 |
PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING:Introduction of Marketing, How is Marketing Done? |
| ROAD MAP:UNDERSTANDING MARKETING AND MARKETING PROCESS >> |

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
Lesson
1
MGT
- 301
PRINCIPLES
OF MARKETING
Overview
of Course:
This
subject/course is designed to teach
the basic principles of Marketing to
diverse
audience/students,
including those who are
studying this as a supporting subject
for their bachelor
degree
program. This course is designed to
provide you the foundations
of Marketing whether
you
intend
to work in field of the marketing or
not.
Marketing
is part of all of our lives
and touches us in some way every day. To be
successful each
company
that deals with customers on a daily
basis must not only be
customer-driven, but
customer-obsessed.
The best way to achieve this
objective is to develop a sound marketing
function
within the organization. To be
understandable and lively means
that we need to
communicate
you. We start every chapter with learning objectives.
The most important thing
you
will
get out of this course is
the basic skills required to succeed in
today's competitive environment.
Marketing
is defined as a
social and managerial process by which,
individuals and groups obtain what they
need
and
want through creating and
exchanging products and value with
others.
Marketing is a key factor
to
business
success. The marketing function
not only deals with
the production and
distribution of
products
and services, but it also is
concerned with the ethical and
social responsibility
functions
found
in the domestic and global
environment.
Introduction
of Marketing
What
image comes to mind when
you hear the word
"marketing"? Some people
think of
advertisements
or brochures, while others
think of public relations (for
instance, arranging for
clients
to appear on TV talk shows). The
truth is, all of these--and
many more things--make
up
the
field of marketing. The Knowledge
Exchange Business Encyclopedia defines marketing
as
"planning
and executing the strategy
involved in moving a good or
service from producer
to
consumer."
With
this definition in mind,
it's apparent that marketing
and many other business
activities are
related
in some ways. In simplified terms,
marketers and others help
move goods and
services
through
the creation and production
process; at that point,
marketers help move the
goods and
services
to consumers. But the connection
goes even further: Marketing
can have a
significant
impact
on all areas of the business
and vice versa.
Understanding
Marketing:
Marketing:
It is the process of creating consumer
value in the form of goods,
services, or ideas
that
can improve the consumer's
life.
Marketing
is the organizational function charged
with defining customer
targets and the best
way
to
satisfy needs and wants
competitively and profitably.
Since consumers and business
buyers face
an
abundance of suppliers seeking to
satisfy their everyday
need,
companies and nonprofit
organizations
cannot survive today by simply
doing a good job. They
must do an excellent job
if
they
are to remain in the increasingly
competitive global marketplace. This is
what we say that
survival
of the fittest. Many studies
have demonstrated that the
key to profitable performance is
to
know
and satisfy target customers
with competitively superior offers.
This process takes
place
today
in an increasingly global, technical, and competitive
environment.
1
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
What
is Marketing?
Marketing
is not only restricted to
selling
and advertising as is
ons
Catal
oti
g
ogue
rtisin
Prom
perceived
but is More than it
s
Adve
Co
advertising
it identifies
and
up
Sal
on
What
is
es
s
satisfies
customers
needs. it
Public
functions
revolve around
wide
Marketing,
relation
e
s
Servic
variety
and range of tasks
and
anyway?
activities
mostly termed as functions
erce
mm
related
to 4ps i.e. Product,
price,
E-co
ry
Delive
place
and promotion. Marketing
is:
ing
Shopp
s
Retai
Spon
ling
el
s
orshi
chann
a.
Creating customer value and
ps
ing
Pric
satisfaction
are at the very
il
ct
ma Res
e
heart
of modern marketing
Billb
Dir
Pack
ear
aging
oard
thinking
and practice.
ch
s
b.
A very simple definition
of
marketing
is that it is the delivery of customer
satisfaction at a profit.
c.
Sound marketing is critical to the
success of every organization.
Marketing
can also be defined as process of
planning and executing the
conception, pricing,
promotion,
and distribution of ideas,
goods, and services to
create exchanges that
satisfy individual
and
organizational objectives."
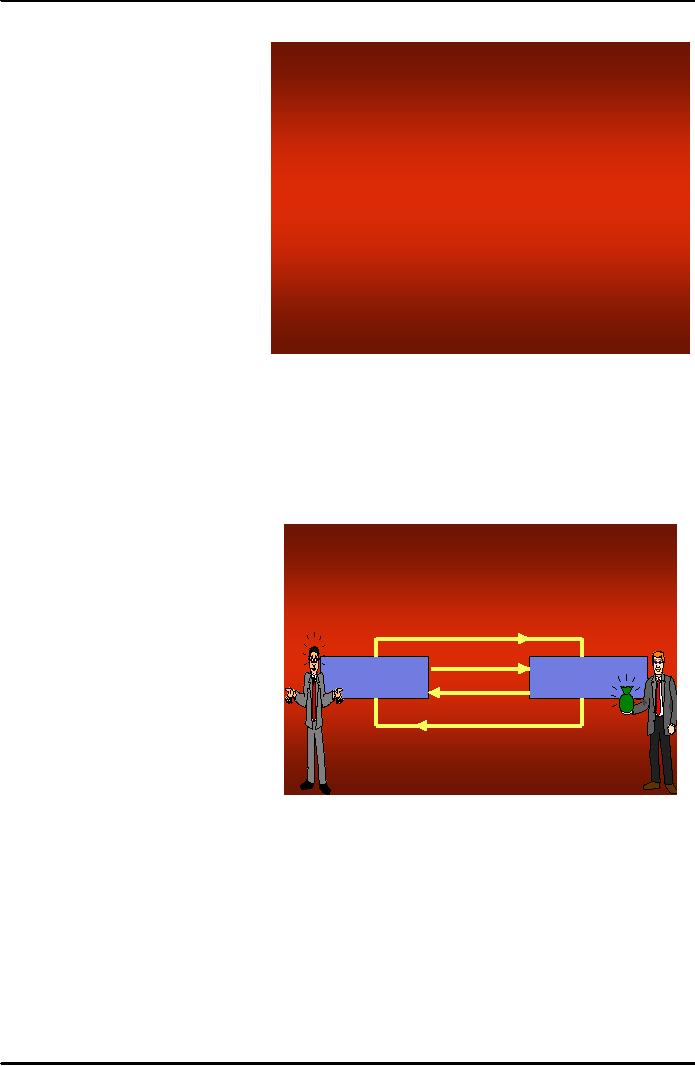
Simple
Marketing System
S
im p le M a r k e tin g
The
concept of Marketing System
brings
one full circle to the concept of
S
y s te m
marketing.
Simple
marketing system comprises of
Communication
different
actors and factors
like
producer/seller,
product/service
Product/Service
something
valuable to exchange in
Producer/Seller
Consumer
Money
return
of product/service (money),
consumer/customer,
communication
process
to
have
two
way
Feedback
communication
like to provide
information
about product or
service
to
customer or consumer and to have
feedback
in same regard from the
customer. Fig presents an
example of a very simple
marketing
system.
Marketing system has
following basic activities:
1)
Sellers
must search for buyers,
identify their needs, design
good products and services,
set
prices
for them, promote them,
and store and deliver
them.
2)
A
modern marketing system includes all of
the elements necessary to
bring buyers and
sellers
together. This might include
such activities as product development,
research,
communication,
distribution, pricing, and
service..
3)
Each
of the major actors in a marketing
system adds value for the
next level of the
system.
There
is often critical interdependency among
network members.
To
learn more about marketing
fist we should learn about
some basics that are
some time termed
as
4ps(Product, price, place, promotion)
and some times even 6 or 7ps
(Product, price,
place
promotion,
position, personal relations, people
and profit) lets have
some definitions in this
regard:
2
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
�
Product--what
are you selling? (It might
be
a
product or a service.)
Price
Product
�
Price--what
is your pricing
strategy?
�
Place
or
distribution--how are
you
distributing
your product to get it into
the
Customers
marketplace?
�
Promotion--how
are
you
telling
consumers
in your target group about
your
Place
Promotion
product?
�
Positioning--what
place do you want
your
product
to hold in the consumer's mind?
�
Personal
relationships--how
are you building relationships
with your target
consumers?
�
People:
public
who can have impact on
organization or can be affected by
organization.
�
Profits:
the
basic objective of organization
that to have something valuable in
return of
product
or service mostly it is in form of
money.
Marketing
assumes that it will proceed
in accordance with ethical actives. It
Identifies the 4
marketing
variables i.e. product,
price, promotion, and
distribution it also states
that the public,
the
customer,
and the client determine the
marketing program. Marketing mainly
emphasizes on
creating
and maintaining relationships and
applies for both non-profit
organizations and profit-
oriented
businesses. Major activities that
are performed in marketing process
include:
Personal
selling Advertising, Making products
available in stores and
Maintaining inventories.
Any
thing
like goods, services, experiences,
events, persons, places, organizations,
information and
ideas
can be marketed to
the
customers in return of something of
value.
How
Does an Organization Create a
Customer?
Organizations
(producer/ seller) can
create the customers by Identifying
customer needs,
designing
goods and services that
meet those needs than
communicating information about
those
goods
and services to prospective buyers Making
the goods or services
available at times
and
places
that meet customers' needs Pricing
goods and services to
reflect costs, competition,
and
customers'
ability to buy and finally
providing for the necessary
service and follow-up to
ensure
customer
satisfaction after the
purchase
Costs
Careers
About
25 to 33% of
About
50% of total
How
is Marketing Done?
the
work force hold
product
costs are
According
to Peter F. Drucker If we want
to
marketing
positions.
marketing
costs
know
what a business is, we have
to start
with
its purpose. And its purpose must
lie
outside
the business itself. In
fact, it must lie
in
society since a business
enterprise is an
Why
Study
organ
of society.
There
is one valid
Marketing
?
definition
of business purpose: to create a
customer.
Contributions
to Society
Reasons
for Studying Marketing:
Marketing
decisions affect
Contributions
to
Marketing
is part of all of our lives
and Individual
Organizations
the
lives of individual
touches
us in some way every day. To be Critical
to the success
consumers
and society as
of
a firm
a
whole
successful
each company that deals
with
customers
on a daily basis must not
only be customer-driven, but
customer-obsessed. The
best
way
to achieve this objective is to develop a
sound marketing function within
the organization.
Major
reason to study marketing
is:
�
Marketing
plays an important role in
society
3

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
�
It is
Vital to business
�
Marketing
offers outstanding career
opportunities
�
Marketing
effects your life every
day
What
do Marketers think
about?
To
have clearer concept in this
regard lets consider an
example of Opening a Book
Shop on
campus.
To do so we have to answer different
questions like:
1.
Is there a need? (Of having
book shop)
2.
What
is my
target market? (Who will be
buying products from your
book shop)
3.
What is my product?(Basic items to be
sold)
4.
How can I produce and
deliver a "product" better
than my competitors?
5.
How shall I promote my product?
6.
How can I insure customer loyalty?
Mostly
before starting any activity of above-mentioned
type marketer performs an analysis
termed
as
SWOT (Strength, Weakness,
Opportunity and Threat).
Marketing is a process of getting
the
right
products to the right people
at the right price and at
the right place and
time with the
right
promotion.
But this requires solution
to certain simple question: like
Simple
Questions, Hard Answers
1.
Who are our customers?
(Target Market)
2.
What important & unique benefits do
we provide? (Product/service)
3.
Are these benefits sustainable?
(Long-term competitive
advantage)
These
questions are apparently very simple
but are very difficult to be
answered theses
questions
like
it is really difficult to define basic
characteristics to be produced in product
and services as per
demands
and requirements pf the customers; and
then to precisely define your
target market and
to
have long-term competitive
advantage through customer
satisfaction.
4
Table of Contents:
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING:Introduction of Marketing, How is Marketing Done?
- ROAD MAP:UNDERSTANDING MARKETING AND MARKETING PROCESS
- MARKETING FUNCTIONS:CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
- MARKETING IN HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE AND EVOLUTION OF MARKETING:End of the Mass Market
- MARKETING CHALLENGES IN THE 21st CENTURY:Connections with Customers
- STRATEGIC PLANNING AND MARKETING PROCESS:Setting Company Objectives and Goals
- PORTFOLIO ANALYSIS:MARKETING PROCESS,Marketing Strategy Planning Process
- MARKETING PROCESS:Analyzing marketing opportunities, Contents of Marketing Plan
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:The Company’s Microenvironment, Customers
- MARKETING MACRO ENVIRONMENT:Demographic Environment, Cultural Environment
- ANALYZING MARKETING OPPORTUNITIES AND DEVELOPING STRATEGIES:MIS, Marketing Research
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS:Developing the Research Plan, Research Approaches
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS (Continued):CONSUMER MARKET
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR:Model of consumer behavior, Cultural Factors
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR (CONTINUED):Personal Factors, Psychological Factors
- BUSINESS MARKETS AND BUYING BEHAVIOR:Market structure and demand
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Steps in Target Marketing, Mass Marketing
- MARKET SEGMENTATION (CONTINUED):Market Targeting, How Many Differences to Promote
- Product:Marketing Mix, Levels of Product and Services, Consumer Products
- PRODUCT:Individual product decisions, Product Attributes, Branding
- PRODUCT:NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, Idea generation, Test Marketing
- NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRODUCT LIFE- CYCLE STAGES AND STRATEGIES
- KEY TERMS:New-product development, Idea generation, Product development
- Price the 2nd P of Marketing Mix:Marketing Objectives, Costs, The Market and Demand
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:General Pricing Approaches, Fixed Cost
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Discount and Allowance Pricing, Segmented Pricing
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Price Changes, Initiating Price Increases
- PLACE- THE 3RD P OF MARKETING MIX:Marketing Channel, Channel Behavior
- LOGISTIC MANAGEMENT:Push Versus Pull Strategy, Goals of the Logistics System
- RETAILING AND WHOLESALING:Customer Service, Product Line, Discount Stores
- KEY TERMS:Distribution channel, Franchise organization, Distribution center
- PROMOTION THE 4TH P OF MARKETING MIX:Integrated Marketing Communications
- ADVERTISING:The Five M’s of Advertising, Advertising decisions
- ADVERTISING:SALES PROMOTION, Evaluating Advertising, Sales Promotion
- PERSONAL SELLING:The Role of the Sales Force, Builds Relationships
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:Managing the Sales Force, Compensating Salespeople
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:DIRECT MARKETING, Forms of Direct Marketing
- DIRECT MARKETING:PUBLIC RELATIONS, Major Public Relations Decisions
- KEY TERMS:Public relations, Advertising, Catalog Marketing
- CREATING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE:Competitor Analysis, Competitive Strategies
- GLOBAL MARKETING:International Trade System, Economic Environment
- E-MARKETING:Internet Marketing, Electronic Commerce, Basic-Forms
- MARKETING AND SOCIETY:Social Criticisms of Marketing, Marketing Ethics
- MARKETING:BCG MATRIX, CONSUMER BEHAVIOR, PRODUCT AND SERVICES
- A NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRICING STRATEGIES, GLOBAL MARKET PLACE