial performance of the
company.
�
Balance
Sheet
Balance
Sheet is a snap-shot of an organization's
financial health at a particular
time. It
shows
what assets are owned by the
business and the sources of
acquiring these
assets.
1

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
�
Statement
of Shareholders' equity
Statement
of shareholders' equity provides the
share of the owners in the
business.
�
Statement
of Cash Flows
Statement
of cash flows explicitly reflects the
cash movement (inflows and
outflows)
during
the operations in an accounting
period.
Taken
together, these statements
give an accounting picture of the
firm's operations and
financial
position. Financial statements
report what has actually
happened to the assets, earnings,
and
dividends over the years.
The analysis of the information contained
in these statements
help
management
of the organization to evaluate the performance
and activities of the concern; it
also
helps
the investors and creditors to have an idea of the
profitability potential and
creditworthiness of
the
business.
Investment
Decisions & Capital
Budgeting:
Investment
decisions are the most critical as
they usually involve huge
sums of money and
these
decisions are likely to bring
prosperity or doom to a business. A
company's future
income
depends
on how much investment is
made, in what type of
assets, and how these
assets add to the
overall
value of the company.
Capital
budgeting is a term strictly related to
investment in fixed assets;
here, the term
capital
refers to the fixed assets that
are used in production,
while budget is a plan which
details
projected
cash inflows and outflows
over some future period.
The following concepts
and
techniques
are employed while analyzing
investment decisions.
Interest
rate formulas
o
Time
Value of Money
o
Discounted
Cash Flows
o
Net
Present Value
o
Internal
Rate of Return
o
Risk
& Return:
Investors,
individual or institutional, invest
their money with the expectations of
earning a
return
on their investment. While investors
wish and attempt to earn maximum
return, they are
constrained
by risk. How the risks and returns
are related and how do
investors make a choice of
their
portfolios is important for
investment decision making.
Following concepts and theories
would
be
discussed while discussing the
risk-return choices of the
investor:
Uncertainty
o
Risk
o
Portfolio
Theory
o
Capital
Asset Pricing Model
o
Corporate
Financing & Capital
Structure:
When
a firm plans to expand, it needs
capital or funds. Acquisition of
funds is considered to
be
a primary responsibility of a finance
department in an organization. There are
numerous ways to
acquire
funds, i.e., finances can be
raised in the form of debt or
equity. The proportion of
debt and
equity
constitutes the capital structure of the firm.
Financial experts attempt to find a
combination of
debt
and equity that could
increase the overall value of the
company, i.e., they try to
find the
optimal
capital structure. The following
concepts would be used to understand
how an optimal
capital
structure could be attained.
Cost
of Capital
o
Leverage
o
Dividend
Policy
o
Debt
Instruments
o
Valuation:
Asset
or company valuation is important not
only for financial managers,
but also for
creditors
and investors. It is important to know the
value of the company or its assets to
make
2
Financial
Management MGT201
VU
important
financing and investment
choices. Different valuation techniques
and factors that
influence
the value of a company or its financial
instruments would be discussed in this
section.
Share
o
Bond
o
Option
o
Corporate
o
Working
Capital & Inventory
Management:
Working
capital and inventory management pertains
to the effective management of
current
assets.
As we will see, an optimal and
effective utilization of working
capital and inventory
increases
the operating efficiency of the
firm.
International
Finance & Foreign Exchange:
With
the increasing importance of international trade and
global markets, the role
of
international
finance has increased
manifold. In a global environment, the
finance managers have
more
choices pertaining to investing
and financing than ever
before. However, it is important
to
understand
the implications of working in a global
environment, since fluctuations in the
currency
rates
can convert a good financing
or investment decision into a
bad one. This section of the
course
would
discuss the international financial
environment and the financial
implications of working in a
global
environment.
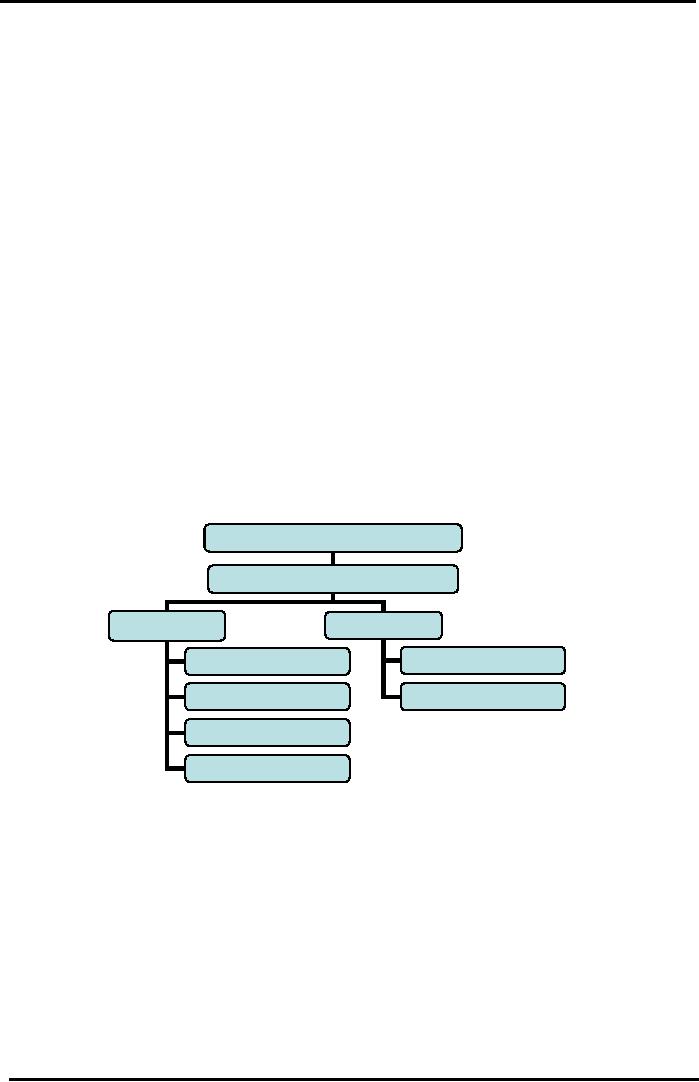
Organizational
Structure
(Who
does the FM
work?)
Chief
Executive Officer
(CEO)
Chief
Financial Officer
(CFO)
Treasurer
Controller
Accounts
Cash
& Investment
Capital
Budgeting
Audit
Capital
Structure
Inventory
Business
Legal Entities
�
Sole
Proprietorship :
It
is an unincorporated business owned by
one individual. Going into a
business as a sole
proprietor
is simple one merely has to
begin business operations. Proprietorship
consists of 80%of
the
total number of businesses
worldwide.
Advantages:
i.
It
is easily & inexpensively
formed.
ii.
It
is subject to few government
regulations.
iii.
The
business pays no corporate income tax;
only personal income tax is paid by
the
proprietor.
3

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Limitations:
i.
It
is difficult for a proprietorship to
obtain large sums of
capital.
ii.
The
proprietor has unlimited personal
liability for the business
debts, which can
result
in losses hat exceed the
money invested by him in the
business.
iii.
The
life of the business
organized as proprietorship is limited to
the life of the
individual
who created it.
Partnership:
A
partnership exists whenever two or more
persons associate to conduct a
non-corporate
business.
It could be registered or unregistered.
Advantages:
i.
Low
cost involved
ii.
Ease
of formation.
Limitations:
i.
Unlimited
Liability.
ii.
Limited
life of the organization.
iii.
Difficulty
of transferring ownership.
iv.
Difficulty
of raising large amounts of
capital.
Corporation:
A
corporation is a limited company and a
separate legal entity registered by the
government. It
is
separate & distinct from
its owners & managers. It Can be
Private Limited (Pvt. Ltd.)
or Public
Limited
(which may be listed on
Stock Exchange). The businesses in the
form of corporations
control
80%
of global sales of products and
services.
Advantages:
i-
Unlimited life:
A
corporation can continue even
after the death of its original
owners.
ii-
Easy transferability of ownership
interest:
Ownership
interests can be divided
into shares of stock, which in
turn can be transferred
far
more
easily than can
proprietorship & partnership
interests.
iii-
Limited Liability:
The
liability of the shareholders is limited
up to the extent of nominal value of
shares held by
them.
Creditors and banks cannot confiscate personal
properties of director & shareholders
in case of its
bankruptcy.
Limitations:
i.
Double
Taxation:
Corporate
earnings may be subject to double
taxation the earnings of the
corporation
are taxed at corporate level, and
then any earnings paid out
as
dividends
are taxed again as income to
the stockholders.
ii.
Legal
Formalities:
Setting
up a corporation, and filing many
official documents, is more
complex
and
time consuming than for a
proprietor ship or a
partnership
�
Hybrids
(Mixed):
Hybrid
organizations are specialized types of partnerships,
which combine the
limited
liability advantage of a corporation with
the tax advantages of a
partnership.
S-Type
Corporation:
S-
Type corporations are
Limited Liability Corporations
without double
taxation.
In a regular corporation, the company
itself is taxed on
business
profits.
In addition, the owners pay individual
income tax on money that
they
draw
from the corporation as
salaries, bonuses, or dividends. In
contrast, in an
4
Financial
Management MGT201
VU
S
corporation, all business
profits "pass through" to the owners,
who report
them
on their personal tax returns (as in
sole proprietorships, partnerships,
and
Limited
Liability Companies). The S corporation
itself does not pay
any
income
tax, although a co-owned S
corporation must file an
informational tax
return
like a partnership or Limited
Liability Companies to tell the
tax
authorities
what each shareholder's
portion of the corporate income
is.
LLP:
Limited
Liability Partnership (LLP) is also a
form of partnership with
allows
limited
liability to the owners and avoids double
taxation. These
organizations
are
similar in many ways to the S
Corporations; however, LLPs
offer more
flexibility
and benefits to the owners.
PC:
Personal
Corporations (PC) or Professional Corporations
are generally formed
by
professionals to protect them against litigations.
Professionals like doctors,
lawyers
and accountants prefer to register
their business as Professional
Corporations.
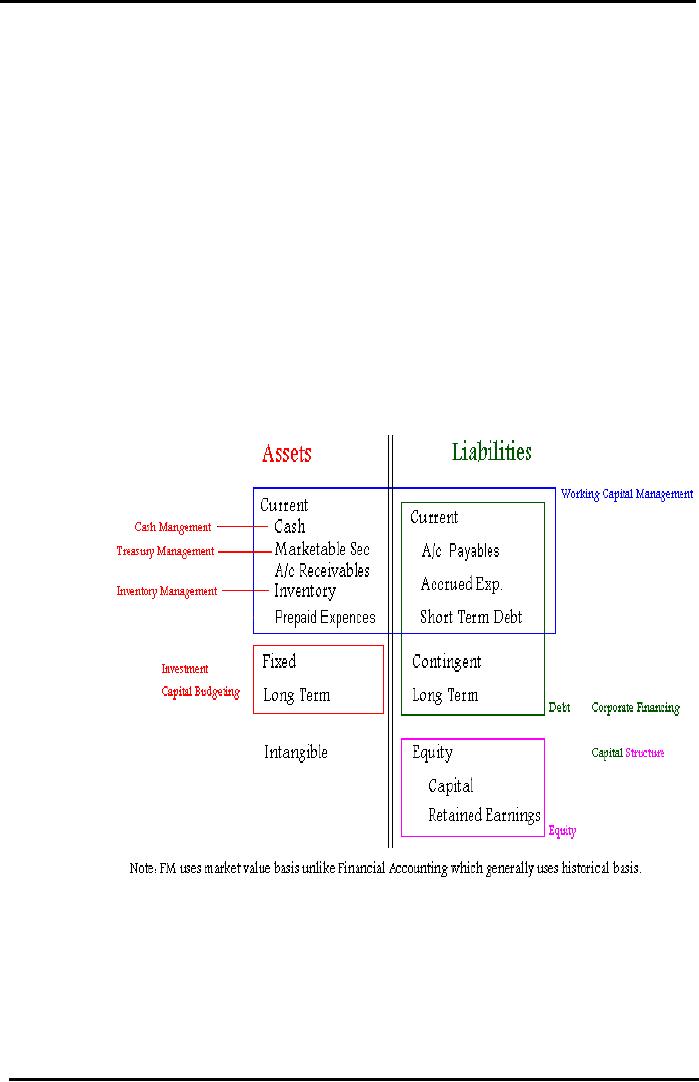
Balance
Sheet An FM Perspective
5
Financial
Management MGT201
VU
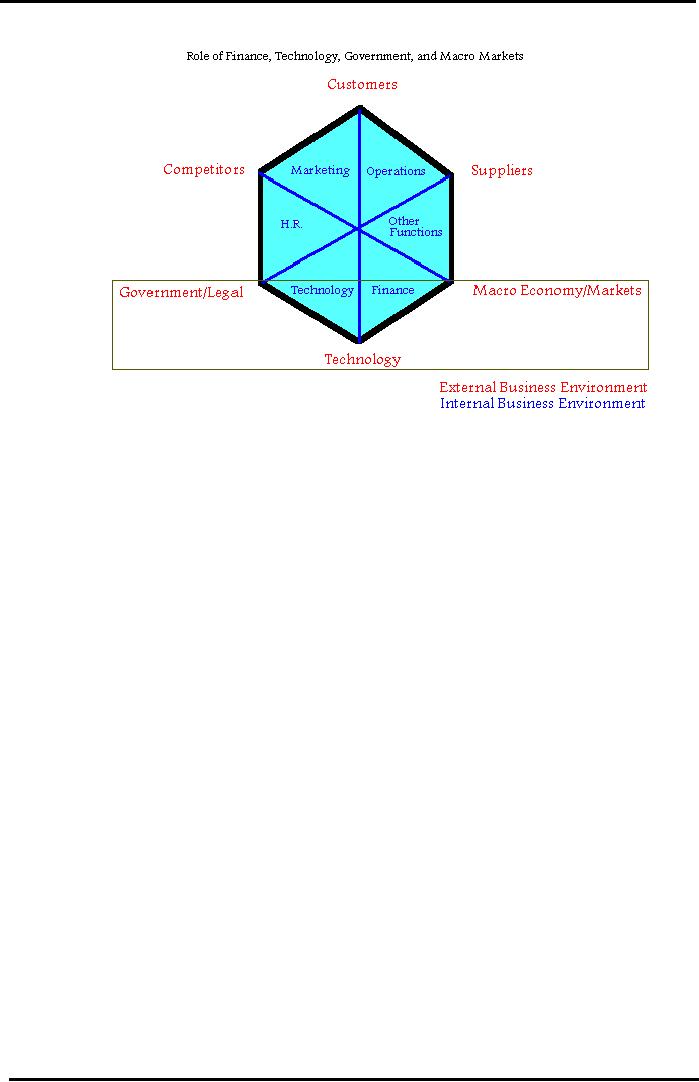
Internal
and External Business
Environment
Internal
Business Environment:
Internal
environment of business normally
consists of the following.
i.
Finance
ii.
Marketing
iii.
Human
Resources
iv.
Operations
(Production, Manufacturing)
v.
Technology
vi.
Other
Functions (Logistics,
Communications)
External
Business Environment:
The
following business environment factors
outside an organization have a profound
effect on
the
functions and operations of an
organization.
i.
Customers
ii.
Suppliers
iii.
Competitors
iv.
Government/Legal
Agencies & Regulations
v.
Macro
Economy/Markets:
vi.
Technological
Revolution
An
analysis which is used in a business is
called SWOT
Analysis.
SWOT is an acronym where
S
stands
for Strengths
W
stands
for Weaknesses
O
stands
for Opportunities
T
stands
for Threats
Strengths
and weaknesses are within an
organization, i.e., they
pertain to the internal
environment
of the organization.
Opportunities
and threats, on the other hand, pertain
to the external environment, i.e.,
outside
the
organization.
6

Financial
Management MGT201
VU
Financial
Markets
�
Capital
Markets:
These
are the markets for the
long term debt & corporate
stocks.
Stock
Exchange:
A
stock exchange is a place where the listed
shares, Term finance
certificates (TFC)
and
national investment trust units
(NIT) are exchanged and traded between buyers
and
sellers.
Long
term bonds:
Long
term government & corporate bonds are
also traded in capital markets.
�
Money
Markets
Money
market generally is a market where there
is buying and selling of short term
liquid
debt
instruments. (Short term means one year
or less). Liquid means something
which is
easily
en-cashable; an instrument that
can be easily exchanged for
cash. Following
financial
instruments
are traded in money markets.
Short
term Bonds
Government
of Pakistan: Federal Investment Bonds (FIB),
Treasury-Bills (T-
o
Bills)
Private
Sector: Corporate Bonds,
Debentures
o
Call
Money, Inter-bank short-term and
overnight lending &
borrowing
Loans,
Leases, Insurance policies, Certificate
of Deposits (CD's)
Badlah
(money lending against shares), Road-side
money lenders
�
Real
Assets or Physical Asset
Markets
Following
are the active markets of
real and physical assets in
Pakistan
Cotton
Exchange, Gold Market, Kapra
Market
o
Property
(land, house, apartment,
warehouse)
o
Computer
hardware, Used Cars, Wheat, Sugar,
Vegetables, etc.
o
7
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Corporate Financing & Capital Structure,
- OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, FINANCIAL ASSETS AND FINANCIAL MARKETS:Real Assets, Bond
- ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Basic Financial Statements, Profit & Loss account or Income Statement
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY:Discounting & Net Present Value (NPV), Interest Theory
- FINANCIAL FORECASTING AND FINANCIAL PLANNING:Planning Documents, Drawback of Percent of Sales Method
- PRESENT VALUE AND DISCOUNTING:Interest Rates for Discounting Calculations
- DISCOUNTING CASH FLOW ANALYSIS, ANNUITIES AND PERPETUITIES:Multiple Compounding
- CAPITAL BUDGETING AND CAPITAL BUDGETING TECHNIQUES:Techniques of capital budgeting, Pay back period
- NET PRESENT VALUE (NPV) AND INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR):RANKING TWO DIFFERENT INVESTMENTS
- PROJECT CASH FLOWS, PROJECT TIMING, COMPARING PROJECTS, AND MODIFIED INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (MIRR)
- SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING:SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING, SOME SPECIAL AREAS OF CAPITAL BUDGETING
- CAPITAL RATIONING AND INTERPRETATION OF IRR AND NPV WITH LIMITED CAPITAL.:Types of Problems in Capital Rationing
- BONDS AND CLASSIFICATION OF BONDS:Textile Weaving Factory Case Study, Characteristics of bonds, Convertible Bonds
- BONDS’ VALUATION:Long Bond - Risk Theory, Bond Portfolio Theory, Interest Rate Tradeoff
- BONDS VALUATION AND YIELD ON BONDS:Present Value formula for the bond
- INTRODUCTION TO STOCKS AND STOCK VALUATION:Share Concept, Finite Investment
- COMMON STOCK PRICING AND DIVIDEND GROWTH MODELS:Preferred Stock, Perpetual Investment
- COMMON STOCKS – RATE OF RETURN AND EPS PRICING MODEL:Earnings per Share (EPS) Pricing Model
- INTRODUCTION TO RISK, RISK AND RETURN FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT:Diversifiable Risk, Diversification
- RISK FOR A SINGLE STOCK INVESTMENT, PROBABILITY GRAPHS AND COEFFICIENT OF VARIATION
- 2- STOCK PORTFOLIO THEORY, RISK AND EXPECTED RETURN:Diversification, Definition of Terms
- PORTFOLIO RISK ANALYSIS AND EFFICIENT PORTFOLIO MAPS
- EFFICIENT PORTFOLIOS, MARKET RISK AND CAPITAL MARKET LINE (CML):Market Risk & Portfolio Theory
- STOCK BETA, PORTFOLIO BETA AND INTRODUCTION TO SECURITY MARKET LINE:MARKET, Calculating Portfolio Beta
- STOCK BETAS &RISK, SML& RETURN AND STOCK PRICES IN EFFICIENT MARKS:Interpretation of Result
- SML GRAPH AND CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL:NPV Calculations & Capital Budgeting
- RISK AND PORTFOLIO THEORY, CAPM, CRITICISM OF CAPM AND APPLICATION OF RISK THEORY:Think Out of the Box
- INTRODUCTION TO DEBT, EFFICIENT MARKETS AND COST OF CAPITAL:Real Assets Markets, Debt vs. Equity
- WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL (WACC):Summary of Formulas
- BUSINESS RISK FACED BY FIRM, OPERATING LEVERAGE, BREAK EVEN POINT& RETURN ON EQUITY
- OPERATING LEVERAGE, FINANCIAL LEVERAGE, ROE, BREAK EVEN POINT AND BUSINESS RISK
- FINANCIAL LEVERAGE AND CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Capital Structure Theory
- MODIFICATIONS IN MILLAR MODIGLIANI CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORY:Modified MM - With Bankruptcy Cost
- APPLICATION OF MILLER MODIGLIANI AND OTHER CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES:Problem of the theory
- NET INCOME AND TAX SHIELD APPROACHES TO WACC:Traditionalists -Real Markets Example
- MANAGEMENT OF CAPITAL STRUCTURE:Practical Capital Structure Management
- DIVIDEND PAYOUT:Other Factors Affecting Dividend Policy, Residual Dividend Model
- APPLICATION OF RESIDUAL DIVIDEND MODEL:Dividend Payout Procedure, Dividend Schemes for Optimizing Share Price
- WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT:Impact of working capital on Firm Value, Monthly Cash Budget
- CASH MANAGEMENT AND WORKING CAPITAL FINANCING:Inventory Management, Accounts Receivables Management:
- SHORT TERM FINANCING, LONG TERM FINANCING AND LEASE FINANCING:
- LEASE FINANCING AND TYPES OF LEASE FINANCING:Sale & Lease-Back, Lease Analyses & Calculations
- MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS:Leveraged Buy-Outs (LBO’s), Mergers - Good or Bad?
- INTERNATIONAL FINANCE (MULTINATIONAL FINANCE):Major Issues Faced by Multinationals
- FINAL REVIEW OF ENTIRE COURSE ON FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:Financial Statements and Ratios