 |
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Lesson
10
ADVERTISING
MESSAGE
LECTURE
OVERVIEW
In
this lecture we will look
further at the universal
advertising standards partially
covered in the
last
lecture. We will also deal with the
designing of messages, format and
structure. We will
further
acquaint you with various
terms used in advertising and
key issues to be analyzed
for
advertisements.
We will also delve upon different
stages of developing a media
plan.
UNIVERSAL
ADVERTISING STANDARDS
�
Does
this advertisement position
product simply & with
unmistakable clarity?
�
Is
this advertising built on
compelling & persuasive consumer
benefit?
�
Does
this advertising create a
brand personality?
�
Is
this advertising unexpected?
�
Is
this advertising single
minded?
�
Does
advertising contain a power
idea?
�
Be describable in simple
word.
�
Likely to attract
attention.
�
Revolve around the
benefit.
�
Allow us to brand the
advertising.
�
Make it possible for the prospect
to experience the product or
service.
�
Does
advertising reward the
prospect?
�
Is
advertising compelling?
�
Is
advertising attractive?
�
Message
Generation.
�
Message
Evaluation & Selection.
�
Message
Execution.
DESIGNING
MESSAGE
1.
What to say?
(content)
2.
How to say logically?
3.
How to say symbolically?
(format)
4.
Who should say it?
(source)
Message
Content
Rational:
benefits like quality,
value,
performance,
economy etc.
Emotional:
Negative - fear, guilt,
shame
Positive
love, pride,
joy.
Moral:
directed
to audience for
used
for social causes.
ADVERTISING
MESSAGE FORMAT
Good
Sequence & manner of presentation
will result in maximum
effectiveness.
21

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
PRINT
MEDIA
headline,
copy, illustration & color will be
used.
RADIO
words
& voice quality
etc.
TELEVISION
words,
voice quality, body
language, facial expressions, dress,
posture etc.
Attractive
source is the best source e.g.
Celebrities, professionals are
used
As
spokes persons.
ADVERTISING
MESSAGE STRUCTURE
�
Order of presentation
�
Verbal vs.
visual
�
Sidedness single /
double
�
Refutation
BASIC
TERMS & CONCEPTS.
Media
Planning
a
process of determining how to
use time & space of media to
achieve advertising objectives.
Media
Plan
a guide for media selection -
plan of action.
Medium
a single form of communication e.g. TV,
radio, billboards, online
media.
Media
Mix.
--
combination of media to be used.
Media
Class.
--
type of medium like TV,
Radio etc.
Media
Vehicle.
--
single program, magazine or
radio station.
Media
Option.
--
full page / half page, color
or black & white
etc.
Above
the line Media.
--
such as broadcast, press, outdoor,
cinema, posters etc in which ad
agency gets
commission.
Below
the line Media.
--
such as direct mail, sales
promotion, exhibitions, sales
literature etc.
Reach
--
measure of the number of
different audience exposed at least
once.
Coverage.
--
refers to potential audience might be
exposed to the ad
message.
22
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Frequency.
--
refers to number of times
the audience is exposed to advertisement
message.
Scheduling.
--
specify how media options
are scheduled.
Flighting
Continuous Pulsing
Timing.
--
Selection of specific
times.
(Marketing
analysis imperative)
KEY
ISSUES TO BE ANALYSED
�
To whom should we advertise?
�
What internal & external
factors may influence media
plan?
�
Where & when should we
focus our efforts?
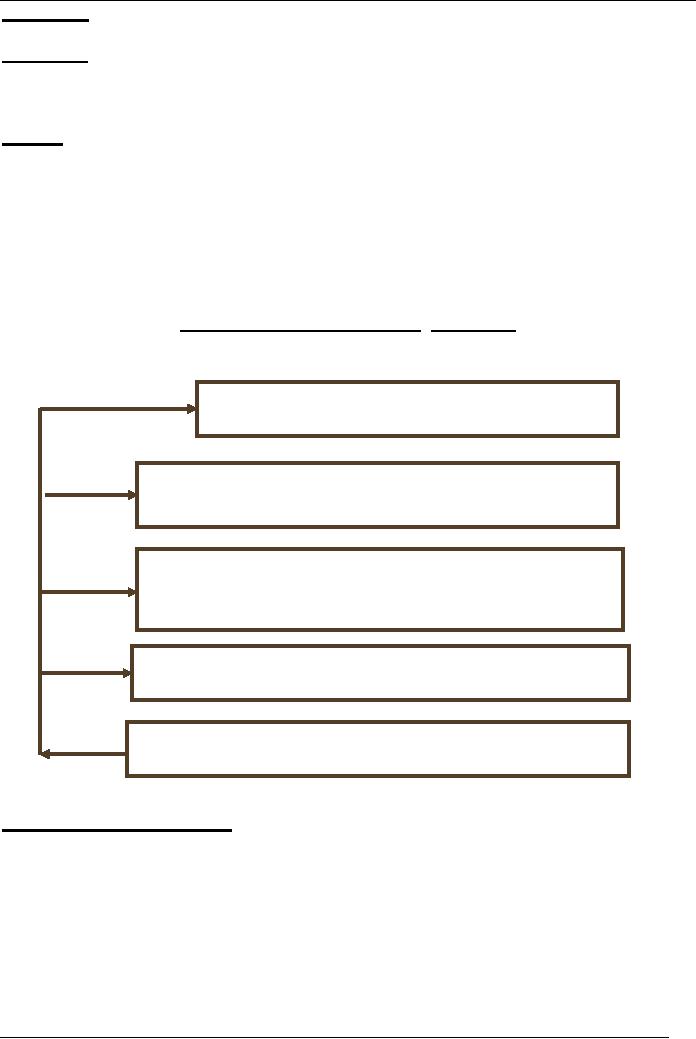
DEVELOPING
MEDIA PLAN -5
STAGES
Market
situation analysis
Developing
media objectives
Identification
& selection of media
strategy
(media mix)
Media
strategy implementation
Evaluation
control
MEDIA
PLAN EXECUTION
Criteria
for Execution
�
Media
Mix.
�
Target
Market Coverage.
�
Geographical
Coverage.
�
Scheduling.
�
Reach.
�
Frequency.
�
Creative
aspects & mood.
�
Flexibility.
23

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
�
Budget
considerations.
ADVERTISING
BUDGET
4
Methods to determine
�
AFFORDABLE
RATE.
�
PERCENTAGE
OF SALES METHOD.
�
COMPETITIVE
PARITY METHOD.
�
OBJECTIVE
& TASK METHOD.
24
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:Its growing importance, Explanation of Personal and non-personal selling
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:ADVANTAGES, Communication, Information, Various Media
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING, IMPACT OF ADVERTISING
- ADVERTISING AND SOCIETY:PRACTICAL BENEFITS, ETHICS IN ADVERTISING, Marketplace & Market space
- MARKETING TOOLS:COMPONENTS OF MARKETING MIX, PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE (PLC) CURVE
- MARKETING TOOLS:SWOT Analysis, Contents & Structure, ROLE & FUNCTION OF ADVERTISING
- ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING:Structure of an Advertising Agency, How to Select an Advertising Agency
- ADVERTISING PLANNING:ADVERTISING OBJECTIVES, Types of Advertising, Positioning Strategies
- POSITIONING:BRANDING, 7 Steps of Creative Process, UNIVERSAL ADVERTISING STANDARDS
- ADVERTISING MESSAGE:Message Content, BASIC TERMS & CONCEPTS
- ADVERTISING BUDGET:4 Methods to determine, ADVERTISING RESEARCH, ADVERTISING RESEARCH
- ADVERTISING REACH:BROAD COMMUNICATION OBJECTIVES, ADVERTISING COPY METHODS, MEDIA RESEARCH
- PRE – PLACEMENT EVALUATION:ACCOUNT PLANNING, MARKET, COMPETITION
- WORKING OF ADVERTISING:12 Steps to develop effective campaign, SOURCE or THE ADVERTISER
- ADVERTISING RESPONSE HIERARCHY MODELS:AIDA MODEL, PROCESS REQUIRED TO GET BIG IDEA
- PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGIES:Procedure to Handle Problems, In brief, Eight principles apply to consumer behavior
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR:ADVERTISING APEALS, MEDIA MIX DECISIONS, Target Rating Point (TRP)
- CREATIVITY IN ADVERTISING:Three aspects are most accepted, Four Rules of Creativity
- COPY WRITER:CHARACTERISTICS OF COPYWRITER, IMPORTANCE OF LANGUAGE
- WHY ADVERTISING:Advertising & Market Education, ADVERTISEMENT CAMPAIGNS
- METHODS TO APPRECIATE A PROBLEM:SPONSORSHIP—an important tool, Special Characteristics
- IMPORTANT TOOL OF ADVERTISING:TELEVISION ADVERTISING, TRANSIT ADVERTISING
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Banners, Logos, Email Ads, Keywords on Search Engines, New Developments
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Structural Challenges, Adobe Photoshop, JAVA, HTML, DHTML, ASP & JSP
- SALES PROMOTION:Consumer Oriented Promotion, HOW TO USE TRADE PROMOTION, Dealing with the Trade
- PUBLICITY:PERSONAL SELLING, ROLE OF SALES PERSON, FUTURE OF GLOBAL ADVERTISING
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:Competitors, The Target Buyer, Segmenting your Market, FUTURE OF MARKET GROWTH
- MARKETING PLAN:Situational Analysis, Macro – Environment Situation, Marketing Objectives, Financial Objectives
- MARKETING PLAN:PROMOTING BUSINESS IN LOW COST, SUPPLY CHAIN, BUYER IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS:CHANNEL BUYERS, HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS 14 RULES
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:HOW TO KEEP CLIENTS (10 Ways), Three Points for Consideration
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:ADVERTISING WITHOUT AN AGENCY, LOGO AND CORPORATE IDENTITY
- NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING:AD PRODUCTION,TYPES OF NEWSPAPER ADS, CIRCULATION
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIUM:HOW TO USE MAGAZINES, HOW TO USE RADIO, Daypart buying options
- UTILITY OF VARIOUS MEDIA:TAPE OR FILM, UTILITY OF TV, DIRECT MAIL PACKAGE
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIA:POINT OF PURCHASE (POP), TRANSIT ADVERTISING, LIMITS OF ADVERTISING
- CONTINUOUS TRACKING:PLANNING CAMPAIGN, HOW TO UNDERSTAND ADS, ASK BASIC QUESTIONS
- SEASONAL ADVERTISING:MAXIMIZING IMPACT, THE WEB ADVERTISING, MEASURING ADVERTISING
- COMPONENTS OF ADVERTISING:BUY - OLOGY OF MIND, BUY - OLOGY OF MIND
- CRITICISM ON ADVERTISING:SHOULD ADVERTISING BE ABOLISHED,
- EFFECT OF ADVERTISING:HOW TO PROMPT AWARENESS, CREATING DESIGN THAT SELLS
- CREATING EFFECTIVE DESIGN:LANGUAGE OF TYPOGRAPHY, HEADLINES THAT COMMUNICATE
- WORKSHEETS:DEMOGRAPHICS OF YOUR TARGET, YOUR COMPETITOR
- GLOSSARY OF ADVERTISING:ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE, PROOF, VOICE OVER
- CONCEPT OF AN AD:HOW TO DEVELOP A CONCEPT OF AN AD