 |
Production & Sales Budget:Illustration 1, Production budget |
| << Production & Sales Budget:Rolling budget, Sales budget |
| FLEXIBLE BUDGET:Capacity and volume, Theoretical Capacity >> |
Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Division
Mar
Jan
Feb
Product
Qty.
Price
Value
Qty.
Pr
Value
Qty.
Pric
Value
(Units)
(Rs.
(Rs.)
(Units)
ice
(Rs.)
(Units)
e
(Rs.)
)
(Rs.)
(Rs.
)
Town
A
54,000
16
8,64,000
50,000
16
8,00,000
62,500
16
10,00,00
X
0
37,500
16
3,75,000
35,000
10
3,50,000
37,500
10
3,75,000
Y
Total
91,500
----
12,2,9000
85,000
----
11,50,000
----
13,75,00
0
Banglore
12,500
10
2,00,000
----
-----
16
X
Town B
61,500
10
6,15,000
55,000
10
5,50,000
62,500
10
6,25,000
Y
Total
74,500
---
8,15,000
55,000
5,50,000
62,500
----
6,25,000
Hyderabad
80,000
16
12,80,000
75,000
16
12,00,000
77,500
16
12,40,00
IX
0
II
Y
9,000
10
90,000
----
----
10
Total
89,000
----
13,80,000
75,000
12,00,000
----
12,40,00
0
Product
1,46,500
16
23,44,000
1,25,000
16
20,00,000
1,40,00
16
22,40,00
X
1,08,500
10
10,80,000
90,000
10
9,00,000
0
10
0
Product
II
1,00,00
10,00,00
Y
0
0
Total
2,54,500
----
34,24,000
2,15,000
29,00,000
2,40,00
----
32,40,00
0
0
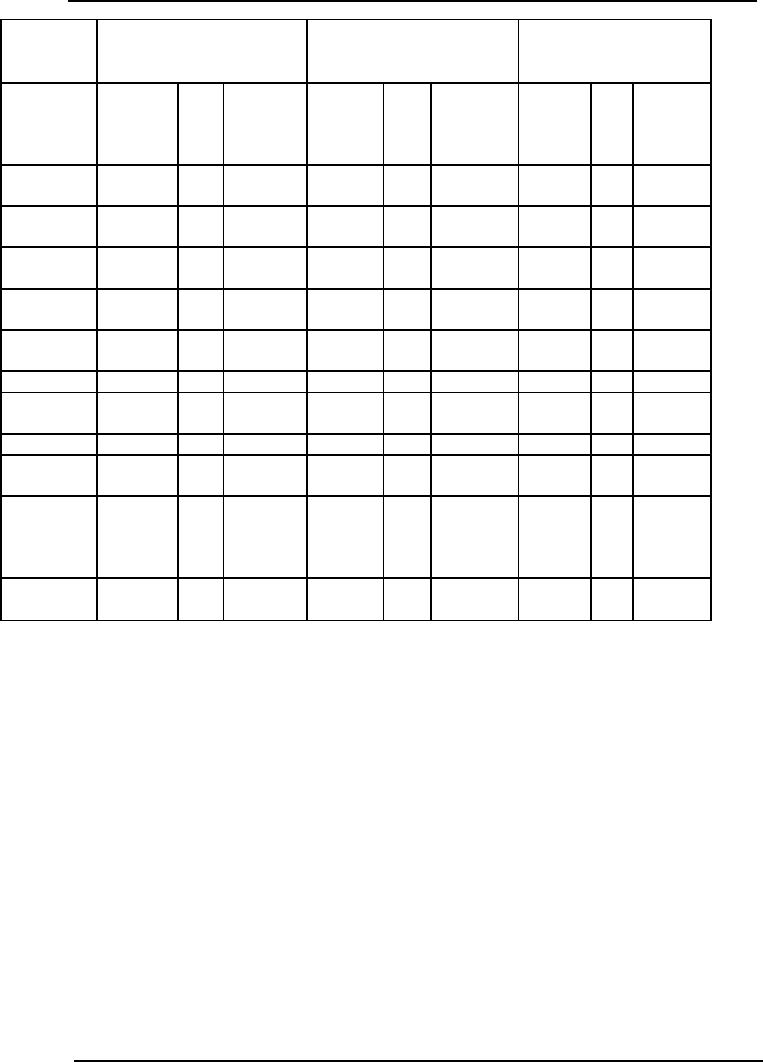
Production
budget
This
budget provides an estimate of the total
volume of production distributed
product-wise with
the
scheduling of operations by days, weeks
and months and a forecast of
the inventory of
finished
products.
Generally, the production budget is
based on the sales -budget.
The responsibility for
the
overall
production budget lies with
Works Manager and that of
departmental production budgets
with
departmental works management Production
budget may be expressed in physical or
financial
terms
or both in relation to production.
The production budgets
attempt to answer questions
like:
(i)
What
is to be produced?
(ii)
When
it is to be produced?
(iii)
How
it is to be produced?
(iv)
Where
it is to be produced?
The
production budget envisages the
production program for achieving the
sales target it serves
as
a
basis Job preparation of related cost-
budgets, e.g., materials
cost budget, labor cost budget,
etc.
It
easily facilities the preparation of a
cash budget. The production budget is
prepared after taking
into
consideration several factors like:
(i)
Inventory
policies. (II)
Sales
requirements, (iii)
Production
stability, (iv)
Plant
capacity, (v)
Availability
of materials and labor,
(vi)
Time
taken in
production
process, etc.
207

Cost
& Management Accounting
(MGT-402)
VU
Activity
2
From
the following details of
Mysore Cement Works Limited, complete
the production budget
for
the
three-month period ending March 31,
19x6 (Production budget for
product P has already
been
worked
out.
Estimated
stock
Estimated
sale during
Desired
closing stock
Type
of product
on
Jan 1, 19x6
Jan-March
1986
on
March 31, 19x6
(Units)
(Units)
(Units)
1,000
5,000
1,500
P
Q
1,500
7,500
2,500
R
2,000
6,500
1,500
S
1,500
6,000
1,000
208
Table of Contents:
- COST CLASSIFICATION AND COST BEHAVIOR INTRODUCTION:COST CLASSIFICATION,
- IMPORTANT TERMINOLOGIES:Cost Center, Profit Centre, Differential Cost or Incremental cost
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Inventory, Direct Material Consumed, Total Factory Cost
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Adjustment in the Entire Production, Adjustment in the Income Statement
- PROBLEMS IN PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Gross Profit Margin Rate, Net Profit Ratio
- MORE ABOUT PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:Conversion Cost
- MATERIAL:Inventory, Perpetual Inventory System, Weighted Average Method (W.Avg)
- CONTROL OVER MATERIAL:Order Level, Maximum Stock Level, Danger Level
- ECONOMIC ORDERING QUANTITY:EOQ Graph, PROBLEMS
- ACCOUNTING FOR LOSSES:Spoiled output, Accounting treatment, Inventory Turnover Ratio
- LABOR:Direct Labor Cost, Mechanical Methods, MAKING PAYMENTS TO EMPLOYEES
- PAYROLL AND INCENTIVES:Systems of Wages, Premium Plans
- PIECE RATE BASE PREMIUM PLANS:Suitability of Piece Rate System, GROUP BONUS SYSTEMS
- LABOR TURNOVER AND LABOR EFFICIENCY RATIOS & FACTORY OVERHEAD COST
- ALLOCATION AND APPORTIONMENT OF FOH COST
- FACTORY OVERHEAD COST:Marketing, Research and development
- FACTORY OVERHEAD COST:Spending Variance, Capacity/Volume Variance
- JOB ORDER COSTING SYSTEM:Direct Materials, Direct Labor, Factory Overhead
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Data Collection, Cost of Completed Output
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Cost of Production Report, Quantity Schedule
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Normal Loss at the End of Process
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:PRACTICE QUESTION
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Partially-processed units, Equivalent units
- PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM:Weighted average method, Cost of Production Report
- COSTING/VALUATION OF JOINT AND BY PRODUCTS:Accounting for joint products
- COSTING/VALUATION OF JOINT AND BY PRODUCTS:Problems of common costs
- MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTING:Contribution Margin, Marginal cost per unit
- MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTING:Contribution and profit
- COST – VOLUME – PROFIT ANALYSIS:Contribution Margin Approach & CVP Analysis
- COST – VOLUME – PROFIT ANALYSIS:Target Contribution Margin
- BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS – MARGIN OF SAFETY:Margin of Safety (MOS), Using Budget profit
- BREAKEVEN ANALYSIS – CHARTS AND GRAPHS:Usefulness of charts
- WHAT IS A BUDGET?:Budgetary control, Making a Forecast, Preparing budgets
- Production & Sales Budget:Rolling budget, Sales budget
- Production & Sales Budget:Illustration 1, Production budget
- FLEXIBLE BUDGET:Capacity and volume, Theoretical Capacity
- FLEXIBLE BUDGET:ANALYSIS OF COST BEHAVIOR, Fixed Expenses
- TYPES OF BUDGET:Format of Cash Budget,
- Complex Cash Budget & Flexible Budget:Comparing actual with original budget
- FLEXIBLE & ZERO BASE BUDGETING:Efficiency Ratio, Performance budgeting
- DECISION MAKING IN MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING:Spare capacity costs, Sunk cost
- DECISION MAKING:Size of fund, Income statement
- DECISION MAKING:Avoidable Costs, Non-Relevant Variable Costs, Absorbed Overhead
- DECISION MAKING CHOICE OF PRODUCT (PRODUCT MIX) DECISIONS
- DECISION MAKING CHOICE OF PRODUCT (PRODUCT MIX) DECISIONS:MAKE OR BUY DECISIONS