 |
DIRECT MARKETING:PUBLIC RELATIONS, Major Public Relations Decisions |
| << SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:DIRECT MARKETING, Forms of Direct Marketing |
| KEY TERMS:Public relations, Advertising, Catalog Marketing >> |

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
Lesson
38
Lesson
overview and learning objectives:
Explain
how companies use public
relations to communicate with their
publics. Public relations,
the
final mass communication
tool described in this
chapter, is an attempt to build
good relations
with
the company's various publics by obtaining favorable
publicity, building up a good
"corporate
image,"
and handling or heading off
unfavorable rumors, stories, or events.
The organization has
a
variety
of tools at their disposal
for accomplishing this feat. One of
the overriding tasks of
public
relations
is to control the exposure
and relationship with the
mass media. By focusing
on
consumer
attitudes, awareness, and knowledge of
the organization, the
company is better
prepared
to
succeed. Public relations have
even been extended to the
Internet and companies are
beginning
to
explore ways to increase
their effects on the newly
emerging world of
e-commerce.
A.
DIRECT MARKETING
B.
PUBLIC RELATIONS
A.
Direct Marketing
a.
Other Marketing Applications through
Databases
Some
of the important uses or
advantages of using database market are
as following:
�
Match
profiles to cross-sell other
products to customers
�
Modify
marketing messages based on customer
profiles
�
Reach
out to customers to reinforce the
purchase decision
�
Find
new customers
�
Gain
insight into who is purchasing
products
�
Improve
customer service
Beside
uses database marketing also
has some disadvantages
like
Marketing
databases can be costly and
time consuming,
Databases
need to be carefully planned
Consumer
privacy issues.
b.
Integrated
Direct Marketing
Too
often, a company's individual direct marketing
efforts are not well
integrated with one another
or
with other elements in its marketing
and promotional mixes. A
more powerful approach
is
integrated
direct marketing, which involves using
multiple-vehicle, multiple-stage
campaigns.
c.
Public Policy and Ethical
Issues in Direct
Marketing
Direct
marketers and their customers
usually enjoy mutually rewarding
relation-ships, however,
occasionally,
a darker side emerges.
Irritation,
unfairness, deception, and fraud are
common
complaints.
Many consumers perceive that
an innocent desire to become
"close" to the customer
really
is an invasion
of privacy (this
is the toughest issues facing
the industry).
1).
Consumers can benefit from
database marketing, but at what
cost to privacy?
2).
in a company's desire to build a
database, they often get
carried away.
3).
in a recent survey, 79 percent of consumers
expressed concern about
their privacy. In
reality,
direct marketing is just too expensive to
waste on consumers who don't
want it.
195
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
B.
Public Relations
Public
relations are very believable--news
stories, features, and
events seem more real
and
believable
to readers than ads do.
Public relations can also
reach many prospects who
avoid
salespeople
and advertisements--the message
gets to the buyers as "news"
rather than as a
sales-
directed
communication. As with advertising,
public relations can dramatize a
company or product.
Marketers
tend to underused public relations or to
use it as an afterthought. Yet a
well-thought-out
public
relations campaign used with
other promotion mix elements
can be very effective
and
economical.
a.
Public Relations
Public
relations involves building good
relations with the company's various publics by
obtaining
favorable
publicity, building up a good corporate
image, and handling or
heading off
unfavorable
rumors,
stories, and events. Major
functions are:
1).
Press relations or press
gentry.
2).
Product publicity.
3).
Public affairs.
4).
Lobbying.
5).
Investor relations.
6).
Development.
Public
relations are used to promote
products, places, ideas, activities,
organizations, even nations.
b.
The Role and Impact of
Public
Relations
The
Rolle of
The
Ro e of
Public
relations can have a strong impact
on
Publliic
Pub
c
public
awareness at a much lower
cost than
Rellatiions
Re
at ons
advertising.
Despite its potential strengths,
public
relations are often described as
a
Executes
Executes
marketing
stepchild because of its limited
and
Ev
alluattes
programs
tto
Ev
a ua es
programs
o
scattered
use. This may be changing,
however. publliic
attttiittudes
gaiin publliic
ga
n
pub
c
pub
c a udes
accepttance
accep
ance
Many
companies today are looking
for public
IIdenttiifiies
den
f es
iissues
off publliic
ssues
o pub c
relations
to take a more active role
in
concern
concern
marketing
and
promotion
planning.
Marketing
public relations departments are
being
formed. Public relation
tools are being used by
the companies in evaluating public
attitudes,
identifying
the issues of public concern
and to execute the different
programs that can gain
public
acceptance.
It means that the public
relations is that marketing function
which evaluates
public
attitudes,
identifies areas within the
organization that the public
may be interested in, and
executes
a
program of action to earn public
understanding and acceptance.
c.
Major
Public Relations Tools
Major
tools include:
1).
News.
2).
Speeches.
W
eb Siite
W
eb Ste
3).
Special events
(mobile
Publlic
Pubic
Serrviice
Se
vce
News
News
marketing).
Actt
ivit ies
Ac
ivit
ies
4).Written
materials (such as
Corrporate
Co
porate
annual
reports, brochures, articles,
IIdentity
dentity
Speeches
Matterials
Maerials
Speeches
and
company newsletters).
5).
Audiovisual materials (such
Speciial
Specal
Audiiovisual
Audovisual
as
films, slide-and-sound programs,
Eventts
Even
s
Matterrials
Ma
e ials
W
rritten
W
itten
video
and audio cassettes).
Matterrials
Ma
e ials
196
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
6)
Corporate identity materials (such as
logos, stationery, brochures,
signs, business
forms,
business
cards, buildings, uniforms,
and company cars and
trucks).
Companies
also improve public relations by
contributing time and money
to public service
activities.
A company's Web site can be a
good public relations vehicle. Consumer
and members of
other
publics can visit the site
for information and
entertainment. Major public relations
decisions
include:
1).
Setting public relations
objectives.
2).
Choosing public relations messages
and
Setttiing
Publliic Re
llattiions Ob jjecttiiv es
Se
ng Pub c Re a ons Ob ec v es
vehicles.
3).
Implementing the public relations
plan.
4).
Evaluating the results.
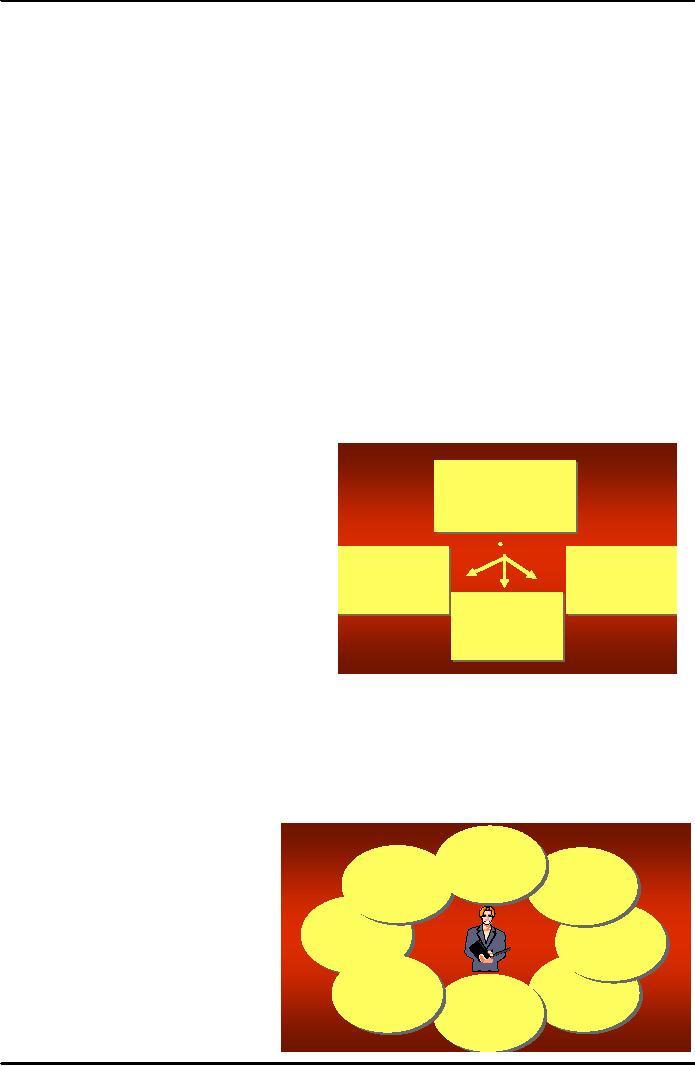
d.
Major Public Relations
Decisions
Choosiing
tthe Publliic Re llattiions
Messages
Choos
ng he Pub c Re a ons Messages
As
shown in the fig major
public relation
decisions
and
Vehiic lles
and
Veh c es
are:
Setting
Public relations objective that means
deciding
what
are the results that the
companies want to
achieve
by using public relation tools,
than second
IImpllementtiing tthe Publliic Rellattiions Pllan
mp
emen ng he Pub c Re a ons P an
step
is choosing the message that
companies can
communicate
to public to fulfill the
role of public
relation,
next step of this system is
implementation of
the
program and finally evaluation of
the program in
Ev
alluattiing Pub lliic Re llattiions Resulltts
Ev
a ua ng Pub c Re a ons Resu s
order
to judge the success level
of public relations
tools
used.
e.
Publicity
Public
information is information about a
company's goods or services appearing in
the mass
media
as a news item. Stimulation of
demand for a good, service,
place, idea, person, or
organization
by unpaid placement of commercially
significant news or favorable
media
presentations.
Publicity is more credible to consumers
than any other promotional
mix element
Although
publicity is generally thought of as not
paid for, firms incur
publicity-related expenses
that
include the cost of
employing marketing personnel assigned to
create and submit
publicity
releases,
printing and mailing costs,
and related expenses.
197
Table of Contents:
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING:Introduction of Marketing, How is Marketing Done?
- ROAD MAP:UNDERSTANDING MARKETING AND MARKETING PROCESS
- MARKETING FUNCTIONS:CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
- MARKETING IN HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE AND EVOLUTION OF MARKETING:End of the Mass Market
- MARKETING CHALLENGES IN THE 21st CENTURY:Connections with Customers
- STRATEGIC PLANNING AND MARKETING PROCESS:Setting Company Objectives and Goals
- PORTFOLIO ANALYSIS:MARKETING PROCESS,Marketing Strategy Planning Process
- MARKETING PROCESS:Analyzing marketing opportunities, Contents of Marketing Plan
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:The Company’s Microenvironment, Customers
- MARKETING MACRO ENVIRONMENT:Demographic Environment, Cultural Environment
- ANALYZING MARKETING OPPORTUNITIES AND DEVELOPING STRATEGIES:MIS, Marketing Research
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS:Developing the Research Plan, Research Approaches
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS (Continued):CONSUMER MARKET
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR:Model of consumer behavior, Cultural Factors
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR (CONTINUED):Personal Factors, Psychological Factors
- BUSINESS MARKETS AND BUYING BEHAVIOR:Market structure and demand
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Steps in Target Marketing, Mass Marketing
- MARKET SEGMENTATION (CONTINUED):Market Targeting, How Many Differences to Promote
- Product:Marketing Mix, Levels of Product and Services, Consumer Products
- PRODUCT:Individual product decisions, Product Attributes, Branding
- PRODUCT:NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, Idea generation, Test Marketing
- NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRODUCT LIFE- CYCLE STAGES AND STRATEGIES
- KEY TERMS:New-product development, Idea generation, Product development
- Price the 2nd P of Marketing Mix:Marketing Objectives, Costs, The Market and Demand
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:General Pricing Approaches, Fixed Cost
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Discount and Allowance Pricing, Segmented Pricing
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Price Changes, Initiating Price Increases
- PLACE- THE 3RD P OF MARKETING MIX:Marketing Channel, Channel Behavior
- LOGISTIC MANAGEMENT:Push Versus Pull Strategy, Goals of the Logistics System
- RETAILING AND WHOLESALING:Customer Service, Product Line, Discount Stores
- KEY TERMS:Distribution channel, Franchise organization, Distribution center
- PROMOTION THE 4TH P OF MARKETING MIX:Integrated Marketing Communications
- ADVERTISING:The Five M’s of Advertising, Advertising decisions
- ADVERTISING:SALES PROMOTION, Evaluating Advertising, Sales Promotion
- PERSONAL SELLING:The Role of the Sales Force, Builds Relationships
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:Managing the Sales Force, Compensating Salespeople
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:DIRECT MARKETING, Forms of Direct Marketing
- DIRECT MARKETING:PUBLIC RELATIONS, Major Public Relations Decisions
- KEY TERMS:Public relations, Advertising, Catalog Marketing
- CREATING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE:Competitor Analysis, Competitive Strategies
- GLOBAL MARKETING:International Trade System, Economic Environment
- E-MARKETING:Internet Marketing, Electronic Commerce, Basic-Forms
- MARKETING AND SOCIETY:Social Criticisms of Marketing, Marketing Ethics
- MARKETING:BCG MATRIX, CONSUMER BEHAVIOR, PRODUCT AND SERVICES
- A NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRICING STRATEGIES, GLOBAL MARKET PLACE