 |

Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Lesson
28
STEREOTYPES,
DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT
Quotations
Leaders
have to break out of old
habits and stereotypes to
build organizations that
continually improve
quality
and reduce costs to prosper
in the turbulent marketplace.
Dean
Tjosvold U.S. psychologist and
author.
I
believe world civilization
can be built only upon the
common basis of international
living...The ideal
life...to
live in an English cottage, with American
heating, and have a Japanese
wife, a French mistress, and
a
Chinese
cook. Lin
Yutang (1895 - 1976),
Chinese-born writer and philologist.
Main
source of conflict is diversity.
Diversity is being different. There are
three sources of
difference!
Categories
of Diversity Issues
Diversity
issues fall into three
main categories.
1. First
category is stereotyping. Stereotyping is the
attribution of thoughts, qualities,
behaviors, and
attitudes
to others based on their
categorization into a social
group.
2.
Second category includes
considerations of culture. This category
includes considerations of culture.
It
includes
issues of language difference, cultural
values, and frames of
reference, and cultural attitude
towards
conflict,
negotiation, and conflict
resolution.
3.
Third category of diversity issue is the
issue of power. Power problems in
diversity conflict include the
disempowerment
of particular social groups and the
existence of bigotry and prejudice
based on social
group
membership.
These
categories frequently influence one
another.
Why
People Stereotype
The
effect of stress and situational complexity; the
more stressful the situation, the more
likely it is that
stereotyping
will occur
Interpersonal
conflict tends to be an inherently
stressful and complex situation that
tends to impose a
high
degree
of cognitive load.
Fatigue,
illness, hunger, and intense
emotion; personal factors
contribute to cognitive load. It also
affects
the propensity to
stereotype.
�
Unfamiliarity
with the other person
�
Unfamiliarity
with the racial, ethnic, religious, or
other social group
�
Social
group salience
�
Strong
category is a social category
associated with a particularly strong
likelihood of stereotypes
application.
�
Strong
categories tend to be those
associated with obvious
physical attributes and rigid
social roles.
(Gender
roles is an example)
Strong
category features:
Physical obviousness and
restricted social role. There are
also greater
propensities
to stereotype people based on social
groups that have two
special qualities.
First,
social groups that are
associated with obvious
physical attributes, such as skin and
hair color, size,
facial
features,
Second,
gender characteristics are
associated with a greater propensity to
stereotype.
Third,
social groups associated
with rigid social roles in
the society are more likely
to be the targets of
stereotyping.
100
Conflict
Management HRM624
VU
Seven
Mental Processes to Prove
Stereotypes
Processes
and stereotype reinforcement: Individuals
may hold their own unique
stereotypes
Processes
of stereotype confirmation: People of a
belief tend to confirm group's
stereotypes.
1.
Ignoring
2.
Explaining away
3.
Memory intrusions (memories of things
that didn't happen)
4.
Selective weighting
processes
5.
Stereotype over
interpretation
6.
Stereotype-consistent perception
7.
Active processes that
confirm stereotypes
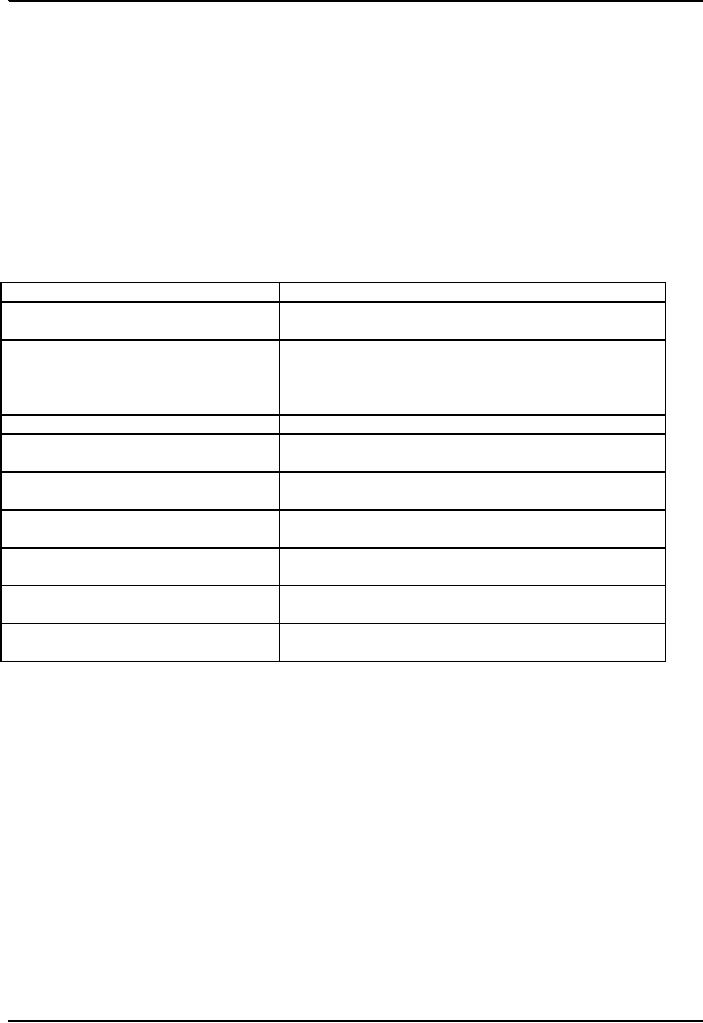
Processes
of Stereotype Confirmation
Process
Explanation
Ignoring
Stereotype
inconsistent traits are ignored, allowing
the
stereotype
to go unchallenged
Explaining
away
Stereotype
inconsistent behavior is explained as either
a
fluke
or a result of special circumstances,
whereas
stereotype
consistent behavior is attributed to
innate
qualities
Memory
intrusion
Stereotype-consistent
aspects of a situation are
imagined
Selecting
Weighting Processes
Stereotype-consistent
events are attributed
greater
importance
than stereotype inconsistent
events
Stereotype
over interpretation
Stereotypes
that are true in a limited
sense are
overextended in
importance or applicability
Stereotype-consistent
perception
Ambiguous
situations are interpreted in a
way that
confirms
stereotypes
Fundamental
attribution error
Behavior
that is due to restricted
social roles is
attributed
to innate
characteristics
Behavioral
confirmation
Responses
to people based on social categorization
tend
to
create a self-fulfilling prophecy
Data
collection errors
Information
available in the overall social
environment is
biased
in favor of prevailing
stereotypes
Summary
Stereotype,
diversity, and conflict are
related concepts. Diversity is
perpetuated and reinforced
through
stereotype
images. Stereotype images
are confirmed through a
step-by-step process. It is interesting
and we
can
learn about this mental
process by experiencing/doing
it.
101
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONFLICT:Dispute, Legal Dispute, Call the police
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION 1:Positive affect in Negotiation, Alternative Dispute Resolution
- DISPUTE RESOLUTION II:Adjudication, Litigation, Mediation-Arbitration
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT I:Pedagogical development, Pressures against Innovation
- PRECONCEPTIONS ABOUT CONFLICT II:Cultural beliefs about interpersonal conflict, Why strategies of change fail
- CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS:Who Needs to Know About Conflict Diagnosis?, Steps in Conflict Diagnosis
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS I:The Seven Steps of Social Behavior, Seven steps to diagnose conflict
- RECURRENT THEMES IN CONFLICT DIAGNOSIS II:Themes of Conflict Diagnosis
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT I:Description of Conflict, Identifying Interpersonal Conflict
- DESCRIBING THE CONFLICT II:Step 1 for Conflict Diagnosis, interpersonal or intrapersonal
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT I:Main Sources of Conflict, Discussing major sources of conflict
- SOURCES AND CAUSES OF CONFLICT II
- INTEREST ANALYSIS I:Analyzing your interests, Analyzing the other disputant’s interests
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:What are interests?, Tips for Interest Trees
- INTEREST ANALYSIS II:Principles and values, Basic Human Needs
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT I, Premises of Deutsch’s Theory
- ASSESSING THE CHARACTER OF THE CONFLICT II:Techniques to transform competitive conflict into cooperative
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE I:What is Mistrust,Trust and business,Three levels of trust
- TRUST AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE II:Advantages of high trust level, Building of trust
- ASSESSING IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVE THE CONFLICT I:Motivation to seek vengeance, Mistrust
- ASSESSING THE IMPEDIMENTS TO RESOLVING THE CONFLICT II:Disempowered Disputant, Unpleasant Disputant
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE I:Dual Concern Model, Dominating or competition style
- ASSESSING THE NEGOTIATING STYLE:Dual Concern Model, Tactics Used In Integrating
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS:Conflict and Power, Kinds of power in the Relationship Domain
- ASSESSING POWER AMONG DISPUTANTS II:Sources of Relationship Power, Context and Power
- POWER, CONFLICT, AND BATNA III:Role of Third Party in BATNA, Dealing with Power Imbalance
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT I:Stereotyping, Stereotyping in Interpersonal Conflict
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY, AND CONFLICT:Categories of Diversity Issues, Seven Mental Processes to Prove Stereotypes
- STEREOTYPES, DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT III:Individual Difference and Social Category, Cultural differences in values
- MEDIATION I:When is mediation required, Processes Related to Mediation, Product of Mediation
- MEDIATION II:Important distinguishing factors, More Advantages and Disadvantages of Pure Mediation
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION I:Efficiency Consideration, Conflict Management and Prevention
- ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF MEDIATION II:Quality of Consent, Effects on the parties to mediation
- PROCESS OF MEDIATION:Stages of Mediation, Facilitative tactics in mediation
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION I:Characteristics of mediation, Confidentiality
- LAW AND ETHICS OF MEDIATION II:Role of ethics in mediation, 8 Dimensions of Ethics in Mediation
- ARBITRATION I:Ways to Resolve Conflict, Advantages of Arbitration, Disadvantages of Arbitration
- ARBITRATION II:Varieties of Arbitration, Process of Arbitration, Contents of Arbitration Act
- NON BINDING EVALUATION:Disadvantage, Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation
- NON BINDING EVALUATION II:Varieties of Non-binding Evaluation, Advantages and disadvantages of Non-binding Evaluation
- MIXED AND MULTIMODAL DISPUTE RESOLUTION:Six System Design Principles, Extensions of Dispute Systems Design
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS I:Introduction, Necessity of conflict diagnosis, Using conflict diagnosis
- POWER TOOLS AND MAGIC KEYS II:Proposed Contents of a Clients’ Interview, Impediments to use facilitative mediation
- PANCHAYAT, LOCAL GOVERNMENT SYSTEM, AND ADR, Definitions of Panchayat, Definition of Jirga
- SUMMARY AND MESSAGE OF THE COURSE:Definitions of conflict, Negotiation, Meditation, Adjudication