 |
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
LESSON#
7
MATERIAL
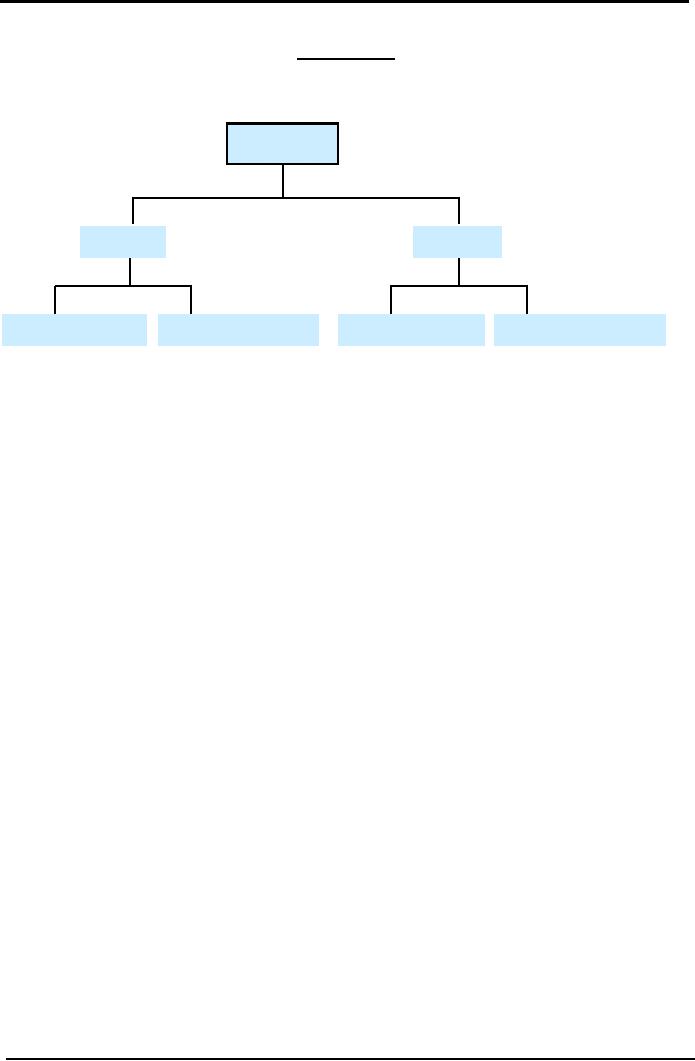
Material
means the inventory that is
used as input for production
of finished output or rendering
of
services or for office use
and packaging.
Categories
Material
Supplies
Direct
Material
Indirect
Material
Office
Supplies
Shipping
Supplies
Categories
of Material & Supplies
1.
Direct Material
2.
Indirect Material
3.
Office Supplies
4.
Shipping Supplies
Direct
Material costs
are those cost of material that
are traceable in full in the
cost of a
product
or services. For example:
cost of wood in production of
table.
Indirect
Material/Factory Supplies is the
cost that is incurred in
producing product but
which
can not traced in full in
the cost unit. For
example: polishing material in production
of
furniture.
Office
Supplies: This
is the cost of those items/goods
which are used in the
offices for
administration
purposes. For example: stationery
items.
Shipping
Supplies: This
is the cost of the material
which is used in packaging of
the finished
product.
Accrual
Concept/Matching Concept
All
of the cost of material and
supplies purchased is not
charged to the production.
Only that
much
cost is charged which
matches the revenue earned in
the period. This concept of
accounting
is
known as accrual concept.
Following
the accrual concept will
leave a stock of unused/unconsumed
supplies and unsold
finished
in the stores or
warehouses.
Inventory
Inventory
is an asset that is
held:
�
as material
and supplies; or
�
in
the production process as
semi finished goods;
or
�
as
finished goods.
Inventory
Maintenance Systems
1.
Periodic Inventory System:
2.
Perpetual Inventory System: `
40

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Perpetual
Inventory System
Under
this system, a complete and
continuous record of movement of each
inventory item is
maintained.
Perpetual records are useful
in preparing monthly quarterly or other
financial
statement.
Record used is normally a "store
ledger card" specifying quantity
wise receipt, issue
and
balance
together with values in
chronological sequence.
Advantages:
1)
It
protects materials from theft or
loss.
2)
It
helps in reducing wastages and
spoilages.
3)
Inventory
levels can be fixed and
observed.
4)
It
serves as a moral
check.
5)
It
helps in highlighting slow
moving and obsolete
inventory.
6)
It
helps in frequent physical
counting.
Disadvantages:
1)
It
is very complex.
2)
It
is costly.
3)
Complex
calculations are required.
4)
Sufficient
technical knowledge is required.
Periodic
inventory System or Physical
system
Under
this system, the value of
inventory is determined at the end of
the year through a
physical
count
of inventory in store/warehouse. It does
not maintain a continuous record of
movement of
each
inventory item.
Advantages
1)
It
is very simple.
2)
It
is very cheap.
3)
No
calculations required.
4)
No
technical knowledge required.
Disadvantages
1)
It
does not protect materials
from theft or loss.
2)
No
help in reducing wastages and
spoilages.
3)
Inventory
levels cannot be fixed and
observed.
4)
It
does not help in
highlighting slow moving and
obsolete inventory.
5)
No
help in frequent physical
counting.
Inventory
costing methods
1.
First In First Out
(FIFO)
2.
Last In First Out (LIFO)
3.
Weighted Average (W.Avg)
First
in First out
(FIFO):
This
method assumes that the
goods firstly received in
the stores or produced firstly
are the
first
ones to be delivered to the
requisitioning department.
For
example a bakery produces
200 loaves of bread on
1st of January at a cost of
Re.1 each, and
200
more on 2nd. at Rs. 1.25 each.
FIFO states that if the
bakery sold 100 loaves on 3rd.,
the
cost of consumption is Re.1
per loaf (recorded on the
income statement) because that
was
the
cost of each of the first
loaves in inventory. The 100
at Re. 1 and 200at Rs.1.25
loaves
would
be allocated to ending inventory (appears
on the balance
sheet).
41

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Features
�
FIFO
gives us a better indication of
the value of ending inventory (on
the balance
sheet)
�
It
also increases net income
because inventory that might
be several years old is used
to
value
the cost of goods
sold.
�
Increasing
net income sounds good, but
do remember that it also has
the potential to
increase
the amount of taxes that a
company must pay.
Advantages:
1)
It
is the method that most
people feel logically as correct
since it assumes that the
stock
issues
are made in the order in
which they are
received.
2)
Issue
prices are based on the
prices actually paid for
the stock.
3)
It
is an acceptable method for
the purposes of financial
reporting.
Disadvantages:
1)
FIFO
complicates stock records as issues
have to be analyzed by
delivery.
2)
Issues
from stock are not recorded
at the most recent prices
paid. This could
influence
costing
of work done and may
ultimately affect the
revenue.
Last
In First Out
(LIFO):
This
method assumes that the
goods received most recently
in the stores or produced
recently
are
the first ones to be delivered to
the requisitioning department.
The
older inventory, therefore,
is left over at
the end of the
accounting
period.
For
the 200 loaves sold on
3rd.
January, the same bakery
would assign Rs. 1.25
per loaf to cost
of
consumption while the remaining
200 at Re.1 and 100 at
Rs.1.25 loaves would be used
to
calculate
the value of inventory at the
end of the period.
Features
�
LIFO is
not a good indicator of ending
inventory value because the
left over inventory
might
be extremely old and,
perhaps, obsolete.
�
LIFO results
in a valuation that is much
lower than today's prices.
LIFO results in
lower
net income because cost of
goods sold is higher.
Weighted
Average Method (W.Avg):
This
method recalculates the
average cost of inventory
held each time a new
delivery is
received.
Issues are then recorded at
this weighted average
price.
It
takes the weighted average of
all units available for
sale during the accounting
period. The
formula
to calculate the weighted average
rate is:
Total
Cost = weighted average rate per
unit
Total
Units
Weighted
Average cost is used to determine
the value of cost of consumption
and ending
inventory.
In
our bakery example, the
weighted average cost for
inventory would be Rs. 1.125
per unit,
calculated
as [(200
x Rs. 1) + (200 x Rs.
1.25)]
400
Features
�
Weighted
Average cost produces results
that fall somewhere between
FIFO and LIFO.
42

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
PRACTICE
QUESTION
Q.
1
Periodic
System
Date
Units
Total
1
Jan
100
@
10
Rs.
1,000
5
Jan
100
@
11
1,100
10
Jan
150
@
12
1,600
During
the period 300 unit were
sold
Required:
Calculate cost of inventory
under each of the costing
methods.
Solution
Cost
of inventory:
As
per FIFO
50
@ 12
=
600
As
per LIFO
50
@ 10
=
500
As
per W.Avg 50 @ 10.5714 =
529
Q.
2
Perpetual
System
100
units of material "M" costing Rs. 8.00
per unit were in stores on
January 1, 2006.
Following
are
the receipts and issues
during January.
Jan.
1
Received
100
units @ 8.50
Jan.
5
Issued
100
units
Jan.
8
Received
200
units @ Rs. 8.85
Jan.
15
Received
100
units @ Rs. 9.25
Jan
25.
Issued
220
units
Jan.
31
Issued
80
units
Required:
Prepare
Materials Ledger card based
on the above information using
each of the
following
methods:
IFO
Method
F
LIFO
Method
Weighted
Average cost Method
43
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Solution
Materials
Ledger Card
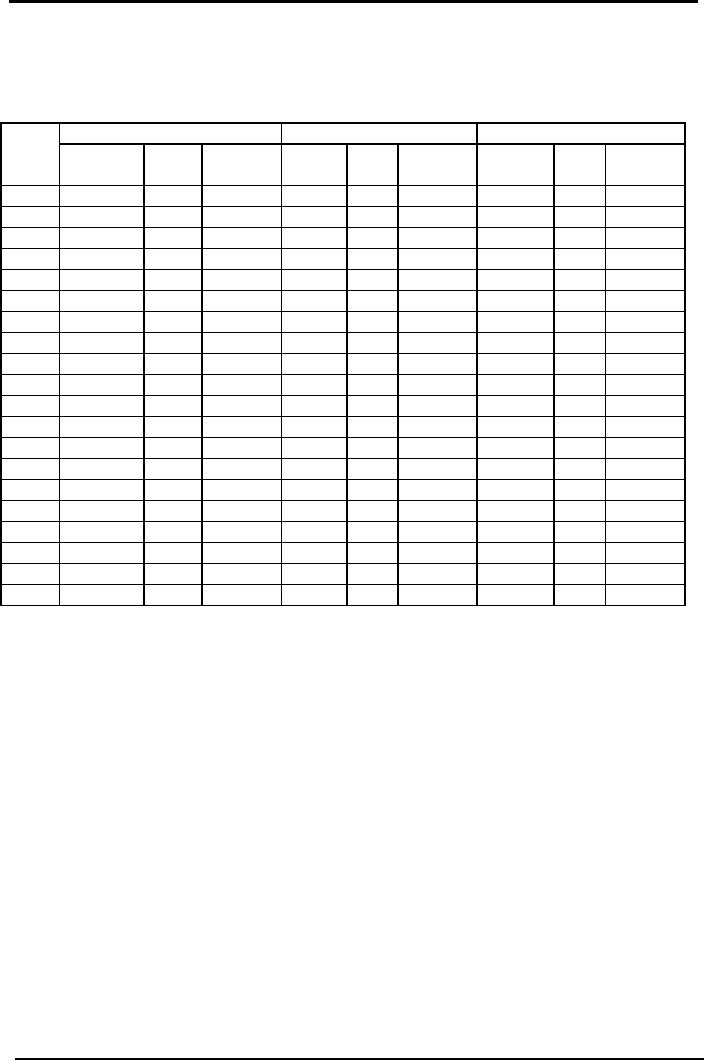
FIFO
Material
M
Received
Issued
Balance
Date
Units
Units
Amount Unit
Unit
Amount Units
Unit
Amount
Cost
Cost
Cost
19xx
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Jan
1
100
8.00
800
Jan
1
100
8.50
850
100
8.00
800
100
8.50
850
Jan
5
100
8.00
800
100
8.50
850
Jan.8
200
8.85
1,770
100
8.50
850
200
8.85
1,770
Jan15
100
9.25
925
100
8.50
850
200
8.85
1,770
100
9.25
925
Jan25
100
8.50
850
80
8.85
708
120
8.85
1062
100
9.25
925
Jan31
80
8.85
708
100
9.25
925
44
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
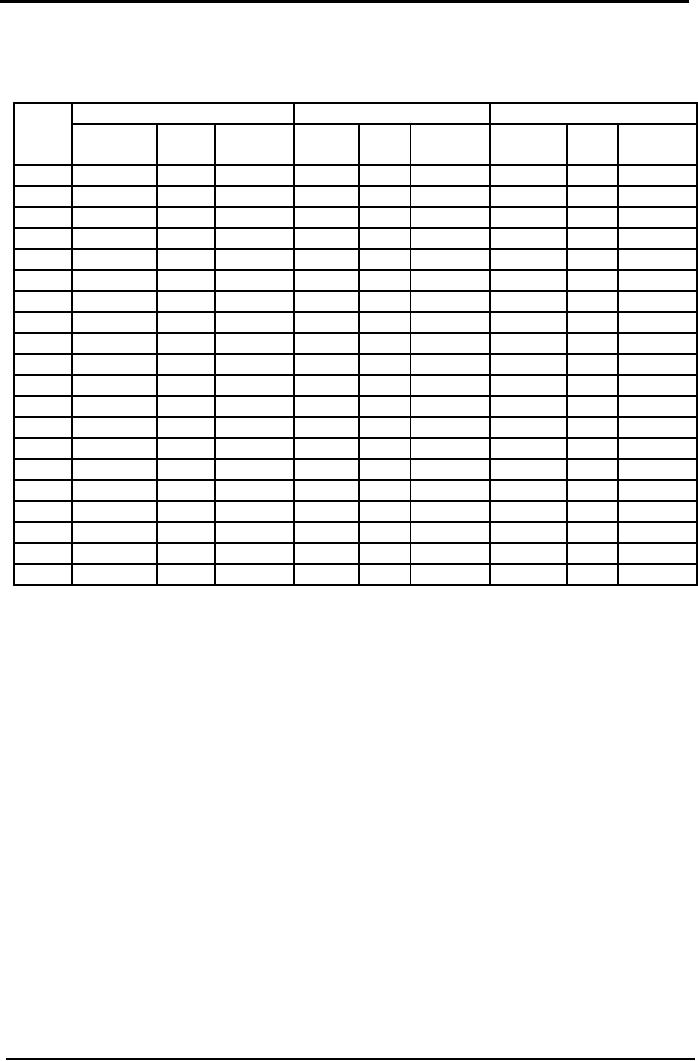
Materials
Ledger Card
FIFO
Material
M
Received
Issued
Balance
Date
Units
Units
Amount Unit
Unit
Amount Units
Unit
Amount
Cost
Cost
Cost
19xx
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Jan
1
100
8.00
800
Jan
1
100
8.50
850
100
8.00
800
100
8.50
850
Jan
5
100
8.50
850
100
8.00
800
Jan.8
200
8.85
1,770
100
8.00
800
200
8.85
1,770
Jan15
100
9.25
925
100
8.00
800
200
8.85
1,770
100
9.25
925
Jan25
100
9.25
925
100
8.00
800
120
8.85
1062
80
8.85
708
Jan31
80
8.85
708
100
8.00
800
45
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
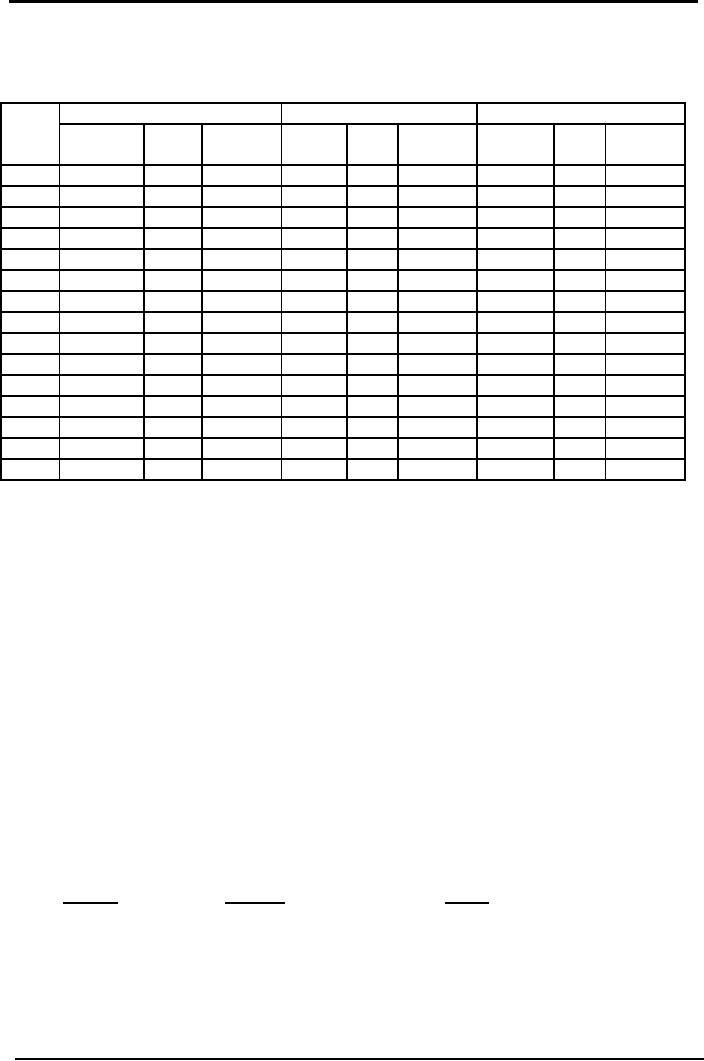
Materials
Ledger Card
Weighted
Average
Material
M
Received
Issued
Balance
Date
Units
Units
Amount Unit
Unit
Amount Units
Unit
Amount
Cost
Cost
Cost
19xx
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Rs.
Jan
1
100
8.00
800
Jan
1
100
8.50
850
200
8.00
1,650
Jan
5
100
8.25
825
100
8.25
825
Jan.8
200
8.85
1,770
300
8.65
2595
Jan15
100
9.25
925
400
8.80
3520
Jan25
220
8.80
1,936
180
8.80
1584
Jan31
80
8.80
704
100
8.80
880
A
comparison, based on above illustration,
of cost of materials issued
and cost of ending
inventory
obtained
under the three methods is
presented below:
FIFO
Average
Cost
LIFO
Cost
of materials issued
Rs.
3,420
Rs.
3,465
Rs.
3,545
Ending
inventory
925
880
800
It
is clear that FIFO gives
the lowest cost of materials
issued and the highest cost
of ending
inventory,
consequently the highest gross
profit. On the other hand
LIFO gives the highest cost
of
issues
and lowest cost ending
inventory, consequently the
lowest gross profit.
Whereas, the cost
and
as a result the gross
profit, calculated under
average cost method are in
between FIFO and
LIFO.
The illustration demonstrates a period of
rising prices. In a period of falling
prices,
naturally,
the results would have been
reverse.
ASSIGNMENT
QUESTIONS
Q.
1
Jamshed
& company is a manufacturing concern.
Following is the receipts &
issues record for the
month
of January, 2006
Receipts
Issues
Date
Jan
1
Opening
Balance 50 @ 40
Jan
8
200
units @ Rs. 50/unit
Jan
11
60
units
Jan
13
150
units @ Rs. 60/unit
Jan
18
100
units @ Rs. 75/unit
Jan
20
150
units
46
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Prepare
Inventory sheets
under:
FIFO
Method
LIFO
Method
Weighted
Average cost Method
Q.
2
Assuming
nil opening stocks prepare
store ledger cards and
calculate the value of the
closing
stock
from the data provided
below using each of the
following methods:
�
FIFO
�
LIFO
�
W.Avg
Receipts
Date
Units
Rate
October
1
100
12.50
October
8
85
15.00
October
16
95
11.95
October
20
115
13.00
Issues
October
55
October
65
October
50
October
25
October
115
Q.
3
Following
transaction appeared in the books of
accounts of a trading concern.
PURCHASE
Month
Quantity
(Units)
Cost
per unit (Rs)
Jan
100
41
Feb
200
50
April
400
51.87
SALES
Month
Quantity
(Units)
Cost
per unit (Rs)
March
250
64
May
350
70
June
100
There
was an opening balance of 100
units for Rs 3,900.
From
the information given above,
for the six month ended
June 30, show the
store ledger
records
including the closing stock balance
and stock evaluation by using weighted
average and
FIFO
methods of costing under periodic and perpetual
system of accounting.
47

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Q.
4
Receipts
1-12-1993
80kg @ Rs. 5 per kg
10-12-1993
80 kg @ Rs. 6 per kg
Issued
2-12-1993
60 kg
11-12-1993
60 kg
What
is the value of 40 units of closing stock
under each of the methods?
Using the
periodic
and perpetual accounting
system.
FIFO
Rs.__________
LIFO
Rs.__________
Weighted
average price
Rs.__________
MULTIPLE
CHOICE QUESTIONS
1)
In most of the industries, the
most important element of cost
is
a)
Material
b)
Labor
c)
Overheads
d)
Prime cost
2)
According to which of the
following method of pricing,
issue; are close to current
economic
values?
a)
Last in first out
price
b)
First in first out
price
c)
Highest in first out
price
d)
Weighted average price
3)
In which of the following of
pricing, costs lag behind
the current economic
values?
a)
Last in first out
price
b)
First in first out
price
c)
Replacement price
d)
Weighted average price
4)
Which of the following items
of cost should not be
treated as direct material?
a)
Electricity representing 90% of the
total cost
b)
Stand paper used in
production
c)
Thread used in stitching
garments
d)
All of the above
5)
When prices fluctuate
widely, the method that
will smooth out the
effect of fluctuation is
a)
Simple average
b)
Weighted average
c)
FIFO
d)
LIFO
Data
for MCQ No. 6 to
9
Given-opening
stock on 1-1-1994
-200
kg @ Rs. 4 per kg.
�
Purchase
on 4-1-1994
-
300 kg @ Rs. 5 per kg
�
Issued
on 8-1-1994
-
350 kg
�
Market
price on8-1-1994 = Rs. 5 per
kg
�
On
the basis of above
information, select the
correct answer in each of
the following:
6)
At what amount materials
issued on 8-1-1994 will be
charged if FIFO method is
used?
48

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
a)
1,100
b)
1,550
c)
1,700
d)
1,750
7)
At what amount materials
issued will be charged if LIFO
method is used?
a)
1,550
b)
1,575
c)
1,700
d)
1,750
8)
At what amount materials,
issued will be charged if
simple average price is
used?
a)
1,550
b)
1,575
c)
1,610
d)
1,700
9)
What amount materials issued
will be charged if weighted average
price is used?
a)
1,575
b)
1,610
c)
1,625
d)
None of these
49
Table of Contents:
- COST CLASSIFICATION AND COST BEHAVIOR INTRODUCTION:COST CLASSIFICATION,
- IMPORTANT TERMINOLOGIES:Cost Center, Profit Centre, Differential Cost or Incremental cost
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Inventory, Direct Material Consumed, Total Factory Cost
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Adjustment in the Entire Production, Adjustment in the Income Statement
- PROBLEMS IN PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Gross Profit Margin Rate, Net Profit Ratio
- MORE ABOUT PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Conversion Cost
- MATERIAL:Inventory, Perpetual Inventory System, Weighted Average Method (W.Avg)
- CONTROL OVER MATERIAL:Order Level, Maximum Stock Level, Danger Level
- ECONOMIC ORDERING QUANTITY:EOQ Graph, PROBLEMS
- ACCOUNTING FOR LOSSES:Spoiled output, Accounting treatment, Inventory Turnover Ratio
- LABOR:Direct Labor Cost, Mechanical Methods, MAKING PAYMENTS TO EMPLOYEES
- PAYROLL AND INCENTIVES:Systems of Wages, Premium Plans
- PIECE RATE BASE PREMIUM PLANS:Suitability of Piece Rate System, GROUP BONUS SYSTEMS
- LABOR TURNOVER AND LABOR EFFICIENCY RATIOS & FACTORY OVERHEAD COST
- ALLOCATION AND APPORTIONMENT OF FOH COST
- FACTORY OVERHEAD COST:Marketing, Research and development
- FACTORY OVERHEAD COST:Spending Variance, Capacity/Volume Variance
- JOB ORDER COSTING SYSTEM:Direct Materials, Direct Labor, Factory Overhead
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Data Collection, Cost of Completed Output
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Cost of Production Report, Quantity Schedule
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Normal Loss at the End of Process
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:PRACTICE QUESTION
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Partially-processed units, Equivalent units
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Weighted average method, Cost of Production Report
- COSTING/VALUATION OF JOINT AND BY PRODUCTS:Accounting for joint products
- COSTING/VALUATION OF JOINT AND BY PRODUCTS:Problems of common costs
- MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTING:Contribution Margin, Marginal cost per unit
- MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTING:Contribution and profit
- COST – VOLUME – PROFIT ANALYSIS:Contribution Margin Approach & CVP Analysis
- COST – VOLUME – PROFIT ANALYSIS:Target Contribution Margin
- BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS – MARGIN OF SAFETY:Margin of Safety (MOS), Using Budget profit
- BREAKEVEN ANALYSIS – CHARTS AND GRAPHS:Usefulness of charts
- WHAT IS A BUDGET?:Budgetary control, Making a Forecast, Preparing budgets
- Production & Sales Budget:Rolling budget, Sales budget
- Production & Sales Budget:Illustration 1, Production budget
- FLEXIBLE BUDGET:Capacity and volume, Theoretical Capacity
- FLEXIBLE BUDGET:ANALYSIS OF COST BEHAVIOR, Fixed Expenses
- TYPES OF BUDGET:Format of Cash Budget,
- Complex Cash Budget & Flexible Budget:Comparing actual with original budget
- FLEXIBLE & ZERO BASE BUDGETING:Efficiency Ratio, Performance budgeting
- DECISION MAKING IN MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING:Spare capacity costs, Sunk cost
- DECISION MAKING:Size of fund, Income statement
- DECISION MAKING:Avoidable Costs, Non-Relevant Variable Costs, Absorbed Overhead
- DECISION MAKING CHOICE OF PRODUCT (PRODUCT MIX) DECISIONS
- DECISION MAKING CHOICE OF PRODUCT (PRODUCT MIX) DECISIONS:MAKE OR BUY DECISIONS