 |

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Lesson
39
NON BINDING
EVALUATION
Quotation
"A
little inaccuracy sometimes
saves a ton of explanation."
H. H.
Munro
We
will learn
1.
Nonbinding evaluation as a class of ADR
that brings out merits
and demerits of the
disputes.
2.
Advantages and disadvantages of
non-binding evaluation compared with
other forms of ADR.
3.
Appropriate uses of nonbinding
evaluation.
Lawyers
with adversarial attitude
like non-binding evaluation.
Non-Binding
Evaluation
Non-binding
evaluation is a group of processes used
in legal disputes to evaluate the
likely outcome of the
dispute
being taken to court. It is also called
mixed or `hybrid' forms of ADR since it
contains the
characteristics
of both negotiation and adjudication. It
is a form of assisted negotiation. It
consists of a
hearing
followed by an evaluation award which is
advisory only. It is an assessment of
strengths and
weaknesses
of both disputants. In adversarial
legal system, it is considered the
best ADR.
Disadvantage:
Following
are the disadvantages of non-binding
evaluation.
1. It
encourages an adversarial perspective
without providing certainty of
adjudicated outcome.
2. The
complexity and formality of the
process is variable.
3. The
process of evidence and
testimonies may be different
for different cases.
4. Outcome
may be a single decision or a
range of decisions.
5.
Non-binding evaluation is a BATNA
clarification.
Varieties of
Non-binding Evaluation
Following
are the various kinds of non-binding
evaluation.
1.
Non-binding arbitration.
2.
Minitrial
3.
Summary jury trial.
4.
Neutral evaluation.
5.
Dispute review board
129
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
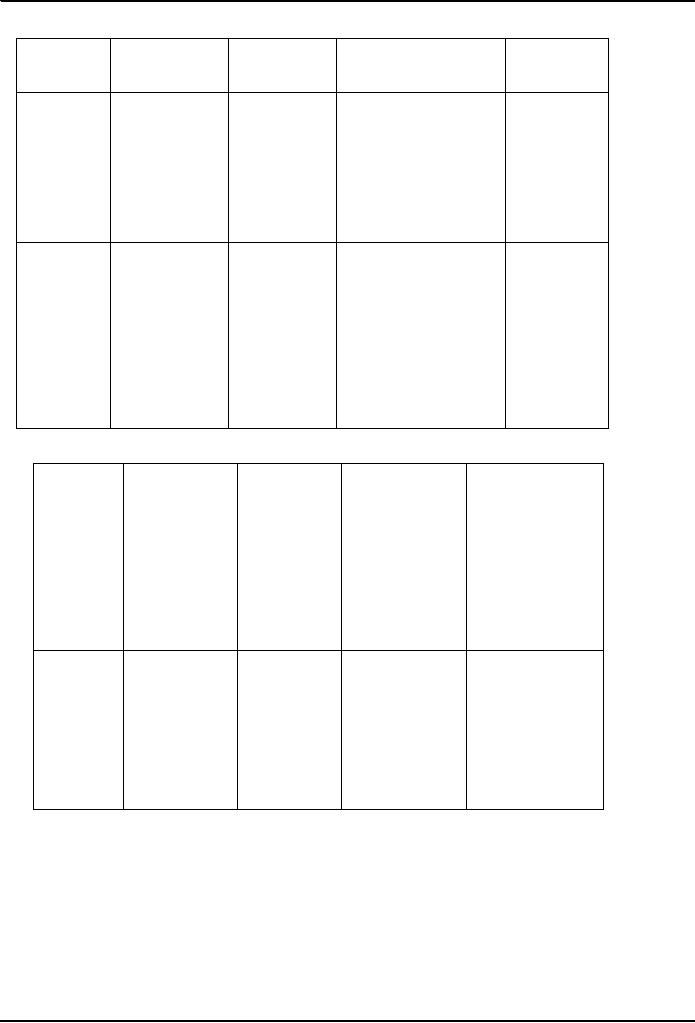
Who is
typically What is
What is
the
Process
Nature
of outcome
typically
process
useful
the
neutral?
presented?
for?
General
Arbitration
award,
Oral
Nonbindin
Arbitrator,
BATNA
advisory
only; may
arguments;
who
may be
g
be
oral, written, or
occasionally
arbitration
an attorney, a
clarification
exhibits
and
retired
judge
both
informal
or an
ADR
testimony
(as
neutral
in
arbitration)
BATNA
Typically,
no outcome
Typically,
Corporate
Minitrial
clarification
per
se;
observations of
oral
executives
with
for
those in a
hearing
provide
arguments;
authority
to
position
to
BATNA
clarification
may
also be
settle;
may also
to
those with authority
some
be a
neutral
settle
to
negotiate
evidentiary
moderator
settlement;
advisory
showing
award
may be issued
by
neutral if no
settlement
reached
Teasing
out of
Abbreviated
Nonbinding
Members
of
Summary
complicated
version
of
the
jury pool
verdict
jury
trial
factual
issues (as
litigated
as
a
in
class
adjudicators;
case
actions/products
judge
or
liability);
retired
judge
BATNA if
jury
as
moderator
trial
expected;
"day in
court" for
litigants
Assessment
of
Typically,
Experts
in
Neutral
BATNA
the
strengths
oral
technical
area
evaluation
clarification;
and
weaknesses
of
dispute, or
arguments
expert
of
each sides
lawyers
with
empowerment
case;
may
expertise
in
include
the
sort of
dispute
being
advisory
award
litigated
130
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
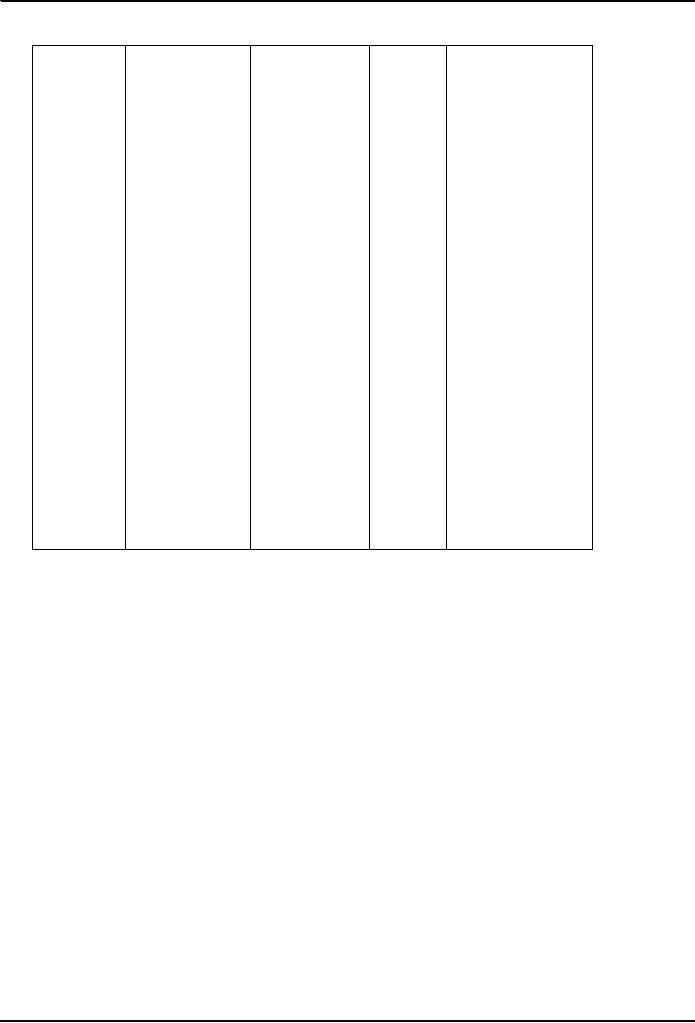
Overcoming
of
A
summary
An
Dispute
A penal
of
costly
impasses
of
disputes
advisor
review
leaders
or
and
delays
that
y
board
other
experts
created
by
threatens
to
decisio
(example
in the
field
disputes
that
delay
or
n
;
M2
involved,
occur
during
derail
a
Motorwa
empanelled
complex
complex
y
by the
owner
construction
construction
construct
and
projects
project
ion
by
contractor
in
Turkish
construction
firm)
project
131
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
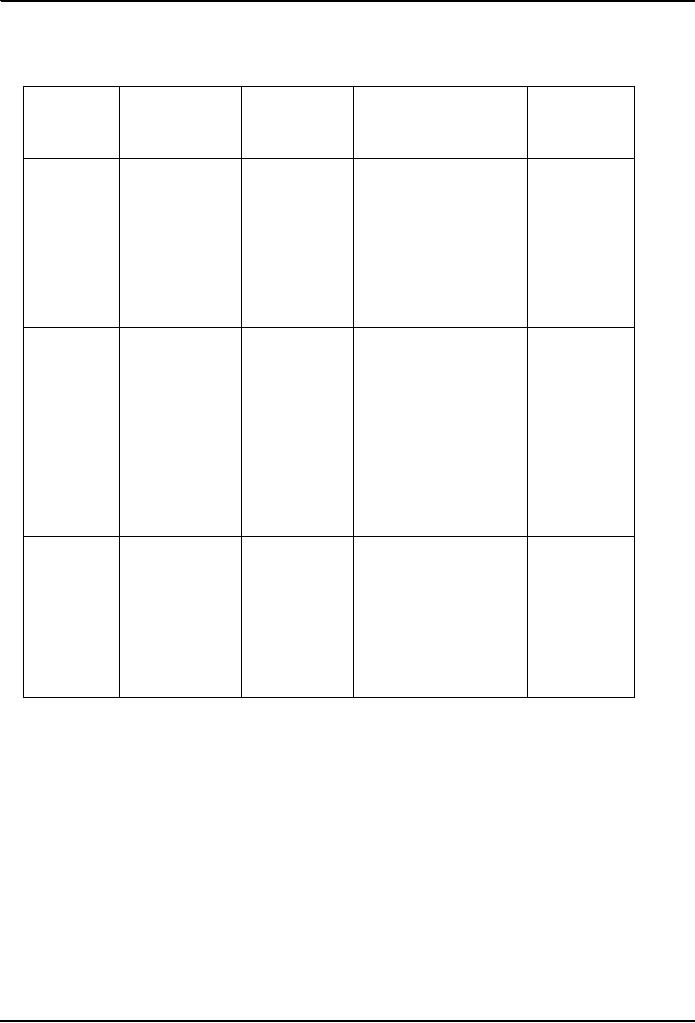
Varieties of nonbinding
evaluation
What is
the
Process
Who is typically the
What is typically
Nature of
outcome
process
useful
neutral?
presented?
for?
Nonbinding
Arbitrator,
who
Oral arguments;
Arbitration award, advisory General
arbitration
may be
an
occasionally
only; may be oral,
written, BATNA
attorney, a
retired
exhibits
and
or
both
clarification
judge or an
ADR
informal
neutral
testimony (as
in
arbitration)
Minitrial
Corporate
Typically,
oral
Typically,
no outcome per
BATNA
executives
with
arguments;
may
se; observations of
hearing
clarification
for
authority
to settle;
also be
some
provide
BATNA
those in
a
may also be
a
evidentiary
clarification
to those with
position
to
neutral
moderator
showing
authority
to negotiate
settle
settlement;
advisory award
may be issued by
neutral if
no settlement
reached
Teasing out
of
Members of the
jury
Abbreviated
Nonbinding
verdict
Summary
jury
complicated
factual
pool as
a
version of
litigated
trial
issues (as in
class
adjudicators;
judge
case
actions/products
or
retired judge as
liability);
BATNA if
moderator
jury
trial expected;
"day in
court" for
litigants
132
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
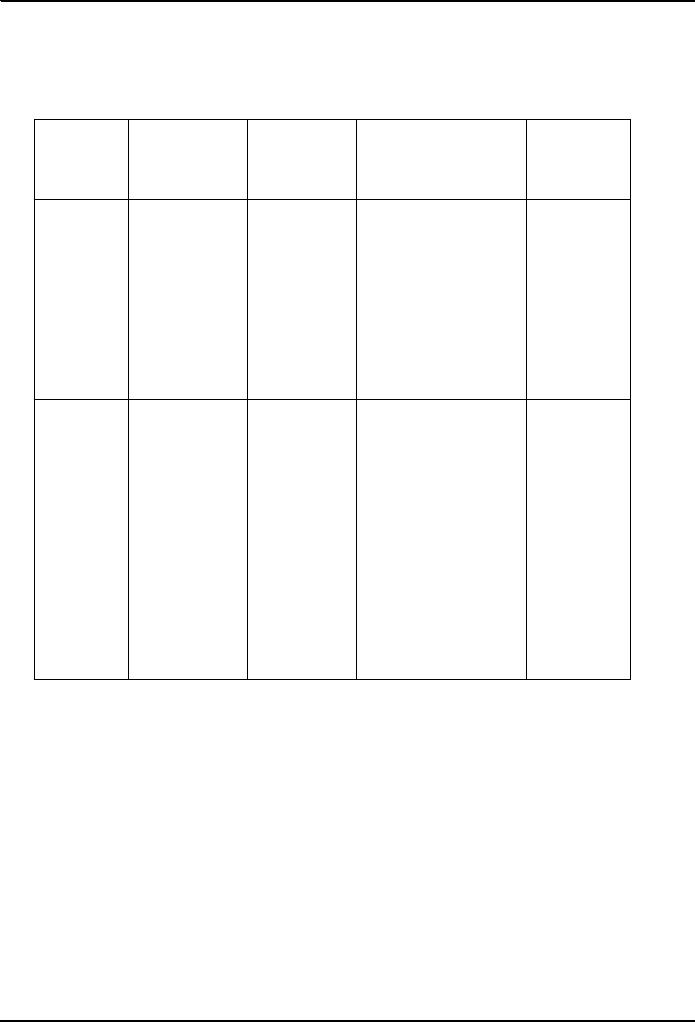
Varieties of
nonbinding evaluation
What is
the
Who is typically
What is
Nature of
outcome
Process
process
useful
typically
the
neutral?
for?
presented?
BATNA
Assessment of
the
Experts
in
Typically,
oral
Neutral
clarification;
strengths and
weaknesses
technical area
of
arguments
evaluation
expert
of each sides
case; may
dispute,
or
empowerment
include advisory
award
lawyers
with
expertise in
the
sort of
dispute
being
litigated
Overcoming
of
A summary of
An advisory decision
A penal
of
Dispute
costly
disputes
that
leaders or
other
review
board
impasses
and
threatens
to
experts in
the
(example;
delays
created
delay or
derail a
field
involved,
M2
by
disputes
complex
empanelled
by
Motorway
that
occur
construction
the owner
and
construction
during
project
contractor in
a
by
Turkish
complex
construction
firm)
construction
project
projects
133
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONFLICT:Dispute, Legal Dispute, Call the police
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION 1:Positive affect in Negotiation, Alternative Dispute Resolution
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION II:Adjudication, Litigation, Mediation-Arbitration
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT I:Pedagogical development, Pressures against Innovation
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT II:Cultural beliefs about interpersonal conflict, Why strategies of change fail
- CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS:Who Needs to Know About Conflict Diagnosis?, Steps in Conflict Diagnosis
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS I:The Seven Steps of Social Behavior, Seven steps to diagnose conflict
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS II:Themes of Conflict Diagnosis
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT I:Description of Conflict, Identifying Interpersonal Conflict
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT II:Step 1 for Conflict Diagnosis, interpersonal or intrapersonal
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT I:Main Sources of Conflict, Discussing major sources of conflict
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT II
- INTEREST ANALYSIS I:Analyzing your interests, Analyzing the other disputant’s interests
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:What are interests?, Tips for Interest Trees
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:Principles and values, Basic Human Needs
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT I, Premises of Deutsch’s Theory
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT II:Techniques to transform competitive conflict into cooperative
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE I:What is Mistrust,Trust and business,Three levels of trust
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE II:Advantages of high trust level, Building of trust
- ASSESSING IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVE THE CONFLICT I:Motivation to seek vengeance, Mistrust
- ASSESSING THE IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVING THE CONFLICT II:Disempowered Disputant, Unpleasant Disputant
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE I:Dual Concern Model, Dominating or competition style
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE:Dual Concern Model, Tactics Used In Integrating
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS:Conflict and Power, Kinds of power in the Relationship Domain
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS II:Sources of Relationship Power, Context and Power
- POWER, CONFLICT, AND BATNA III:Role of Third Party in BATNA, Dealing with Power Imbalance
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT I:Stereotyping, Stereotyping in Interpersonal Conflict
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT:Categories of Diversity Issues, Seven Mental Processes to Prove Stereotypes
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT III:Individual Difference and Social Category, Cultural differences in values
- MEDIATION I:When is mediation required, Processes Related to Mediation, Product of Mediation
- MEDIATION II:Important distinguishing factors, More Advantages and Disadvantages of Pure Mediation
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION I:Efficiency Consideration, Conflict Management and Prevention
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION II:Quality of Consent, Effects on the parties to mediation
- PROCESS OF MEDIATION:Stages of Mediation, Facilitative tactics in mediation
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION I:Characteristics of mediation, Confidentiality
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION II:Role of ethics in mediation, 8 Dimensions of Ethics in Mediation
- ARBITRATION I:Ways to Resolve Conflict, Advantages of Arbitration, Disadvantages of Arbitration
- ARBITRATION II:Varieties of Arbitration, Process of Arbitration, Contents of Arbitration Act
- NON BINDING EVALUATION:Disadvantage, Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation
- NON BINDING EVALUATION II:Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation, Advantages and disadvantages of Non-binding Evaluation
- MIXED AND MULTIMODAL DISPUTE RESOLUTION:Six System Design Principles, Extensions of Dispute Systems Design
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS I:Introduction, Necessity of conflict diagnosis, Using conflict diagnosis
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS II:Proposed Contents of a Clients’ Interview, Impediments to use facilitative mediation
- PANCHAYAT, LOCAL GOVERNMENT SYSTEM, AND ADR, Definitions of Panchayat, Definition of Jirga
- SUMMARY AND MESSAGE OF THE COURSE:Definitions of conflict, Negotiation, Meditation, Adjudication