 |
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
Lesson
20
Lesson
overview and learning objectives:
In
last Lesson we discussed the
concept of the marketing mix elements. We
had a detailed view
about
the classification of the
product today we will continue
with same topic i.e.
Product.
o
PRODUCT
A.
Individual product decisions
We
will focus on the important
decisions in the development
and marketing of individual
products
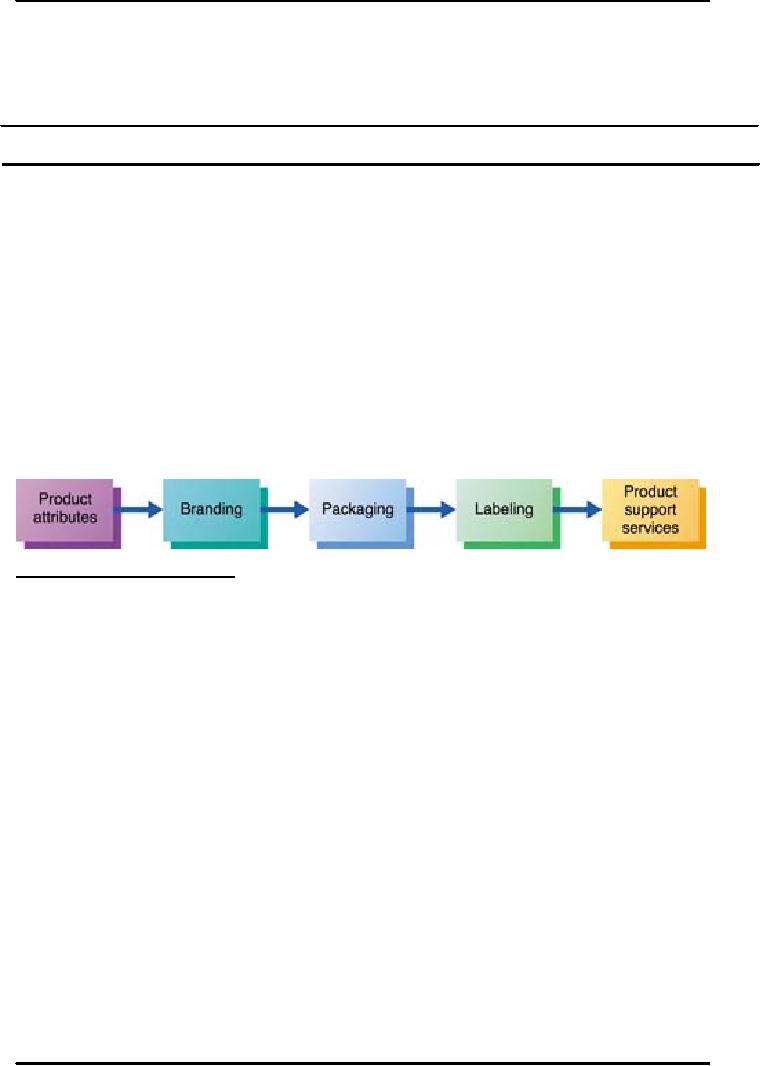
and
services. These decisions
are about product
attributes, branding, packaging,
labeling, and
product
support services. Companies
have to develop strategies for
the items of their
product
lines.
Marketers make individual product
decisions for each product
including: product
attributes
decisions,
brand, packaging, labeling, and
product-support services decisions.
Product attributes
deliver
benefits through tangible aspects of the
product including features,
and design as well as
through
intangible features such as quality
and experiential aspects. A brand is a
way to identify
and
differentiate goods and
services through use of a
name or distinctive design element,
resulting
in
long-term value known as brand
equity. The product package
and labeling are also
important
elements
in the product decision mix,
as they both carry brand
equity through appearance
and
affect
product performance with
functionality. The level of
product-support
services provided
can also
have
a major effect on the appeal
of the product to a potential
buyer.
Individual
product decisions
a)
Product Attributes
Developing
a product or service involves
defining the benefits that it
will offer. These benefits
are
communicated
to and delivered by product attributes
such as quality,
features, style and design.
i.
Product
Quality
Quality
is one of the marketer's major
positioning tools. Product
quality has two
dimensions--
level
and consistency. In developing a product,
the marketer must first
choose a quality
level that
will
support
the product's position in
the target market. Here,
product quality means
performance
quality--the
ability of a product to perform its
functions beyond quality
level, high quality also
can
mean
high levels of quality
consistency.
Here,
product quality means
conformance
quality--freedom
from
defects and consistency
in
delivering a targeted level of
performance. All companies
should
strive
for high levels of
conformance quality.
ii.
Product
Features
A
product can be offered with
varying features. A stripped-down
model, one without any extras,
is
the
starting point. The company
can create higher-level
models by adding more
features. Features
are
a competitive tool for
differentiating the company's product
from competitors' products.
Being
the
first producer to introduce a
needed and valued new feature is one of
the most effective
ways
to
compete.
How
can a company identify new
features and decide which
ones to add to its product?
The
company
should periodically survey buyers who
have used the product
and ask these
questions:
How
do you like the product? Which
specific features of the
product do you like most?
Which
features
could we add to improve the
product? The answers provide
the company with a rich
list
of
feature ideas. The company
can then assess each
feature's value
to customers
versus its cost
to
the
95

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
company.
Features that customers value little in
relation to costs should be dropped;
those that
customers
value highly in relation to costs
should be added.
iii.
Product
Style and Design
Another
way to add customer value is through
distinctive product
style and design. Some
companies
have
reputations for outstanding style
and design. Design is a
larger concept than style. Style
simply
describes
the appearance of a product.
Styles can be eye catching or
yawn producing. A
sensational
style
may grab attention and
produce pleasing aesthetics, but it
does not necessarily make
the
product
perform
better.
Unlike style, design
is
more than skin deep--it goes
to the very heart of a
product.
Good design contributes to a
product's usefulness as well as to its
looks.
Good
style and design can attract
attention, improve product performance,
cut production costs,
and
give the product a strong
competitive advantage in the
target market
b)
Branding
Perhaps
the most distinctive skill
of professional marketers is their
ability to create,
maintain,
protect,
and enhance brands of
their
products and services.
A
brand
is a name, term,
sign,
Childre
n's
No
g g in
Anthropology
symbol,
or design, or a
Arena
Cable
Ne t
P&E
BET
on
Jazz
Clas
s ic al
combination
of these, that
Knowledge
Mus
ic
TV
identifies
the maker or seller
of
a
product
or
service.
Ovatio
n
Ne
w S cie nce
Animal
Consumers
view a brand as an
Pla
ne t
Ne
twork
KIDS
important
part of a product,
CIVILIZATION
and
branding can add value
to
Cla
s s ic Arts
a
product. For example,
most
Showcas
e
C-S
P AN
consumers
would perceive a
Bo
o kne t
The
a te r
DIY
rts
& Antique s
bottle
of White Linen
perfume
Cha
nne l
A
as
a high-quality, expensive
Mus
eum
product.
But the same
perfume
Channel
BLOOMBERG
in
an unmarked bottle
would
NEWS
INFORMATION
Trave
l
SCIENCE
likely
be viewed as lower in
Cha
nne l
EOP
quality,
even if the fragrance
were
identical. Branding has
become
so strong that today hardly
anything goes unbranded.
Branding helps buyers in many
ways.
Brand
names help consumers identify
products that might benefit
them. Brands also tell
the buyer
something
about product quality.
Buyers who always buy
the same brand know
that they will
get
the
same features, benefits, and
quality each time they
buy. Branding also gives
the seller several
advantages.
The brand name becomes
the basis on which a whole
story can be built about
a
product's
special qualities. The
seller's brand name and
trademark provide legal protection
for
unique
product features that otherwise
might be copied by competitors.
Branding also helps
the
seller
to segment markets.
i.
Brand:
A
brand
is a
name, sign, symbol, or
design, or a combination of these
that
identifies
the
maker
or seller of a product or
service.
ii.
Brand
equity
is
the value of a brand, based on
the extent to which it has
high brand loyalty, name
awareness,
perceived
quality, strong brand
associations, and other
assets such as patents, trademarks,
and
channel
relationships. Powerful brand names
command strong consumer preference
and are
96

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
powerful
assets. Perhaps the most
distinctive skill of professional
marketers is their ability
to
create,
maintain, protect, and
enhance brands. Measuring the
actual equity of a brand
name is
difficult.
However, the advantages of
having it include:
1).
High consumer awareness and
loyalty.
2).
Easier to launch brand extensions
because of high brand
credibility.
3).
A good defense against
fierce price
competition.
4).
It is believed to be the company's most
enduring asset. Customer
equity tends
to aid
marketing
planning in assuring loyal
customer lifetime value.
iii.
Selecting
The Brands Name:
Selecting
a brand name is an important
step. The brand name
should be carefully chosen
since a
good
name can add greatly to a
product's success. Desirable
qualities of a good brand
name
include:
1).
It should suggest something
about the product's benefits
and qualities.
2).
It should be easy to pronounce,
recognize, and remember.
3).
It should be distinctive.
4).
It should translate easily into
foreign languages.
5).
It should be capable of registration and
legal protection. Once
chosen, the brand
name
must
be protected.
iv.
Sponsorship
options for Branding:
A
manufacturer has four sponsorship
options:
1).
A manufacturer's
brand (or national brand)
is a
brand created and owned by
the
producer
of a product or service (Examples include
IBM and Kellogg).
2).
A private
brand (or middleman, distributor, or
store brand) is a
brand created and
owned
by a reseller of a product or
service.
3).
A licensed
brand (a
company sells it's output
under another brand
name).
4).
Co-branding
occurs
when two companies go
together and manufacture one
product
(General
Mills and Hershey's make
Reese's' Peanut Butter Puffs
cereal).
Combined
brands create broader customer
appeal and greater brand
equity.
It
may allow a company to
expand its existing brand into a
category it might otherwise
have
difficulty
entering alone. But at the
same time there are certain
disadvantages of combine branding
like:
Complex
legal contracts and licenses
are involved.
Coordination
efforts are often
difficult.
Trust
is essential between partners. It is
often hard to come
by.
At
one time manufacturer's brands
were the most popular
and profitable. Today,
however, an
increasing
number of private brands are
doing well. Though hard
to
establish
and maintain,
private
brands can
yield higher profit margins.
"The
battle of the brands" (the
competition
between
manufacturer's and private brands)
causes resellers to have
advantages, and they
charge
manufacturer's
slotting
fees (payments
demanded by retailers from producers
before they will
accept
new products and find
"slots" for them on the
shelves). As store brands
are improving in
quality,
they are posing a stronger
threat to the manufacturer's
brands. This is especially
true in
supermarkets.
v.
Branding
Strategy:
A
company has four choices
when it comes to brand
strategy. It
can:
97

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
1).
Introduce line
extensions.
Existing brand names are
extended to new forms,
sizes, and
flavors
of an existing product category. A
company might introduce line
extensions as a low-cost,
low-risk
way of introducing new products in
order to:
a).
Meet consumer desires for
variety.
b).
Meet excess manufacturing
capacity.
c).
simply command more shelf
space.
Risks
include:
a).
An overextended brand might lose its
specific meaning.
b).
Can cause consumer frustration or
confusion.
2).
Introduce brand
extensions.
Existing brand names are
extended to new or
modified
product
categories. Advantages
include:
a).
Helps a company enter new
product categories more
easily.
b).
Aids in new product
recognition.
c).
Saves on high advertising
cost.
3).
Introduce multibrands.
New
brand names are introduced
in the same product
category.
Advantages include:
a).
They gain more shelf
space.
b).
Offering several brands to capture
"brand switchers." The
company can establish
flanker
or fighter brands to
protect its major
brand.
c).
It helps to develop healthy competition
within the
organization.
Drawbacks
include:
a).
Each brand may only obtain a
small market share and be
unprofitable.
4).
Introduce new
brands. New
brand names in new
categories are
introduced.
Advantage
include:
a).
Helps move away from a
brand that is
failing.
b).
Can get new brands in
new categories by corporate acquisitions.
Some companies
are
now pursuing mega
brand strategies.
Drawbacks
can include:
a).
Spreading resources too
thin.
c)
Packaging
Packaging
involves designing and
producing the container or wrapper
for a product. The
package
may
include the product's
primary container (the tube
holding Colgate toothpaste); a
secondary
package
that is thrown away when
the product is about to be
used (the cardboard box
containing
the
tube of Colgate); and the
shipping package necessary to store,
identify, and ship the
product (a
corrugated
box carrying six dozen tubes of
Colgate toothpaste). Labeling, printed
information
appearing
on or with the package, is
also part of
packaging.
Traditionally,
the primary function of the
package was to contain and
protect the product.
In
recent
times, however, numerous
factors have made packaging
an important marketing
tool.
Increased
competition and clutter on retail
store shelves means that
packages must now
perform
many
sales tasks--from attracting
attention, to describing the
product, to making the
sale.
Companies
are realizing the power of
good packaging to create
instant consumer recognition of
the
company or brand. Developing a
good package for a new
product requires making
many
decisions.
First, the company must
establish the packaging
concept, which
states what the
package
should
be
or
do
for
the product. Should it
mainly offer product
protection, introduce a
new
dispensing
method, suggest certain qualities
about the product, or
something else? Decisions
then
must
be made on specific elements of
the package, such as size,
shape, materials, color,
text, and
brand
mark. These elements must
work together to support the
product's position and
marketing
strategy.
The package must be consistent
with the product's advertising,
pricing, and
distribution.
98

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
d)
Labeling
Labels
may range from simple
tags attached to products to
complex graphics that are
part of the
package.
They perform several
functions. At the very
least, the label identifies
the product or
brand,
such as the name Sunkist stamped on
oranges. The label might
also describe several
things
about
the product--who made it,
where it was made, when it
was made, its contents, how
it is to
be
used, and how to use it
safely. Finally, the label
might promote the product
through attractive
graphics.
e)
Product Support Services
Customer
service is another element of product
strategy. A company's offer to the
marketplace
usually
includes some services, which
can be a minor or a major
part of the total offer.
Later in the
chapter,
we will discuss services as
products in themselves. Here, we
discuss product
support services--
services
that augment actual products.
More and more companies
are using product
support
services
as a major tool in gaining
competitive advantage.
A
company should design its
product and support services
to profitably meet the needs
of target
customers.
The first step is to survey
customers periodically to assess the value of
current services
and
to obtain ideas for new
ones. For example, Cadillac
holds regular focus group
interviews with
owners
and carefully watches
complaints that come into
its dealerships. From this
careful
monitoring,
Cadillac has learned that
buyers are very upset by
repairs that are not done
correctly
the
first time.
Once
the company has assessed
the value of various support services to
customers, it must next
assess
the costs of providing these
services. It can then develop a
package of services that
will both
delight
customers and yield profits to the
company.
99
Table of Contents:
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING:Introduction of Marketing, How is Marketing Done?
- ROAD MAP:UNDERSTANDING MARKETING AND MARKETING PROCESS
- MARKETING FUNCTIONS:CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
- MARKETING IN HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE AND EVOLUTION OF MARKETING:End of the Mass Market
- MARKETING CHALLENGES IN THE 21st CENTURY:Connections with Customers
- STRATEGIC PLANNING AND MARKETING PROCESS:Setting Company Objectives and Goals
- PORTFOLIO ANALYSIS:MARKETING PROCESS,Marketing Strategy Planning Process
- MARKETING PROCESS:Analyzing marketing opportunities, Contents of Marketing Plan
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:The Company’s Microenvironment, Customers
- MARKETING MACRO ENVIRONMENT:Demographic Environment, Cultural Environment
- ANALYZING MARKETING OPPORTUNITIES AND DEVELOPING STRATEGIES:MIS, Marketing Research
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS:Developing the Research Plan, Research Approaches
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS (Continued):CONSUMER MARKET
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR:Model of consumer behavior, Cultural Factors
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR (CONTINUED):Personal Factors, Psychological Factors
- BUSINESS MARKETS AND BUYING BEHAVIOR:Market structure and demand
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Steps in Target Marketing, Mass Marketing
- MARKET SEGMENTATION (CONTINUED):Market Targeting, How Many Differences to Promote
- Product:Marketing Mix, Levels of Product and Services, Consumer Products
- PRODUCT:Individual product decisions, Product Attributes, Branding
- PRODUCT:NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, Idea generation, Test Marketing
- NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRODUCT LIFE- CYCLE STAGES AND STRATEGIES
- KEY TERMS:New-product development, Idea generation, Product development
- Price the 2nd P of Marketing Mix:Marketing Objectives, Costs, The Market and Demand
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:General Pricing Approaches, Fixed Cost
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Discount and Allowance Pricing, Segmented Pricing
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Price Changes, Initiating Price Increases
- PLACE- THE 3RD P OF MARKETING MIX:Marketing Channel, Channel Behavior
- LOGISTIC MANAGEMENT:Push Versus Pull Strategy, Goals of the Logistics System
- RETAILING AND WHOLESALING:Customer Service, Product Line, Discount Stores
- KEY TERMS:Distribution channel, Franchise organization, Distribution center
- PROMOTION THE 4TH P OF MARKETING MIX:Integrated Marketing Communications
- ADVERTISING:The Five M’s of Advertising, Advertising decisions
- ADVERTISING:SALES PROMOTION, Evaluating Advertising, Sales Promotion
- PERSONAL SELLING:The Role of the Sales Force, Builds Relationships
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:Managing the Sales Force, Compensating Salespeople
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:DIRECT MARKETING, Forms of Direct Marketing
- DIRECT MARKETING:PUBLIC RELATIONS, Major Public Relations Decisions
- KEY TERMS:Public relations, Advertising, Catalog Marketing
- CREATING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE:Competitor Analysis, Competitive Strategies
- GLOBAL MARKETING:International Trade System, Economic Environment
- E-MARKETING:Internet Marketing, Electronic Commerce, Basic-Forms
- MARKETING AND SOCIETY:Social Criticisms of Marketing, Marketing Ethics
- MARKETING:BCG MATRIX, CONSUMER BEHAVIOR, PRODUCT AND SERVICES
- A NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRICING STRATEGIES, GLOBAL MARKET PLACE