 |

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Lesson
3
DISPUTE
RESOLUTION II
Quotations
A
man's greatest battles are
the ones he fights within
himself.
Ben
Okri (1959 - ) Nigerian
novelist, short-story writer, and
poet.
"We
have met the enemy and it is
us." Walt
Kelly
Dispute
resolution processes can be
divided into two main
categories, according to the identities of
the
persons
who decide the outcome.
These two categories are
called Adjudication and
Negotiation.
Adjudication
In adjudication the
decision maker is a neutral third party,
rather than the disputants.
Kinds of
Adjudication
Following
are the important forms of
Adjudication
a)
Litigation
b) Agency
Adjudication
c)
Arbitration
Litigation
Litigation
is an adjudication in court system, under
legal auspices, in which the adjudicator
is the judge.
a)
Only certain situations can
legally be taken to court.
b)
Process is very formal and
structured to protect the due
process rights of the litigants.
c) In
litigation only certain kinds of
outcomes are legally
possible.
Agency
adjudication
Agency adjudication
is similar to litigation. Except that the
law underlying recourse to the
process is
regulatory.
1.
Adjudicator is often called an
administrative law judge or hearing
officer.
2. May
be less formal and
structured than
litigation.
Arbitration
Arbitration
is the form of adjudication in which
authority of adjudicator is conferred by
disputants'
contract.
It may
be provided for by a court rather
than privately but if
so,
1. The
parties are free to decline
arbitration, or
2. If the
parties must participate , they are
free to disregard the results (making
this non binding
evaluation)
Negotiation
and Adjudication: Basic
Distinction
In
negotiation the disputants decide the
issue whereas in adjudication the neutral
third party decides the
issue.
12
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Negotiation
The
process in which disputants
seek to resolve an interpersonal conflict
through dialogue or another
form
of communication is
called negotiation. In negotiation, the
disputants themselves decide
mutually whether,
and on
what terms, the conflict should be
resolved.
Forms
of Negotiation
There
are various types of
negotiation.
a)
Assisted (Facilitated) Negotiation
b)
Unassisted (simple)
Negotiation
Simple
negotiation
In this type of
negotiation only participants are the
disputants.
Assisted
(or facilitated) negotiation
In
assisted negotiation the disputants
are joined by others.
Types of
Assisted Negotiation
Following
are the various types of
assisted negotiation.
a) Agent
or advocate-assisted disputants'
representatives conduct the
negotiation
b) Mediation-
neutral
third party assists the disputants in
settling the dispute.
c) Nonbinding
evaluation- neutral
third party renders a nonbinding
evaluation of the conflict
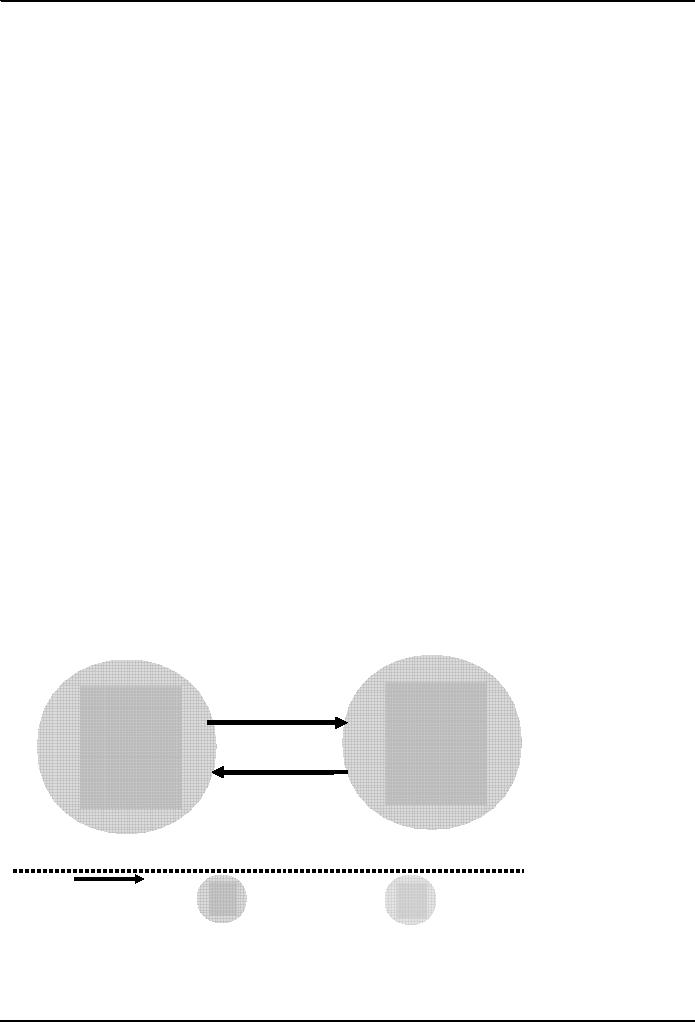
Simple
Negotiation
Disputant
Disputant
"Persuade"
Other
Decision
makers
directions
participants
13
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
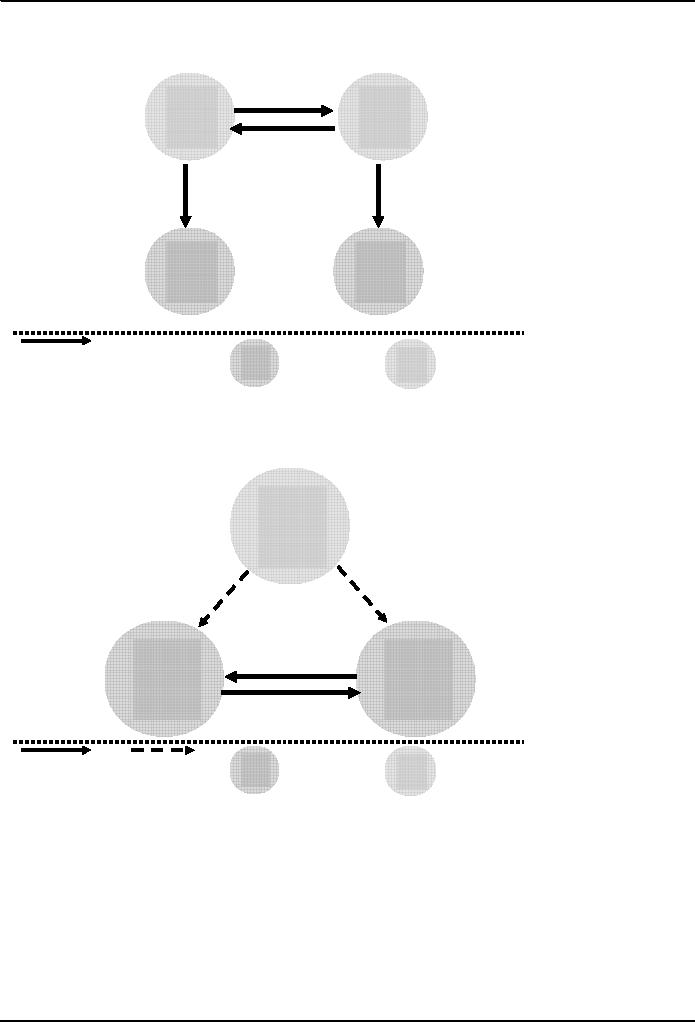
Negotiation
with Agents or
Advocates
Agent
Agent
or
or
advocate
advocate
Disputant
Disputant
"Persuade"
Other
Decision
makers
directions
participants
Mediation
Neutral
Disputant
Disputant
"Persuade"
"Assist"
Other
Decision
makers
directions
directions
participants
14
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
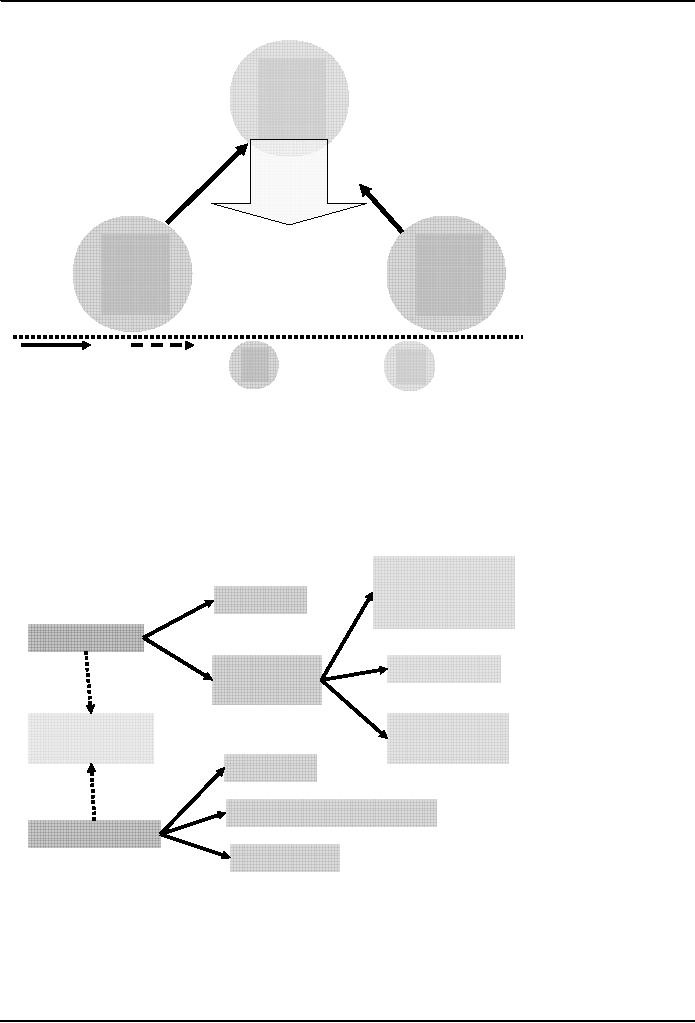
Nonbinding
Evaluation
Neutral
Non-
binding
decision
Disputant
Disputant
"Persuade"
"Assist"
Other
Decision
makers
directions
directions
participants
Mixed
(Hybrid) Processes
Processes
that combine the attributes of two or
more of the major forms of dispute
resolution are called
mixed
(hybrid) processes.
It
combines elements of mediation, adjudication,
and/or nonbinding evaluation.
Basic
Dispute Resolution
Forms
Agent
or
advocate-
Simple
assisted
Negotiation
Assisted/
Mediation
Facilitated
Mixed/Hybrid
Nonbinding
ADR
Evaluation
Litigation
Agency
Adjudication
Adjudication
Arbitration
Some
of the Types of Mixed Dispute Resolution
Processes
15

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
1.
Mediation-Arbitration
In this
process mediating parties submit their
dispute to arbitration if mediation does
not result in
settlement.
2.
Arbitration-mediation
In this
process an arbitrator issues an
award, but keeps it a secret
and destroys it if the disputants
reach
agreement
in a subsequent mediation.
16
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONFLICT:Dispute, Legal Dispute, Call the police
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION 1:Positive affect in Negotiation, Alternative Dispute Resolution
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION II:Adjudication, Litigation, Mediation-Arbitration
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT I:Pedagogical development, Pressures against Innovation
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT II:Cultural beliefs about interpersonal conflict, Why strategies of change fail
- CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS:Who Needs to Know About Conflict Diagnosis?, Steps in Conflict Diagnosis
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS I:The Seven Steps of Social Behavior, Seven steps to diagnose conflict
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS II:Themes of Conflict Diagnosis
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT I:Description of Conflict, Identifying Interpersonal Conflict
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT II:Step 1 for Conflict Diagnosis, interpersonal or intrapersonal
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT I:Main Sources of Conflict, Discussing major sources of conflict
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT II
- INTEREST ANALYSIS I:Analyzing your interests, Analyzing the other disputant’s interests
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:What are interests?, Tips for Interest Trees
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:Principles and values, Basic Human Needs
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT I, Premises of Deutsch’s Theory
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT II:Techniques to transform competitive conflict into cooperative
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE I:What is Mistrust,Trust and business,Three levels of trust
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE II:Advantages of high trust level, Building of trust
- ASSESSING IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVE THE CONFLICT I:Motivation to seek vengeance, Mistrust
- ASSESSING THE IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVING THE CONFLICT II:Disempowered Disputant, Unpleasant Disputant
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE I:Dual Concern Model, Dominating or competition style
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE:Dual Concern Model, Tactics Used In Integrating
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS:Conflict and Power, Kinds of power in the Relationship Domain
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS II:Sources of Relationship Power, Context and Power
- POWER, CONFLICT, AND BATNA III:Role of Third Party in BATNA, Dealing with Power Imbalance
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT I:Stereotyping, Stereotyping in Interpersonal Conflict
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT:Categories of Diversity Issues, Seven Mental Processes to Prove Stereotypes
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT III:Individual Difference and Social Category, Cultural differences in values
- MEDIATION I:When is mediation required, Processes Related to Mediation, Product of Mediation
- MEDIATION II:Important distinguishing factors, More Advantages and Disadvantages of Pure Mediation
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION I:Efficiency Consideration, Conflict Management and Prevention
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION II:Quality of Consent, Effects on the parties to mediation
- PROCESS OF MEDIATION:Stages of Mediation, Facilitative tactics in mediation
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION I:Characteristics of mediation, Confidentiality
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION II:Role of ethics in mediation, 8 Dimensions of Ethics in Mediation
- ARBITRATION I:Ways to Resolve Conflict, Advantages of Arbitration, Disadvantages of Arbitration
- ARBITRATION II:Varieties of Arbitration, Process of Arbitration, Contents of Arbitration Act
- NON BINDING EVALUATION:Disadvantage, Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation
- NON BINDING EVALUATION II:Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation, Advantages and disadvantages of Non-binding Evaluation
- MIXED AND MULTIMODAL DISPUTE RESOLUTION:Six System Design Principles, Extensions of Dispute Systems Design
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS I:Introduction, Necessity of conflict diagnosis, Using conflict diagnosis
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS II:Proposed Contents of a Clients’ Interview, Impediments to use facilitative mediation
- PANCHAYAT, LOCAL GOVERNMENT SYSTEM, AND ADR, Definitions of Panchayat, Definition of Jirga
- SUMMARY AND MESSAGE OF THE COURSE:Definitions of conflict, Negotiation, Meditation, Adjudication