 |
Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Lesson
16
BUILDING
SELF-CONFIDENCE
"Confidence
gives you courage and
extends your reach. It lets
you take greater risks
and achieve far
more
than
you ever thought possible"
(Capitalism Magazine,
2002).
Self
Confidence:
Self-confidence
is extremely important in almost
every aspect of our lives,
yet so many people struggle
to
find
it. People who lack
self-confidence can find it
difficult to become successful. We
have learnt that
self-
esteem
is a sum-total of self-confidence and
self-respect. Self-respect mostly depends
upon self-confidence.
Self-confidence
is emphasized because of its importance
in self-efficacy and performing
well at job and in
personal
life. Many early careerists
need to develop their self-confidence
before they can be effective
leaders.
The
importance of self-confidence and
self-efficacy:
Self-confidence
is the ability and belief in
our self to do those tasks
that are given to us by our
self or by
other
people in our family or from
our employers. It is a kind of
mental and physical force to do the
job we
are
assigned to do.
For
solving day-to-day problems, a moderate amount of
self-confidence may be good enough
but growing
confidence
through doing of things can
lead to ever-increasing potential to do
more and more; and
thereby
attaining
successes throughout our
life.
Self-confidence
is also important because it
leads to self-efficacy (the belief in
one's capability to perform a
task).
An
experiment with unemployed people showed
that self-efficacy can be
boosted through training. A
leader
with
high self-efficacy will
usually believe that a task
is doable.
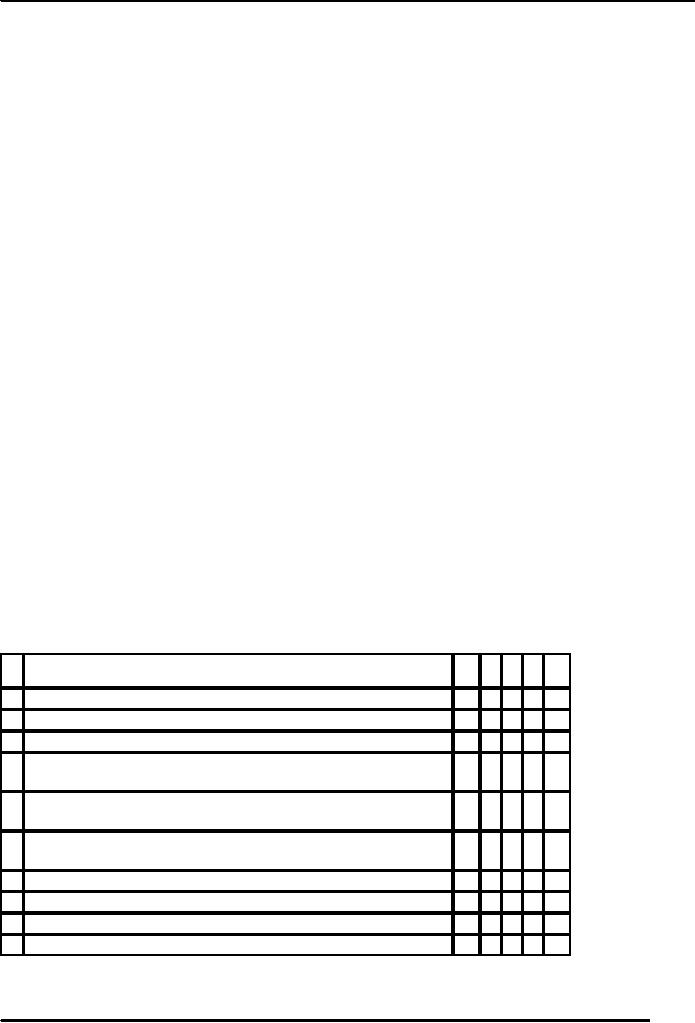
Assessing
self-confidence:
Self
confidence can be assessed. Here is an
instrument through which we can
find out the level of
self-
confidence.
Assessing the level of self-confidence we
can boost up the level of
confidence.
Indicate
the extent to which you agree
with each or the following
statement.
Use
a 1-5 scale: 1=disagree strongly;
2=disagree; 3=neutral; 4=agree;
5=agree strongly
Sr
Dimension
DS
D N A AS
1
I
frequently say to people, "I am
not sure".
5
4321
2
I
perform well in most
situations in life.
1
2345
3
I
willingly offer advice to
others.
1
2345
4
Before
making even a minor decision, I
usually consult with 5 4 3 2
1
several
people.
5
I am generally willing to attempt new
activities for which I have 1 2 3 4
5
very
little related skill or
experience
6
Speaking in front of the class or
other group is a frightening 5 4 3
2 1
experience
for me
7
I experience stress when people
challenge me on the spot.
5
4321
8
I feel comfortable attending a social event by
myself.
1
2345
9
I am much more of a winner
than loser.
1
2345
10
I am cautious about making substantial
change in my life.
5
4321
Total
score .........................
Scoring
and interpretation: Calculate
your total score by adding the
numbers ticked.
A
tentative interpretation of the scoring
is as follows:
45

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
45-50
Very
high self-confidence with
perhaps a tendency toward
arrogance
38-44
A
high, desirable level of
self-confidence
30-37
Moderate
or average self-confidence
10-29
Self-confidence
needs strengthening
Source:
DuBrin,
Andrew J. `Human Relations: Career
and Personal Success',
Pearson Prentice Hall,
2005,
p412.
Developing
self-confidence:
Self-confidence
really can be learned and
built on. And, whether you're
working on your own
self-
confidence
or building the confidence of people around you, it's
well-worth the effort! All
other things
being
equal, self-confidence is often the
single ingredient that
distinguishes a successful person
from
someone
less successful.
Self-confidence
is generally achieved by succeeding in a
variety of situations.
Specific
methods of boosting self-confidence are
given below.
Steps
to build self-confidence:
These
are certain steps which
can be followed to build up
self-confidence
A.
Write
down Personal Assets and
Achievements:
Reflect
on what's good about you to
increase self-appreciation and therefore
self-confidence. A written
list
of
assets is particularly useful. An
important supplement to listing
your own assets is hearing
the opinion of
others
on your good points.
List
of personal attributes:
We
must have an inventory of
our personal attributes.
·
Good
listener
·
Most
people like me
·
Good
handwriting
·
Good
posture
·
Inquisitive
mind
·
Good
at solving problems
·
Above-average
Internet search
skills
·
Good
sense of humour
·
Patient
with people who make
mistakes
·
Good
looking
·
Graduated
tenth in a class of 50
·
Achieved
first place in local cricket
tournament
·
Daughter
has an excellent
career
·
Good
mechanical skills including
automotive and computer repair
·
Work
well under pressure
·
Good
dancer
·
Friendly
with strangers
·
Great
physical health
·
Good
cook
·
Can
laugh at my own
mistakes
·
Favourable
personal appearance
·
Respectful
to your authorities
·
Made
award-winning suggestion that saved
company a lot of
money
·
Scored
winning goal in college
hockey match
·
Saved
a child from drowning
46

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
B.
Develop
a Solid Knowledge
Base:
A
bedrock strategy for projecting
self-confidence is to develop a base of knowledge
that enables a person
to
provide
sensible alternative solutions to
problems.
C.
Use positive self
talk:
A
basic method of building
self-confidence is to engage in positive
self-talk, saying positive things
about
oneself
to oneself. First, state the incident
that casts doubt about
self-worth. Second, state what the
incident
does
not mean, followed by third,
what it does mean. Fourth,
objectively account for the
cause of the
incident.
Fifth, identify ways to
prevent the incident from happening
again. Sixth, use positive
self-talk.
D.
Avoid Negative
Self-Talk:
Minimize
negative statements about yourself in
order to bolster self-confidence.
Negative self-statements
such
as "I may be stupid but..." and "I know
I'm usually wrong but..."
detract from
self-confidence.
E.
Use Positive Visual
Imagery:
Again,
visualization is important for acquiring
human relations skills. Positive visual
imagery is picturing a
positive
outcome in one's mind. The
technique is effective for gaining
control of an upcoming,
challenging
situation.
F.
Strive
for Peak
Performance:
Strive
to do the best what you can.
Peak performance is the mental
state necessary for
achieving maximum
results
from minimum effort.
a.
Experiencing
peak performance in various
tasks over a long period of
time would move a
person
toward
self-actualization.
b.
It involves extraordinary focus and
concentration.
c.
Peak
performers have a mission in
their work and personal
lives.
d.
Charles Garfield says that
peak performers have a mission in
their work and lives,
and are therefore
fully
committed.
G.
Bounce Back from
Setbacks and Embarrassments:
An
effective confidence builder is to convince yourself
that you can conquer
adversity such as setbacks
and
embarrassments,
thus being resilient. Do not take
set backs personally.
H.
Get Past the Emotional
Turmoil:
The
emotional impact of severe
job adversity can rival the
loss of a personal relationship, and
creates stress.
Accept
the reality of your problem and do
not take the setback personally.
Get help from your
support
network.
I.
Find
a Creative Solution to Your
Problem:
To
search for creative solutions to the
adversity problem, use the
problem-solving and
decision-making
steps
learnt in previous lectures.
Balanced
Self-Confidence:
Neither
being over-confident nor being under-confidence is
good for people. There must
be balance
between
the two extremes. Good
self-confidence is about having the right
amount of confidence, founded
on
your true abilities and skills.
With the right amount of self-confidence,
you will take informed
risks and
do
not stretch yourself unnecessarily. On
the other hand, if you are
under-confident, you'll avoid
taking
risks
and stretching yourself. In this way
you will not make
use of your potential fully.
So, self-confidence is
something
based on realistic expectations on
your skills and experience,
for achieving your
goals.
47

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
References:
Dubrin,
A.J. (2005). Human Relations:
Career and Personal Success.
Upper Saddle River, New
Jersey,
07458.
48
Table of Contents:
- HUMAN RELATIONS:Some Guidelines for Effective Human Relations, Communication has 3meanings
- CULTURE AND PERSONALITY:Definition of sub culture, Definition of Personality, Types of Persons
- PERSONALITY AND STRESS:Personality, PERSONAL TOOLS TO CONTROL STRESS
- PERCEPTION AND INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOUR:Three concepts of personality, Bias in Perception
- PERCEPTION AND GROUP BEHAVIOR:Characteristics of Groups, Individual and Group Behavior
- ATTITUDE AND BEHAVIOUR:Types of Attitudes, Steps to turn attitude into action
- PERSONAL MOTIVATION AND ACHIEVEMENT:Needs and Motivation, Self-discipline and motivation
- SOLVING PROBLEMS SKILLFULLY:Problem solving and cognition, Ways to solve problems
- CREATIVITY IN PROBLEM SOLVING:Barriers to creativity, Tips to solve problems creatively
- HANDLING PERSONAL ISSUES:Self-Defeating Behaviour, Positive attitude to tackle personal problems
- CONFLICT RESOLUTION:WHY SO MUCH CONFLICT EXISTS, TECHNIQUES FOR RESOLVING CONFLICTS
- COMMUNICATION AND HUMAN RELATIONS:Process of communication, Improving gender barriers to communication
- ORGANIZATIONAL COMMUNICATION:To improve listening skills, Types of organizational communication
- UNDERSTANDING COMMUNICATION STYLES:Modeling communication style, Sociability continuum
- SELF-ESTEEM:Building process of self-esteem, Self-esteem and public image
- BUILDING SELF-CONFIDENCE:The importance of self-confidence and self-efficacy, Balanced Self-Confidence:
- BECOMING A LEADER-1:Assessing leadership role, Traits and Characteristics of Effective Leaders
- BECOMING A LEADER-II:Theories of leadership, Developing leadership potential
- GLOBALIZATION AND CROSS-CULTURAL DIFFERENCES:Religious Values and Bicultural Identities
- IMPROVING CROSS-CULTURAL COMPETENCE:Strategies to improve cross-cultural relations, More steps to improve Cultural Relations
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH MANAGERS:Impressing your manager, Coping with a problem manager
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CO-WORKERS:Make Co-workers feel important, Maintain Honest and Open Relationships
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CUSTOMERS:Salesperson Represents the Business, Approaching the Customer, Excuses vs. Objections
- CHOOSING A CAREER-1:Ten Myths about Choosing a Career, Attitude toward and Perceptions about Myself
- CHOOSING A CAREER-II:Choosing a career and developing a portfolio Career, Suggestions for career Preparation
- FINDING A JOB:Targeting your job search, The Internet and Résumé Database Services, Extreme Job Hunting
- SIGNIFICANCE OF RESUME:Major types of resumes, Electronic Submission of the Résumé
- IMPROVING INTERVIEW SKILLS:Successful interview, Knowing the employer or Organization
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-1:Reasons of procrastination, Techniques for Reducing Procrastination
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-2:Developing the proper attitudes and values, Time-management techniques
- NEW MODEL OF CAREER ADVANCEMENT:Career portability, HUMAN RELATIONS SELF-ASSESSMENT
- TAKING CONTROL OF YOURSELF:Develop Outstanding Interpersonal Skills, Business etiquettes
- EXERTING CONTROL ON OUTSIDE ENVIRONMENT:Important communication tip, Exerting control over the outside world
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-1:Your personal financial plan, Steps in budget making
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-2:Basic investment principles, Tolerance for Investment Risks, Types of investments
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-1:Finding happiness and enhancing your personal life, The key to happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-2:The Five Principles of Psychological Functioning, Your mind and Happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-3:Need for intimacy, Working out issues with relationships
- APATHY AND ITS REMEDIES:Let us try to understand the various definitions of apathy, Coping strategies for apathy
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-1:Influence of Culture, Common ethical problems
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-2:Common ethical problems, Guidelines for Behaving Ethically
- HELPING OTHERS GROW:Being a Nurturing, Positive Person, A list of mentoring behaviour, Coaching skills and techniques
- REVIEW-I:What is a Human Relation?, Meanings of Communication, Two types of stress, Some personal problem, Communication style
- REVIEW-II:Steps to build self-confidence, Globalization, Building Good Relations with Co-workers, Good work habits
- REVIEW-III:New model of career advancement, Choosing your investment, Tactics for Dealing with Difficult People