 |
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Lesson
43
POWER
TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS
II
Invisible
Veil Consideration
Reasons
for needing conflict
diagnosis are often hidden.
Conflict escalation obscures
important information
and
disempowers participants. Anger is part
of the invisible veil. It hampers
rationality and curtails
your
capability to
see the hidden interests. As a
consequence, your ability to
understand conflict is impaired.
Factors
thought to impede the
usefulness of facilitative
mediation
FACTORS
EFFECTS
Other
disputant/team refusing
May
not be possible to use facilitative
mediation. Even if other
teams
to
participate
participation
can be coerced, quality of
consent may be
impaired.
Unfamiliar
format disturbing
Quality
of consent may be
impaired.
to other
disputant/team
One or
both disputants or their
Quality of consent may be
impaired.
teams
unsure of their
BATNAs
Large
differences in
Impasse
may result unless BATNAs are
clarified
perceptions
of fact or law
Immediate
enforcement
Irreparable
harm may result from failure
to act decisively.
needed
Untrustworthy
disputant
Irreparable
harm may result from failure
to act decisively.
Underlying
interest in legal
Consensual
processes may not address
underlying interests.
reform
Disempowered
disputant
Exploitation
of disempowered disputant may occur in
any dispute
resolution
process. Decisions will reflect poor
quality of consent
unless
disputant acquires more
power.
Time
and/or money very
Facilitative
mediation can take longer than more
evaluative, informal
limited
processes.
Proposed
Contents of a Clients'
Interview
1.
A
summary of the client's
interview
2.
A description of
the client's presenting problems
and goals
3.
A description of
the likely sources of the
conflict
4.
A
sociogram showing he participants and
their roles
5.
An
exploration of the client's underlying
interests and goals, as well
as the other disputants
likely
goals
and interests (it is helpful
analytically to use interest
trees)
6.
Analysis
of how the other participants interests
may play into exacerbating or resolving
the conflict
7.
A
sense of how escalated the
conflict has become and the
state of trust between the
parties
8.
An
initial list of the apparent
impediments to cooperative
resolution
9.
An
assessment of the various sources of
power held by the client and the other
disputant
10.
An
analysis of the client's BATNA,
including a case evaluation, and the
same for the other
disputant
11.
A list
of the information needed to prepare the
case, including any analysis
of the legal and
factual
issues
12.
An
analysis of what strategy would
best help the client meet
his or her underlying goals,
interests,
and
needs, with the discussion of the
tactics that might be
useful
13.
A
section discussing "next
steps"--further interviews, investigation, legal
research, referrals, and
so
fourth
145

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Collaborative
Law
A form
of lawyering currently seen primarily in
family law and based on a
contractual relationship between a
lawyer
and a client is called collaborative
law. This contract generally
specifies the lawyer's duty to
seek
collaborative
and interest-based document with the
other disputant. If litigation commences,
the lawyer is
required to
withdraw from representing the
client.
Fitting
the Forum to Fuss
(Brainchild of Frank Sander and
Stephen Goldberg)
Basic
Ideas:
Different
dispute resolution processes
are better at different things and
different things are important
to
different
people.
Fitting
the Forum to the Fuss
Sander/Goldberg
List of Client
Objectives
1. Minimize
costs
2. Speed
3. Privacy
4. Maintain/improve
relationships
5. Obtain
vindication
6. Obtain
neutral opinion
7. Obtain
precedent
8. Maximize
or minimize recovery
How to use fitting
the forum to the
fuss
VALUE
CLIENT
OBJECTIVE
("I")
Minimize
costs
5
Speed
Privacy
Maintain
or improve relationship with
other disputant
Obtain
vindication
Obtain
a neutral opinion
Obtain
a precedent
Maximize
or minimize recovery
OTHER
-
Describe___________________________________
146
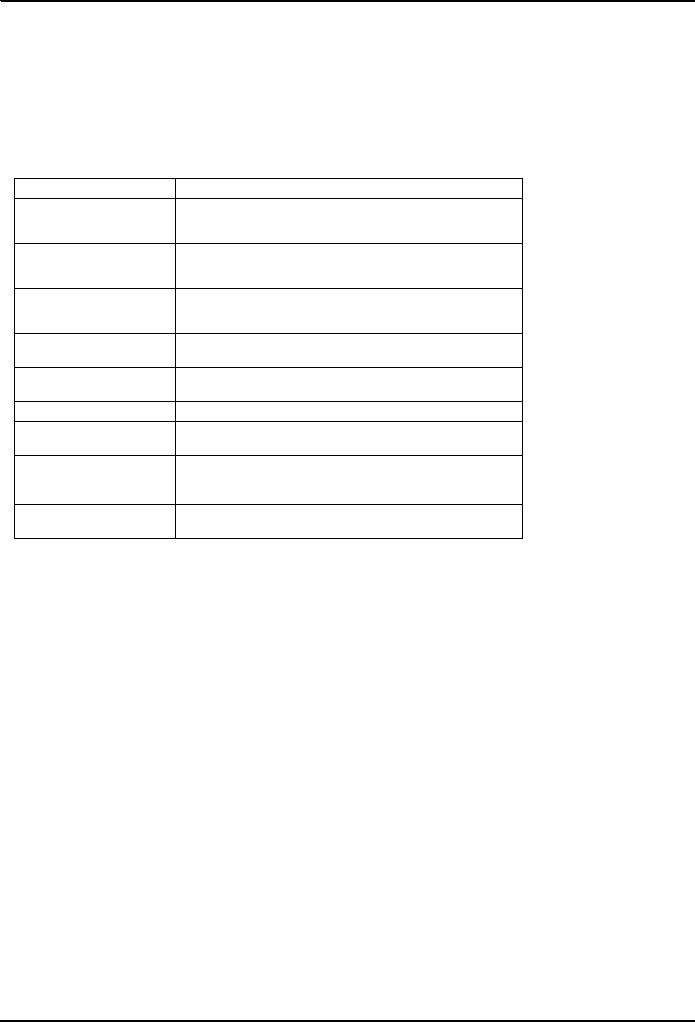
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Filling in
the Grid - Step 1
Early
Neutral
Summary
Evaluation
Jury
Trial
Arbitration
Litigation
Mediation
Minitrial
3x 5 15 2x
5 10 2x
5 10 3x
5
15 1x
5
5
Costs
0
2x
3x
2x
3x
1x
0
Speed
Privacy
3x
3x
2x
2x
0
3x
Maintain/
Improve
3x
2x
2x
1x
1x
0
Relationships
Obtain
2x
3x
1x
1x
1x
0
Vindication
Obtain
neutral
3x
3x
0
3x
3x
3x
opinion
Obtain
2x
3x
0
0
0
0
precedent
Maximize/
1x
1x
0
1x
Minimize
2x
3x
Recovery
SUM
Another
client objective filled
in
VALUE
CLIENT
OBJECTIVE
("I")
5
Minimize
costs
Speed
Privacy
Maintain
or improve relationship with
other
disputant
Obtain
vindication
Obtain
a neutral opinion
Obtain
a precedent
Maximize
or minimize recovery
OTHER
-
Describe___________________________________
147
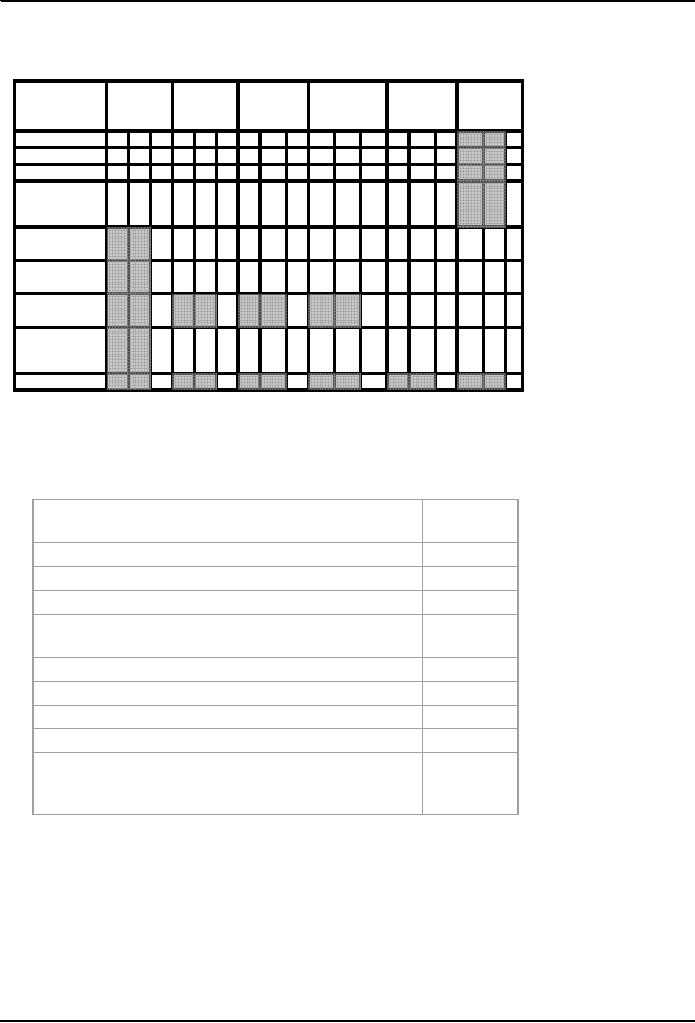
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Filling in
the Grid Next
Step
Early
Neutral
Summary
Evaluation
Jury
Trial
Arbitration
Litigation
Mediation
Minitrial
Costs
2x
2x
3x
1x
3x
0
2x
2x
3x
1x
3x
0
Speed
Privacy
3x
2x
2x
3x
3x
0
Maintain/
Improve
2x
2x
1x
1x
3x
0
Relationships
Obtain
2x
3x
0
1x
1x
1x
Vindication
Obtain
neutral
0
3x
3x
3x
3x
3x
opinion
Obtain
2x
3x
0
0
0
0
precedent
Maximize/
Minimize
0
1x
1x
1x
2x
3x
Recovery
SUM
More client
objectives filled in
VALUE
CLIENT
OBJECTIVE
("I")
5
Minimize
costs
Speed
Privacy
Maintain
or improve relationship with
other
disputant
Obtain
vindication
Obtain
a neutral opinion
Obtain
a precedent
Maximize
or minimize recovery
OTHER
-
Describe___________________________________
148
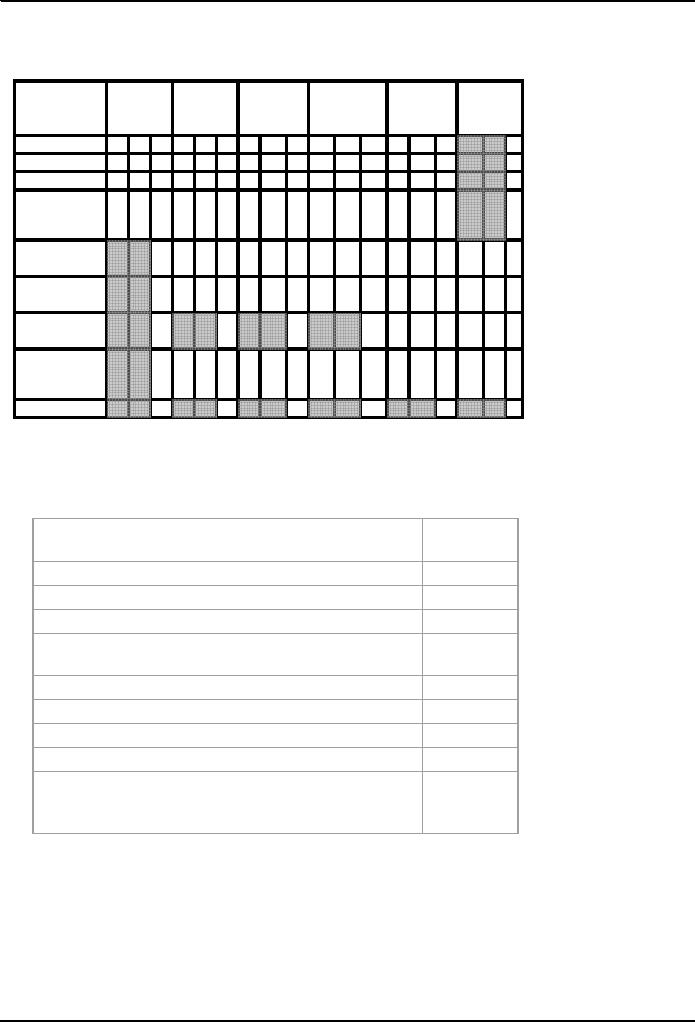
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Filling in more of
the Grid
Early
Summary
Neutral
Mediation
Minitrial Jury Trial Evaluation Arbitration Litigation
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
Costs
0
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
0
Speed
Privacy
3x
3x
2x
2x
3x
0
Maintain/
Improve
3x
2x
2x
1x
1x
0
Relationships
Obtain
2x
0
1x
1x
1x
3x
Vindication
Obtain
neutral
0
3x
3x
3x
3x
3x
opinion
Obtain
2x
3x
0
0
0
0
precedent
Maximize/
0
1x
1x
1x
Minimize
2x
3x
Recovery
SUM
Completing
the client objectives
VALUE
CLIENT
OBJECTIVE
("I")
5
Minimize
costs
Speed
1
Privacy
Maintain
or improve relationship with
other
5
disputant
Obtain
vindication
Obtain
a neutral opinion
Obtain
a precedent
Maximize
or minimize recovery
OTHER
-
Describe___________________________________
149
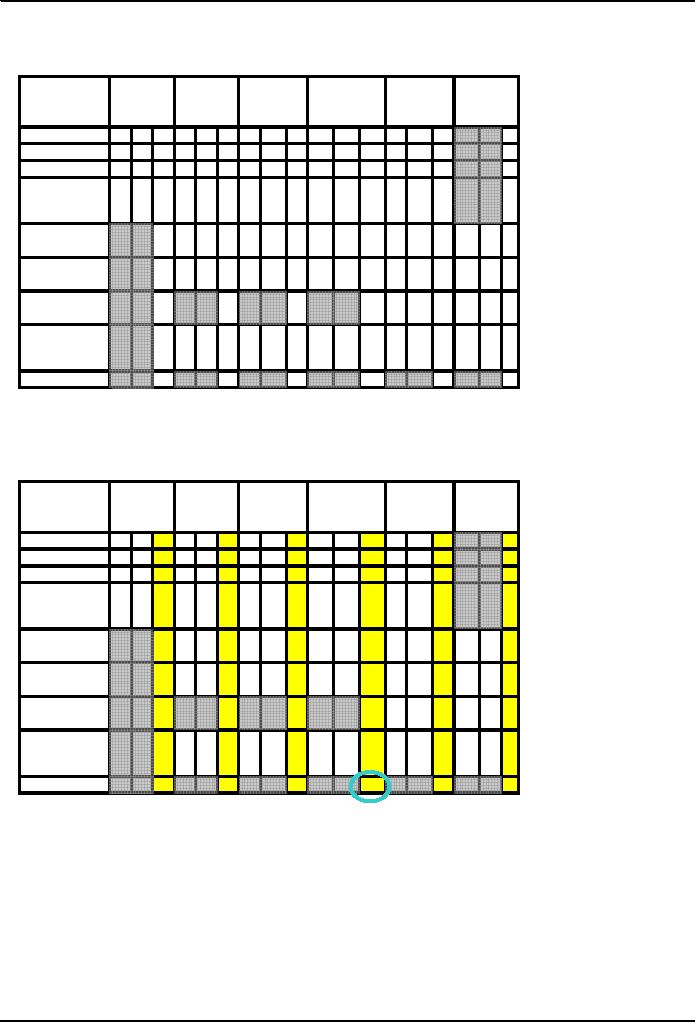
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Entering
Remaining Objective Utilities on
the Grid
Early
Summary
Neutral
Mediation
Minitrial Jury Trial
Evaluation Arbitration
Litigation
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
Costs
0
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
0
Speed
1 3 3x 1 3 2x 3 6 2x 3 6 3x 3 9
Privacy
3x
0
Maintain/
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 1x 5 5
55
3x
1x
Improve
0
Relationships
Obtain
2x
22
2 2
26
2 2 1x
2 4
3x
0
1x
1x
Vindication
Obtain
neutral
3x
3x
0
2 6
6
26
2 6 3x
2
6 3x
2
3x
opinion
Obtain
13
2 3x
1
2x
0
0
0
0
precedent
Maximize/
4 4 1x 4
4 1x
4 2x 4
4
0
1x
8
4 12
3x
Minimize
Recovery
SUM
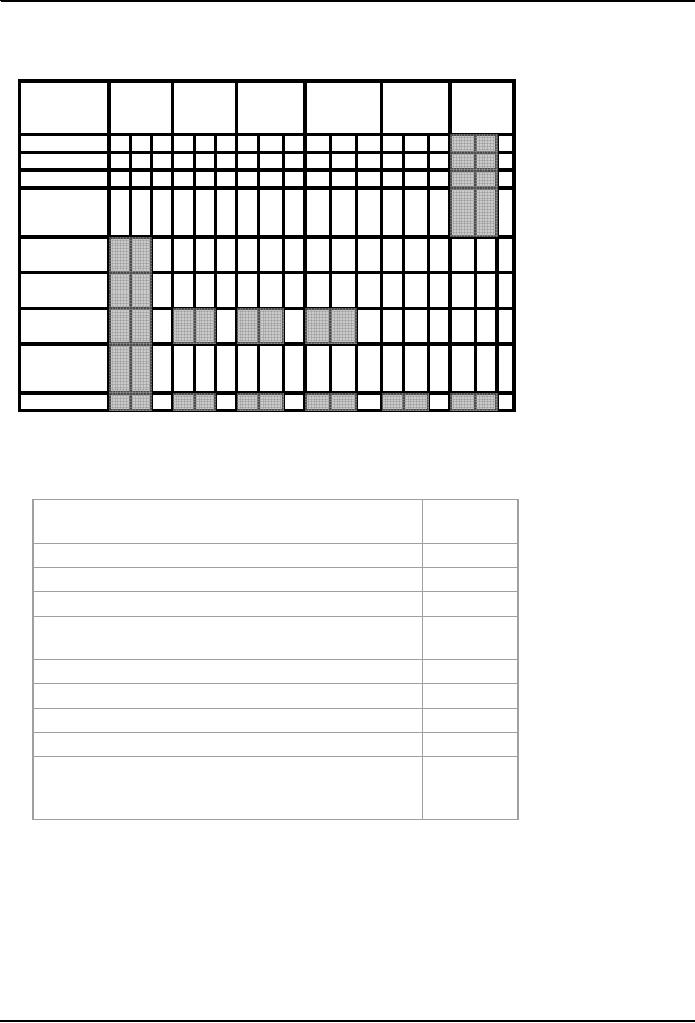
Calculating
the Scores for Dispute
Resolution Processes
Early
Summary
Neutral
Mediation
Minitrial Jury Trial
Evaluation Arbitration
Litigation
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
Costs
0
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 3x 5 15 1x 5 5
3x
0
Speed
1 3 3x 1 3 2x 3 6 2x 3 6 3x 3 9
Privacy
3x
0
Maintain/
5 15 2x 5 10 2x 5 10 1x 5 5
55
3x
1x
Improve
0
Relationships
Obtain
2x
22
2 2
26
2 2 1x
2 4
0
1x
1x
3x
Vindication
Obtain
neutral
3x
3x
0
2 6
6
26
2 6 3x
2
6 3x
2
3x
opinion
Obtain
13
2 3x
1
2x
0
0
0
0
precedent
Maximize/
4 4 1x 4
4 1x
4 2x 4
4
1x
0
8
4 12
Minimize
3x
Recovery
48
45
48
53
44
27
SUM
Conflict
Diagnosis Approach
1. Facilitative
mediation is the default choice
2. If
there are reasons not to
use facilitative mediation:
Try
to work around them
If
not possible, use fallback
choices
150

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
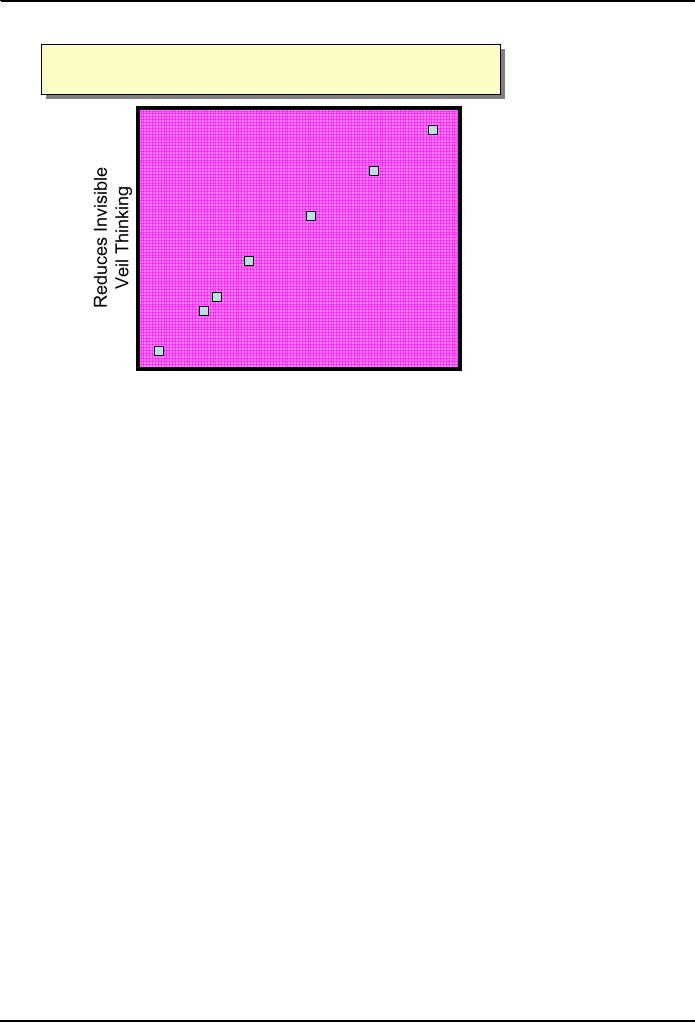
Diispute
Resollution,
IInvisible-Veil
Thiinking,
D spute Reso
ution,
nvisible-Veil Thnking,
&
Quallity off Consentt
& Qua
it
y o
Consen
effective
Pure
and Transformative Mediation
Facilitative
Mediation
Featuring
Compromising
Evaluative
Mediation
Nonbinding
Evaluation
Med-Arb
Arbitration
Litigation
ineffective
low
high
Resulting
Quality of Consent
Impediments
to use facilitative mediation
There
are certain hindrances to
use facilitative mediation
which are given below.
1. The
other team won't play
2. Worry
about signaling weakness
3. Unknown
or uncertain BATNA
4. Wildly
divergent BATNA assessments
5. Limited
time, money
6. Need
for immediate enforcement
7. Other
disputant a nasty fellow
8. Underlying
interest in legal
reform
9. Facilitative
process already tried,
settlement did not
result
Theories
of conflict, cooperation, and
competition, and negotiation
style, suggest that the best
processes for
promoting
constructive, equitable, and
efficacious dispute resolution
are those in which the participants
are
consistently
guided away from invisible
veil, zero-sum thinking and
toward collaborative, integrative
problem
solving. These processes include (1) pure
mediation geared directly toward
promoting collaborative
problem
solving and (2) transformative
mediation.
151
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONFLICT:Dispute, Legal Dispute, Call the police
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION 1:Positive affect in Negotiation, Alternative Dispute Resolution
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION II:Adjudication, Litigation, Mediation-Arbitration
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT I:Pedagogical development, Pressures against Innovation
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT II:Cultural beliefs about interpersonal conflict, Why strategies of change fail
- CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS:Who Needs to Know About Conflict Diagnosis?, Steps in Conflict Diagnosis
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS I:The Seven Steps of Social Behavior, Seven steps to diagnose conflict
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS II:Themes of Conflict Diagnosis
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT I:Description of Conflict, Identifying Interpersonal Conflict
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT II:Step 1 for Conflict Diagnosis, interpersonal or intrapersonal
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT I:Main Sources of Conflict, Discussing major sources of conflict
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT II
- INTEREST ANALYSIS I:Analyzing your interests, Analyzing the other disputant’s interests
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:What are interests?, Tips for Interest Trees
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:Principles and values, Basic Human Needs
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT I, Premises of Deutsch’s Theory
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT II:Techniques to transform competitive conflict into cooperative
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE I:What is Mistrust,Trust and business,Three levels of trust
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE II:Advantages of high trust level, Building of trust
- ASSESSING IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVE THE CONFLICT I:Motivation to seek vengeance, Mistrust
- ASSESSING THE IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVING THE CONFLICT II:Disempowered Disputant, Unpleasant Disputant
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE I:Dual Concern Model, Dominating or competition style
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE:Dual Concern Model, Tactics Used In Integrating
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS:Conflict and Power, Kinds of power in the Relationship Domain
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS II:Sources of Relationship Power, Context and Power
- POWER, CONFLICT, AND BATNA III:Role of Third Party in BATNA, Dealing with Power Imbalance
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT I:Stereotyping, Stereotyping in Interpersonal Conflict
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT:Categories of Diversity Issues, Seven Mental Processes to Prove Stereotypes
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT III:Individual Difference and Social Category, Cultural differences in values
- MEDIATION I:When is mediation required, Processes Related to Mediation, Product of Mediation
- MEDIATION II:Important distinguishing factors, More Advantages and Disadvantages of Pure Mediation
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION I:Efficiency Consideration, Conflict Management and Prevention
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION II:Quality of Consent, Effects on the parties to mediation
- PROCESS OF MEDIATION:Stages of Mediation, Facilitative tactics in mediation
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION I:Characteristics of mediation, Confidentiality
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION II:Role of ethics in mediation, 8 Dimensions of Ethics in Mediation
- ARBITRATION I:Ways to Resolve Conflict, Advantages of Arbitration, Disadvantages of Arbitration
- ARBITRATION II:Varieties of Arbitration, Process of Arbitration, Contents of Arbitration Act
- NON BINDING EVALUATION:Disadvantage, Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation
- NON BINDING EVALUATION II:Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation, Advantages and disadvantages of Non-binding Evaluation
- MIXED AND MULTIMODAL DISPUTE RESOLUTION:Six System Design Principles, Extensions of Dispute Systems Design
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS I:Introduction, Necessity of conflict diagnosis, Using conflict diagnosis
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS II:Proposed Contents of a Clients’ Interview, Impediments to use facilitative mediation
- PANCHAYAT, LOCAL GOVERNMENT SYSTEM, AND ADR, Definitions of Panchayat, Definition of Jirga
- SUMMARY AND MESSAGE OF THE COURSE:Definitions of conflict, Negotiation, Meditation, Adjudication