 |

Human
Resource Management
(MGT501)
VU
Lesson
13
STRATEGIC
PLANNING AND HRIS
After
studying this chapter, students should be
able to understand the
following concepts:
Strategic
Planning
Human
Resource Information Systems
(HRIS)
Relationship
of HRIS with overall
MIS
A.
Strategic
planning:
It
is the process by which top
management determines overall
organizational purposes and
objectives
and how they are to be
achieved. The linking of HRM
with strategic goals and
objectives
in
order to improve business
performance and develop organizational
cultures that foster
innovation
and flexibility." The role
of HR in the strategic planning process
depends on the
organization's
view of HR. There are three
views detailed in the text
which involve HR as an
operational
function, HR as a "fitting" function,
and HR as an equal partner in the
strategic
planning
process. Obviously, it is our
contention that the latter is the
appropriate view. In this
view,
HR's role would include environmental
scanning, competitive intelligence,
internal strengths
and
weaknesses analysis, and the
implementation of the strategies. HR
process involves following
activities
or steps.
I.
HR Planning Process:
a.
Determine the organizational
mission:
It
states Organization's overall purpose
and basic business scope
and operations it provides
information
like, why does our
organization exist? What unique
contributions can it
make?
b.
Scan the organizational
environment.
This
is also known as SWOT
analysis through this process
organizations identify
different
opportunities
available in the market and the
threats that can be faced by
the organization,
and
the weaknesses and strengths
possessed by organizations are
also measured and
identified
through this process.
c.
Set strategic
goals:
To
achieve the overall mission or
purpose of the organization it is required to set
specific
long-term
and short term objectives and
goals. The goal can be
defined as desired
outcomes
to accomplish mission. Following
are the characteristics of effective
goals.
�
Specific
�
Challenging
�
Measurable
d.
Formulate a strategic
plan:
Courses
of action is designed to meet strategic
goals, also specifies
functional or
departmental
goals are selected at this
step.
II.
Strategic Planning and Strategic
Trends
a.
The Basics of Strategic Planning
A strategy is the company's plan
for how it will
balance
its
internal strengths and
weaknesses with its external
opportunities and threats
and
maintain
a competitive advantage. Managers engage
in three levels of strategic
planning:
corporate-level
strategy, business-level competitive
strategy, and functional
strategies.
b.
The Strategic Planning Process
entails conducting a SWOT analysis to
identify its
strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities, and
threats.
c.
Basic
Strategic Trends
Globalization
refers to the tendency of firms to extend
their sales,
ownership,
and/or manufacturing to new markets
abroad. For
62
Human
Resource Management
(MGT501)
VU
businesses
everywhere, the rate of globalization in
the past decade has
been
enormous, and has several
strategic implications for firms.
Technological
Advances have been forcing,
and enabling, firms to
become
more competitive.
The
Nature of Work is changing
due to new technological
demands.
The
Workforce demographics are
changing as well. It's
becoming
more
diverse as women, minority-group
members, and older
workers
enter
the workforce.
d.
Managerial Consequences of the Basic Trends
Managers have to craft strategies
that
balance
opportunities and threats
(like those previously discussed)
with their firm's
strengths
and weaknesses, such as
global expansion and
improved competitiveness
strategies.
These types of strategies
are driving other organizational
changes.
III.
HR's Strategic
Role
a.
HR's
Evolving Role It's the
firm's workforce that provides
the
competitive
advantage for the firm.
HR's role is shifting
from
protector
and screener to strategic partner
and change agent.
b.
Strategic Human Resource
Management refers to improving
business
performance
and developing an organizational culture that
fosters
innovation
and flexibility by linking HRM
with the strategic goals
and
objectives
of the firm.
c.
HR's
Role As a Strategic Partner
can be seen as either adapting
individual
HR practices to fit specific corporate
and competitive
strategies
or as an equal partner in the strategic
planning process.
1.
HR's
Role in Executing Strategy
Execution has been HR's
traditional
strategic
role.
2.
HR
and Value Chain Analysis
Strategy execution usually involves
identifying
and
reducing costs, and therefore
value chain analysis.
3.
HR's
Role in Formulating Strategy HR
management can play a role
in
environmental
scanning by assisting in identifying
and analyzing external
opportunities
and threats that may be
crucial to the company's
success.
B.
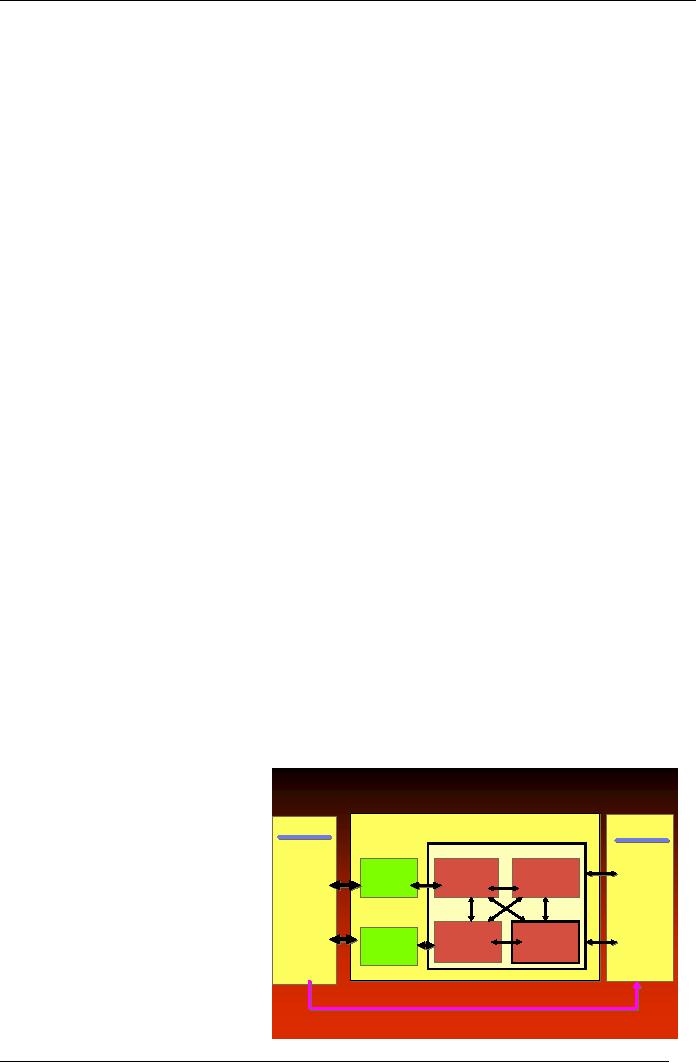
Human
Resource Information
System
HRISs
are systems used to collect,
record, and store, analyze,
and retrieve data concerning
an
organization's
human
resources.
The collection of
information
on aspects of
work
life as diverse as salary
M
anag er
M
anag em en t Inform ation S
ystem
Environment
and
payroll, compensation,
De
veloping inform
ation
leave,
accidents,
An
aly sis
Assessing
Internal
Managem
ent
superannuating
and employee
inform
ation
Micro-
records
intelligence
needs
Environment
benefits
has always been part
P
lann ing
forces
of
the human resource
Leading
M
anagem ent
manager's
function. In the
decision
Research
Distributing
Control
support
early
history of
personnel
inform
ation
Macro-
analysis
environment
management,
administrative
forces
aspects,
including
data
M
anag em en t decisions and
com m unication
collection,
took up a great deal
of
time. Reviews of employee
63

Human
Resource Management
(MGT501)
VU
salary
and leave entitlements often dominated
the activities of earlier personnel officers,
reflecting
both
management priorities and
their own clerical
backgrounds.
Such
early information systems
were manual, and were mainly
used to notify employees of
leave
entitlements,
to ensure accurate salary
and wage payments and to
process workers'
compensation
and
superannuating claims. The
data was seldom used to
predict trends, identify problem
areas and,
or
aid in the longer-term staffing
process.
I.
The development of human resource
information systems
(HRIS)
In
the early development of human resource
management, information systems,
although often
accurate
and comprehensive, were mainly
used for administrative and operational
purposes. Forms
were
used to collect leave requests,
workers compensation and
accident data, and salary
variation
and
superannuation entitlements. During the
1970s and 1980s, several
factors radically
changed
attitudes
towards human resource
information systems. The
increasing complexity of
payroll
systems
in this period demanded more
flexibility in, and access
to information system. These
needs
happily
coincided' with the development of increasingly
sophisticated computer hardware
and
software
systems. In large organizations,
centralized payroll processing
sections began to be
separated
from other human resource
functions. Some organizations contracted
their payroll
responsibilities
to external payroll bureaus with
greater technological expertise, and
for reduced
costs.
II.
Nature and benefits of
HRIS
Modern
human resource information
systems are comprehensive,
accurate and accessible
systems
for
recording employee and work
data relevant to HRM, HR and
organizational planning.
An
HRIS is:
The
system used to acquire,
store. Manipulate, analyze, retrieve
and distribute pertinent
information
regarding
an organization's human resources. Its
purpose is to facilitate, or support, straight,
tactical
and
operational decision making, to avoid
litigation, to evaluate programs,
policies, or practice
and
daily
operations
Specific
benefits of such systems include:
i.
Improved
planning and program development using
decision support software.
Faster
information
processing and improved
response times
ii.
Decreased
administrative and HR costs
iii.
Accuracy
of information
iv.
Enhanced
Communication at all levels.
Not
all systems fulfill all
these requirements, nor is
such a complete system
suitable for all
organizations.
Essentially however all HRIS contain
information on:
�
Employees
�
Jobs
and work conditions
�
Positions
�
HR
events (e.g. recruitment. training
and development, performance appraisals,
and
terminations).
III.
Uses of HRIS
Comprehensive
and integrated information systems
can be used widely -in
administrative, operational and
strategic
fields by HR and other managers. On the
operational level HRIS data can be
used to identify
potential
internal applicants for job
vacancies, saying external recruitment
costs and assuring employees
of
career
opportunities. Strategically, such
information may be used to
gauge the effectiveness of current
recruitment
or promotional systems, their
costs and/ or
benefits, and
enable subsequent changes of
direction
in
line with proposed organizational
strategies.
IV.
Strategic HR planning and HR information
systems
Proactive
HR managers ensure that
their HRIS contributes to organizational
performance. A recent
development
in the uses of HRIS in many
has been the linking of 'benchmarking'
practices to the design,
choice
and implementation of such
systems as a directly strategic
initiative. Integration with
organizational
64

Human
Resource Management
(MGT501)
VU
strategic
objectives is achieved by the subsequent
establishment of performance targets
and quantitative
measures.
As a strategic 'tool', HRIS
can be used to contribute to the
development and modification of HR
plans,
on both quantitative and
qualitative bases, and to
feed into specific HRM functions. HR
data, if
collected
effectively and contained within
computerized, accessible systems,
can both compare
organizational
HR 'bottom line' outcomes by HRM
function, between functions
and with national or
international
performance benchmark
V.
HRIS Applications
A
computerized HRIS contains
hardware and software applications
that work together to help
managers
make
HR decisions. HRIS software applications
currently available to business include
those for employee
information,
applicant tracking, skills inventory,
payroll, and benefits
administration.
VI.
HRIS Security and
Privacy
The
HR department must develop policies and
guidelines to protect the integrity
and security of the
HRIS
so
that private employee
information does not fall
into the wrong hands. To maintain the
security and
privacy
of HRIS records, companies should
control access, develop policies
and guidelines that govern
the
utilization
of information, and allow
employees to check their
records.
VII.
Purposes of HRIS
All
organizations and their HR
mangers need to consider whether
their HRIS will be primarily
used for
collecting,
analyzing, interpreting or reporting
employee information. The
nature of the system
chosen
should
reflect this primary purpose, based upon
a realistic analysis of needs
prior to its
introduction.
Small
organizations with stable workforces
and secure markets do not
require complicated data analysis,
but
can
benefit from comprehensive
and accurate databases for
reporting purposes. On the other
hand, large
organizations
in competitive and dynamic
industries demand strategic
HRIS. Every organization needs
to
assess
its particular needs and
identify the most appropriate information
system for its chosen
purposes.
VIII.
Common HRIS Functions
Mainly
following functions are
performed by the HRIS in different
organizations.
�
Job
analysis information can be
placed in the HRIS.
�
The
program can write job
descriptions and job
specifications.
�
Constant
monitoring of compliance with
EEO legislation.
�
Maintain
records of rejected
applicants.
�
Saves
money and time in compiling
reports.
�
Ensure
that women and minorities or
not be adversely
affected.
�
Track
minority hiring, recruitment, and
advancement.
�
Forecast
supply and demand of labor
from both the internal and
external labor markets.
�
Useful
for internal recruiting.
�
Can
post job opening for
employees to access.
�
Can
search for match between
job specifications and applicant
qualification.
�
Applicant
tracking system.
�
Administering
and scoring ability
tests.
�
Scanning
resumes submitted online (web
based or e-mail) or in person
(or mail).
�
Structured
interviews.
�
Matching
qualifications with open positions (finding a
good fit).
�
Also,
consider budgetary
concerns.
�
Help
with registration, tracking training,
monitor training costs, and
schedule training.
�
Used
to deliver training.
�
Career
and managerial succession
planning.
�
Used
to provide assessment tests to
help employee's plan their
own career.
�
Predict
career paths.
�
Provide
PA instruments and
results.
65

Human
Resource Management
(MGT501)
VU
�
Comparisons
between employees, groups, or
supervisors ratings.
�
Monitor
attendance.
�
Monitor
compliance with Labor
Standards.
�
Individual
sale data can be accessed
(tracking commissions).
�
Benefits
can be managed and
administered by computers.
�
Planned
raises and wage
histories.
�
Provides
reports for Occupational Safety and
Health Administration
(OSHA).
�
Track
hazardous materials.
�
Track
accidents and costs of
accidents.
�
Record
employee safety
training.
�
Record
employee exposure to various
conditions and
chemicals.
�
Track
disciplinary actions and
grievances.
�
Labor
contract data.
�
Worker
seniority list. Etc..
C.
Relationship of HRIS with overall
MIS
Information
is the backbone of healthy and efficient
business management. An information
system allows
the
collection and processing of
data to produce useful
information for designated
users at each level of
management.
Information management must
conform to well-defined principles, run
on appropriate
software,
and be completely adapted to your
organization within an integrated system
usually known as
Management
Information System (MIS).
Management Information System is the
entire set of systems
and
activities
required to manage, process, and
use information as a resource in the
organization. Stated slightly
differently,
MIS is the management and
use of computer-based systems,
computer-resident data,
and
telecommunications
for the support of business
decision processes. HRIS is the
part of MIS that
provides
the
information regarding workforce in the
organization and facilitates the decision
makers in decision
making
process in this regard.
Key
Terms
Strategic
planning:
It is the
process by which top
management determines overall
organizational purposes
and
objectives and how they are
to be achieved.
Human
Resource Information System:
HRISs
are systems used to collect,
record, and store, analyze,
and
retrieve
data concerning an organization's
human resources.
66
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO HRM:Growing Importance of HRM, Road Map of the Course
- ESSENTIALS OF MANAGEMENT:Concepts and Essential of Management, Manager’s Roles
- ORGANIZATION AND COMPONENTS OF ORGANIZATION:Open versus Closed Systems, The Hawthorne Studies
- PEOPLE AND THEIR BEHAVIOR:Why to work in organizations?, The Goals of Organizational Behavior
- INDIVIDUAL VS. GROUP BEHAVIOR:What Are Roles?, Problem solving Team
- PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT TO HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT:Records and Administration, Competitive Advantage
- HRM IN A CHANGING ENVIRONMENT:Productivity, New Trends at Work Place
- How organization Cultivate a Diverse Workforce, STEPS TOWARD MANAGEMENT OF DIVERSITY
- FUNCTIONS AND ENVIRONMENT OF HRM:Compensation and Benefits, Safety And Health, Interrelationships of HRM Functions
- LINE AND STAFF ASPECTS OF HRM:Authority, Line versus Staff Authority, Staff Manager
- LEGAL CONTEXT OF HR DECISIONS:Doing the Right Thing, Affirmative Action, Unintended Consequences
- HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING (HRP):Benefits of HR Planning, Forecasting Human Resource Availability
- STRATEGIC PLANNING AND HRIS:HR’s Strategic Role, Human Resource Information System, Common HRIS Functions
- JOB ANALYSIS:Purposes of the job Analysis, Questions Job Analysis Should Answer
- JOB ANALYSIS:Methods of Collecting Job Analysis Information, Observation, Source of Data
- JOB ANALYSIS (CONTD.):SURPLUS OF EMPLOYEES FORECASTED, Diversity through Recruiting Efforts
- SOURCES OF RECRUITMENT:ALTERNATIVES TO RECRUITMENT, Quantity of the Applicants, Quality of the Applicants
- SELECTION:Initial Screening, Advantages of Successful Screening
- SELECTION TESTS:Characteristics of Properly Designed Selection Tests, Guidelines for Conducting an Interview
- SELECTION PROCESS… CONTD:Background Investigations, Physical Exam, Selecting Managers
- SOCIALIZATION:Compensation and Benefits, Team Membership, Stages in socialization Process, Training and Development Trends
- TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT:Learning, Phases of Training, Why Transfer of Training Fails
- MAXIMIZING LEARNING:Following up on Training, Repetition, Feedback, Purposes of T & D
- CAREER MANAGEMENT:Individual career planning, Career Planning and Development Methods
- PERFORMANCE:Determinants of Job Performance, Why is performance measured?, Performance Management
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:What to Evaluate, The Appraisal Interview, PROBLEMS IN PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
- JOB EVALUATION AND PRICING:THE APPRAISAL PERIOD, Ranking method,
- COMPENSATION SYSTEM:Pay, Job Pricing, Compensation: An Overview, Compensation Surveys
- BENEFITS:Total Compensation, Discretionary Benefits (Voluntary), Workplace Flexibility
- ROLE OF MONEY IN PERFORMANCE OF EMPLOYEES:Types of Pay-for-Performance Plans, Empower Employees
- MOTIVATION:The Motivation Process, Motivational Theories, Challenges of motivating employees
- OCCUPATION, HEALTH & SAFETY:Physical Conditions, Accident Investigation, Smoking in The work place
- STRESS MANAGEMENT:Symptoms of Stress, Managing Stress,
- COMMUNICATION IN ORGANIZATION:Burnout, Social Support at Work & Home, Communication in organization, Meetings
- TRADE UNIONS:Collective Bargaining, The HRM Department in a Nonunion Setting, Phases of Labor Relations
- CONFLICT AND NEGOTIATION:Transitions in Conflict Thought, Individual Conflict Management Styles
- POWER AND POLITICS:Sources of Power, Advantages and Disadvantages of PowerPower and Politics in Context
- EMPLOYEE RIGHTS AND DISCIPLINE:Contractual Rights, Management Rights, Disciplining Employees,
- DISCIPLINE (CONT...):Factors to Consider when Disciplining, Disciplinary Guidelines, Employee Separations
- LEADERSHIP:The Leader’s Behavior, Situational Theories of Leadership, Becoming a Leader
- REVISION (LESSON 12-21):Plans, Job Specification, Human resource planning, Selection Process, Corporate Culture
- REVISION (LESSON 22-26):Training, Case Study Method, Training, Performance
- REVISION (LESSON 27-35):Classification Method, Compensation, Empowerment, Mediation
- INTERNATIONAL DIMENSIONS OF HRM:Global Corporation, Type of staff members, Approaches to Global Staffing
- CONCLUSION & REVIEW:Strategies for Gaining Competitive Advantage, High-performance Work System