 |

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Lesson
04
PERCEPTION
AND INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOUR
"Perception
is a process through which people
select, organize, interpret, retrieve
and respond to
information."
Perception
is word which means "a
process of knowing." How do
you know a reality, how
you see things
and
interpret them. It may be
related to reality or may
not.
Three
concepts of personality:
Communication
has many forms. Everyone who
communicates through a picture, verbal
design or with a
landscape
has its three
meanings.
(1)
Intended meanings, the
meanings which I want to convey to the
audience.
(2)
The
second meaning is dictionary
meaning e.g.
communication material, words I have
used.
(3)
Most
important is "perceived
meanings" the
meanings that you are
getting .your meanings will
b
based
on meanings that you are
getting from the other person's
speech.
So
perceived meanings are critically
important, e.g. during a
lecture many a time what I say
you don't take it
the
way I said and this leads to
misunderstanding. The difference between
intended and perceived
meanings
is called misunderstanding.
Life
World
In
sociology there is a concept
"life
world".
Every person has a different
life world. What are
his life
experiences?
Due to different experiences a
person views different things in
different way, e.g. I was
an
M.A
student. The psychology
professor brought a vague
painting and placed it on the wall.
Then he asked
the
student to write a story on it. There
were 20 students and all of
them write a different story. The
idea is
actually
depicted differently by all the
students because everybody interpreted a
same piece of
information
according
to his/her own experiences,
although the source of information
was same. "Truth and
False"
may
be very important but in terms of
determining the behaviors of the individuals
"perception" is
important
but not the truth, e.g. a
young boy and man came
home late at night and
thought that if I
will
knock
at door my dad will be angry
so he climbed the gate and went in just
to avoid his dad's anger.
Dad
thought
he is a thief, he picked up the gun and he
shot him dead. Now what is
important more is "truth
or
perception".
In this case it is clear that perception
played a role but truth
was son but his action
was due to
perception.
So, it is perception which determines
individual's behavior not the
truth.
Perception
of individual is reality for that
individual. If you understand this
thing you would know
that
source
of major conflicts among people is due to
different perception of different
individuals.
Whenever
you get a message you
try to understand that this
message has some intended
meanings and
these
meanings came from culture or
from your own socialization,
e.g. a delegation from china went
to
Canada,
during lunch some Chinese
took a burp at the lunch, the Canadians
felt a disgust and thought
that
Chinese
are ill mannered and
don't know how to behave in
a meeting. But someone other
may understand
a
different meaning by that
burp and may thought
that Chinese are
appreciating food by taking
burp.
Chinese
are conveying it good about to their
host but the Canadians are
taking it negatively. This is a
difference
between intended and
perceived meaning. Source of
misunderstanding is the gap
between
intended
and perceived
meaning.
The
gateway arch in mono Louis
height and width are
same 192 m but it is just a vertical,
horizontal
illusion
that which cause people to see vertical
lines longer as compare to horizontal
lines. I took this
slide
from
encyclopedia. It shows that the
height is taller than the width. It is
just an illusion. As it is
illusionary
to
see such a thing and you
get a different
message.
9
Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
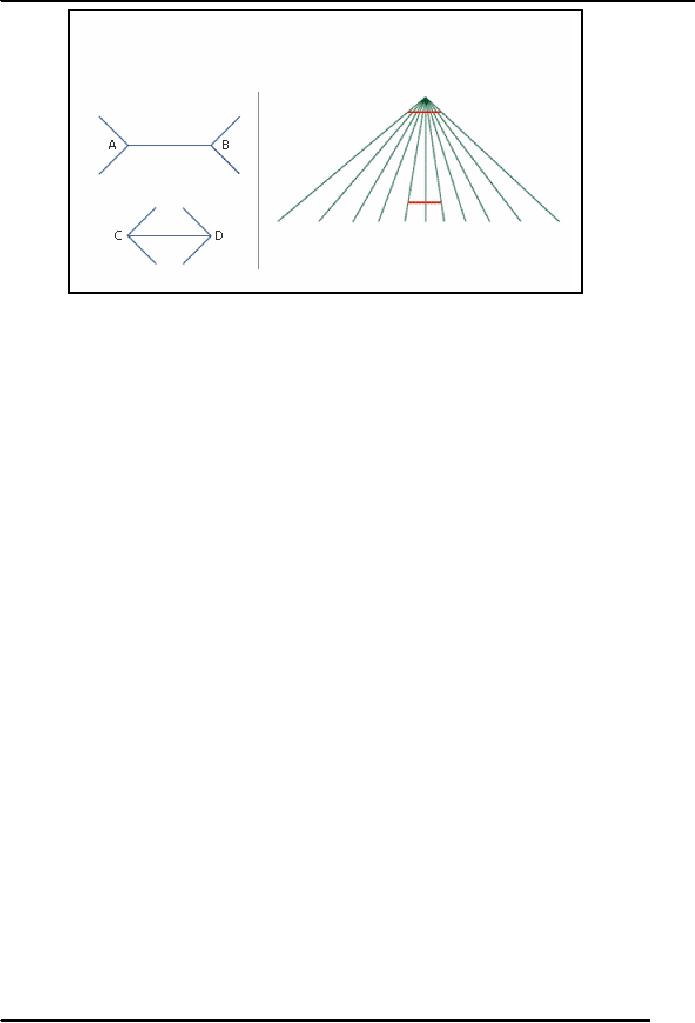
In
this illusion you look on
left the length of lines A, B, C, D.
you will notice that lines
A, B will look
longer
than the line C, D although they are
same in length. On right there is a
"PONZO" illusion in
which
you
see red lines. The top
red lines look larger than
lower red lines, but
all are same in real.
These are
illusion.
This is communication in the form of picture.
You are going to make judgment on the
basis of
truth
or perception. As earlier a father shot
his son because he perceived
him to be a thief.
Any
message or letter through
which you communicate, you
have to put yourself in others
shoes to
understand
the meaning others want to convey
you.
How
you develop perception: you develop perception
through your experiences,
circumstances and action.
All
these things influence the process of perception
development. Perception is a process of giving
the
meaning,
the things influence it. And which
are the things that forces people to
perceive the things in a
way,
which are the factors that
influence the process of perception. How it
influences the way you look
on
different
things.
Bias
in Perception
(Development
of Perception)
Following
are main factors that
influence the process of perception
development.
(1)
Stereotype
images
(2)
Expectations
(3)
Projection
(4)
Interest
(5)
Selective
exposure
(6)
Frame
of reference
If
you look on one by one,
you can realize that
how each one of them influence the
process of perception
development.
Now as I am a professor of sociology. If
you ask that is there
any structural flaw in
this
building.
I can not look at those
flaws. I can look on
people's behavior, communication pattern. I
can look
and
describe what is going on in society, but
I can not look on the design
of the building because the
focus
of
my knowledge is toward another direction.
Structural engineer can look
on these. This bias is due to
my
education,
my interest. I look on things from my
own point of view. A
structural engineer can not
look on
human
relations. The bias comes
through your education,
interest and life
experiences. My experiences
are
due
to the teaching of sociology, by practicing of sociology. So I am
so confident to look on the things
in
term
of social dynamics, human relationship,
personal and interpersonal relationship. On the
other hand a
technical
man, an engineer who is in the lab
all the time handling with the
instruments may not know
many
human
dynamics as a person like
me. We as a sociologist better understand
the behavior of mobs,
crowds
as
compare to those who are
working with instruments/
equipments.
10

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Therefore
the meaning I am trying to deliver is
that the perceptions vary because
life experiences are
different.
How this bias of different
individual develops and how
different perception of particular things
occurs.
(1)
Stereotype Images
We
have certain images about
different things i.e. about caste. We
ask about someone's caste
because we
have
certain image about that
caste i.e. Sheikh, Rajput,
Kashmiri etc. These images
are stereotype
images.
So
that we have some knowledge or
some information about that
person. If some one came in
contact
with
us we want to know about that
person's sex, age just to
have a view that what type of
life experiences
that
person could have. Society
tells us about those images.
Different individuals with
different age, sex
can
have
different life experiences,
i.e. education, occupation, age
and sex all create
different type of images.
We
make guess about peoples after
knowing their
qualification.
So
stereotype images are very
important in term of developing your
biases about different
peoples
according
to your own perception.
(2)
Frame of Reference
It
looks on things with narrow focus. An
individual works in an organization. That
organization wants
more
work from that individual
for efficiency but the individual
think that organization wants
extra work
for
that amount. Now that organization
and individual both have
different focus. Organization is
looking
for
efficiency. On the other hand if there is
a union in that organization, it may be
look on different things
like
being exploited. Individual look on the
things from there narrow
frame of reference, narrow in the
sense
that they have limited
focus. They never look beyond; they
only look within their
frame of interest.
11
Table of Contents:
- HUMAN RELATIONS:Some Guidelines for Effective Human Relations, Communication has 3meanings
- CULTURE AND PERSONALITY:Definition of sub culture, Definition of Personality, Types of Persons
- PERSONALITY AND STRESS:Personality, PERSONAL TOOLS TO CONTROL STRESS
- PERCEPTION AND INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOUR:Three concepts of personality, Bias in Perception
- PERCEPTION AND GROUP BEHAVIOR:Characteristics of Groups, Individual and Group Behavior
- ATTITUDE AND BEHAVIOUR:Types of Attitudes, Steps to turn attitude into action
- PERSONAL MOTIVATION AND ACHIEVEMENT:Needs and Motivation, Self-discipline and motivation
- SOLVING PROBLEMS SKILLFULLY:Problem solving and cognition, Ways to solve problems
- CREATIVITY IN PROBLEM SOLVING:Barriers to creativity, Tips to solve problems creatively
- HANDLING PERSONAL ISSUES:Self-Defeating Behaviour, Positive attitude to tackle personal problems
- CONFLICT RESOLUTION:WHY SO MUCH CONFLICT EXISTS, TECHNIQUES FOR RESOLVING CONFLICTS
- COMMUNICATION AND HUMAN RELATIONS:Process of communication, Improving gender barriers to communication
- ORGANIZATIONAL COMMUNICATION:To improve listening skills, Types of organizational communication
- UNDERSTANDING COMMUNICATION STYLES:Modeling communication style, Sociability continuum
- SELF-ESTEEM:Building process of self-esteem, Self-esteem and public image
- BUILDING SELF-CONFIDENCE:The importance of self-confidence and self-efficacy, Balanced Self-Confidence:
- BECOMING A LEADER-1:Assessing leadership role, Traits and Characteristics of Effective Leaders
- BECOMING A LEADER-II:Theories of leadership, Developing leadership potential
- GLOBALIZATION AND CROSS-CULTURAL DIFFERENCES:Religious Values and Bicultural Identities
- IMPROVING CROSS-CULTURAL COMPETENCE:Strategies to improve cross-cultural relations, More steps to improve Cultural Relations
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH MANAGERS:Impressing your manager, Coping with a problem manager
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CO-WORKERS:Make Co-workers feel important, Maintain Honest and Open Relationships
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CUSTOMERS:Salesperson Represents the Business, Approaching the Customer, Excuses vs. Objections
- CHOOSING A CAREER-1:Ten Myths about Choosing a Career, Attitude toward and Perceptions about Myself
- CHOOSING A CAREER-II:Choosing a career and developing a portfolio Career, Suggestions for career Preparation
- FINDING A JOB:Targeting your job search, The Internet and Résumé Database Services, Extreme Job Hunting
- SIGNIFICANCE OF RESUME:Major types of resumes, Electronic Submission of the Résumé
- IMPROVING INTERVIEW SKILLS:Successful interview, Knowing the employer or Organization
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-1:Reasons of procrastination, Techniques for Reducing Procrastination
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-2:Developing the proper attitudes and values, Time-management techniques
- NEW MODEL OF CAREER ADVANCEMENT:Career portability, HUMAN RELATIONS SELF-ASSESSMENT
- TAKING CONTROL OF YOURSELF:Develop Outstanding Interpersonal Skills, Business etiquettes
- EXERTING CONTROL ON OUTSIDE ENVIRONMENT:Important communication tip, Exerting control over the outside world
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-1:Your personal financial plan, Steps in budget making
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-2:Basic investment principles, Tolerance for Investment Risks, Types of investments
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-1:Finding happiness and enhancing your personal life, The key to happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-2:The Five Principles of Psychological Functioning, Your mind and Happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-3:Need for intimacy, Working out issues with relationships
- APATHY AND ITS REMEDIES:Let us try to understand the various definitions of apathy, Coping strategies for apathy
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-1:Influence of Culture, Common ethical problems
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-2:Common ethical problems, Guidelines for Behaving Ethically
- HELPING OTHERS GROW:Being a Nurturing, Positive Person, A list of mentoring behaviour, Coaching skills and techniques
- REVIEW-I:What is a Human Relation?, Meanings of Communication, Two types of stress, Some personal problem, Communication style
- REVIEW-II:Steps to build self-confidence, Globalization, Building Good Relations with Co-workers, Good work habits
- REVIEW-III:New model of career advancement, Choosing your investment, Tactics for Dealing with Difficult People