 |
LEGAL CONSIDERATION REGARDING AUDITING |
| << What is Reasonable Assurance |
| Appointment, Duties, Rights and Liabilities of Auditor >> |

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
Lesson
06
LEGAL
CONSIDERATION REGARDING
AUDITING
The
Audit Requirement
� Not
all limited companies are
required to have their financial
statements audited. Nor are
all
companies
required to produce financial statements in the same
formats as many exemptions
may
apply to
small and medium sized
companies.
� Broadly
speaking, small companies
are exempt from the audit
requirement, small and medium
sized
companies
may file abbreviated accounts
with the registrar of companies
and small companies
may
prepare
accounts with reduced
disclosures for their
members.
Appointment,
Duties, Rights and Liabilities of
Auditor
Appointment:
First
Auditors
a)
The
first auditors of a company shall be
appointed by the directors within 60
days of
incorporation
of the company [252(3)]
b)
The
first auditors will hold
office till the first annual
general meeting
[252(3)].
c)
If the
directors fail to appoint the
first auditors, the members
shall appoint the
first
auditors,
provided further that the auditors
such appointed shall not be
removed during
the
tenure expect through a
special resolution
[(252(6)].
d)
Where
the first auditors are not
appointed either by the directors or by the
members within
120
days of incorporation of the company, the
Securities & Exchange Commission
of
Pakistan
(Commission) will appoint the
auditor [252(6)].
Subsequent
Auditors
(a) At
each annual general meeting
the company (members) shall
appoint the auditors [252(1)].
(b)
The auditors shall hold
office from the conclusion of
that meeting till the
conclusion of
next
annual general meeting
[Section 252(1)].
(c) If
no auditors are appointed at annual
general meeting Commission
shall appoint an
auditor.
To
exercise this power the company must give
notice to Commission within one
week of
these
powers having become exercisable
[252(7)].
Note:
Provided
that an auditor or auditors appointed in
a general meeting may be
removed before
conclusion
of the next annual general
meeting through a special
resolution [252(1)].
Casual
Vacancy
a)
Any casual vacancy
shall be filled by directors.
[Sec 252(4)].
b)
Auditors so appointed shall
hold office till next
annual general meeting.[Sec
252(5)]
c) If
directors do not appoint auditors to
fill casual vacancy within
30 days, Commission
may
appoint
an auditor.[Sec 252(6)]
Commission's
powers to appoint auditors
[252(6)]
The
Securities & Exchange Commission of
Pakistan may appoint an
auditor if the following situations
arise:
a) First auditors
are not appointed within
120 days from
incorporation;
b)
Subsequent auditors are not
appointed in annual general
meeting;
c)
Casual vacancy is not filled
within 30 days; and
d)
Auditors appointed are
unwilling to act as
auditors.
To
exercise this power, the company must
give notice to Commission within one
week of its powers
becoming
exercisable.
15
Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
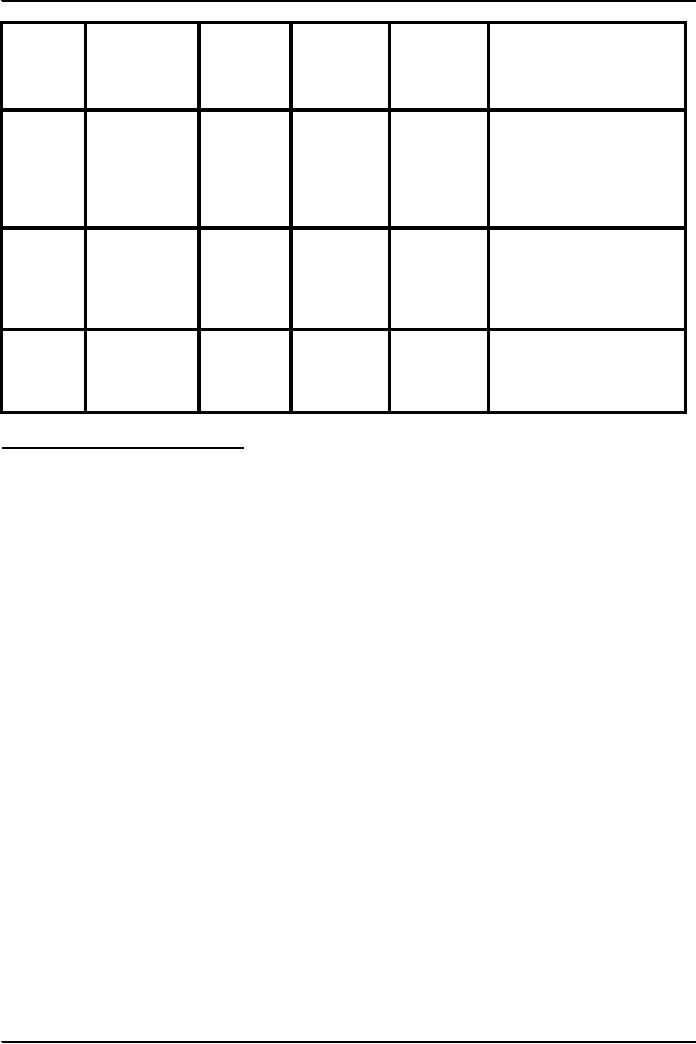
SUMMARY
Auditors
Time
of
Appointing
Term of
Appointing
Remarks
appointment
Authority
Office
Authority
in
default
First
1st
Within
60 days
Directors
Till
first
Members
Members
shall appoint 1st
Auditors
of
AGM
auditors at a
general meeting
Incorporation
within
120 days. After
120
days
SECP may make the
appointment.
Subsequent
AGM
Members
Till
next
SECP
If auditors
are not appointed
Auditors
AGM
in
Auditors AGM. AGM,
SECP
may appoint auditors.
Casual
Within
30 days
Directors
Till
next
SECP
After
30 days of vacancy.
Vacancy
of the
vacancy
AGM
Vacancy
of the vacancy
AGM
SECP may appoint
auditors.
Remuneration
of Auditors [252(8)]
Fixation
of remuneration of auditors depends upon the
authority appointing the auditors,
i.e.
i)
If auditors
are appointed by directors,
directors shall fix the
remuneration.
ii)
If auditors
are appointed by COMMISSION,
COMMISSION shall fix
remuneration.
iii)
In all
other cases, the members
(Company) shall fix the
remuneration.
Note:
Minimum
hourly rates are also
recommended by The Institute of
Chartered Accountants of Pakistan
(ICAP)
which is specified in members'
Handbook Volume II (Part II
ATR-14).
SUMMARY
Appointing
Authority Remuneration Fixed
by
a)
Directors
Directors
b)
Commission
Commission
c)
In all
other case Members
(Company)
Procedure
for Change of Subsequent
Auditors/ Removal of Auditors /
Appointment of New
Auditors
(Section-253)
New
auditors can be appointed in place of
retiring auditors if the following
requirements are
fulfilled.
a)
Notice
from a member is required for a
resolution at the AGM (253(1)).
b)
The
member shall give notice to the company
at least 14 days before the AGM that
he
intends to
propose the appointment of another person
as auditor (253(2)).
c)
On
receipt of the notice the company shall
send a copy of such notice to
the:
i)
retiring
auditor, forthwith
ii)
members,
at least seven days before the
AGM. (253(2))
d)
In
case of a listed company, notice
shall be published at least in one
issue of an English
and an
Urdu daily newspaper having circulation in the
province where the
stock
exchange(s)
is situate on which the shares of the
company are listed.
e)
The
retiring auditor can make
representations and the company
shall send a copy of
representation
to a member or it may be read at
AGM.
Provided
that the representation cannot be sent OR
read at the AGM if the Registrar does
not
permit
so on the application of the company or
any other person. (253
(3)).
f)
A
company within 14 days after the AGM
shall notify to the Registrar of
the
i)
appointment
of new auditors with their
consent letter. 253(5).
16

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
ii)
retirement or
removal of auditors. Section
253(6)
Note:
Under
the Schedule-I Part-I of the Chartered
Accountant Ordinance, 1961 new
auditor accepting
the
appointment without communicating with
the previous auditor shall be deemed to
be guilty of
professional
misconduct. The Institute of
Chartered Accountant of Pakistan
has issued Auditing
Technical
release
(ATR-2) explaining what does the
word "Communication" means. Therefore, it
is necessary for the
new
auditors to communicate with the previous auditors
before accepting the appointment to
ascertain that
he has
no objection on professional grounds,
regarding the appointment. Clause 7 of
the Schedule requires
that
incoming auditor should ensure before
accepting the appointment, that
requirements of the Companies
Ordinance,
1984 regarding his
appointment have been
fulfilled.
Change
of Auditors - Checklist
Timing
Actions
Required
Notice
from a member from the date
of AGM
At
least 14 days
Send
Copy of the notice to:
a)
The
retiring auditor
forthwith
b)
Members
At
least 7 days before
The
date of AGM Publication of the fact in
newspapers anytime before the AGM. That
notice has been
received.
Representation by auditors Sent to
members before AGM or read at AGM.
Notification
of the change to the Registrar within 14
days after the date of
AGM.
Removal of
Auditors
i)
First
auditor appointed by the directors
may be removed by the members in a
general
meeting.
ii)
Another
person nominated by a member shall be
appointed in place of the
outgoing
auditor.
iii)
The
notice of nomination of the proposed
auditor should be given to the member's at
least
14
days before the general meeting
and all the procedure stated
above would be required to
be
followed in this case
also.
iv)
An
auditor or auditors appointed in an
annual general meeting may
be removed before
conclusion
of the next annual general
meeting through a special
resolution.
v)
In the
above case, SECP may
appoint the auditor(s) of the
company.
Qualification
& Disqualification of
Auditors
Qualification
254(1)
For
appointment as auditor
of:
a)
a Public
Company or
b)
a Private
Company which is a subsidiary of a Public
Company.
c)
a Private
Company having paid up capital of three
million rupees or
more.
The
person must be a Chartered
Accountant within the meaning of the
Chartered Accountants Ordinance,
1961.
Note:
For
listed companies an auditor
must have a satisfactory QCR
(quality control review) rating
issued
by
ICAP.
Disqualifications
254(3)
Following
persons are not qualified to
become auditors of a company:
i)
Present
directors, other officer or
employees of the company or who held
these offices
during
the last three years.
ii)
A partner or
employee of a director, other officer or
employee of the company.
iii)
A
spouse of a director.
17

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
iv)
A
person who is indebted to the
company.
v)
A body
corporate.
vi)
A
person or his spouse or
minor children or in case of
firm all partners of such
firm who
holds
any shares of an audit
client or any of its
associated companies.
Provided
that if such a person holds
shares prior to his
appointment as auditors, whether as an
individual or
a partner in a
firm the fact shall be disclosed on
his appointment as auditor
and such person shall
disinvest
such
shares within ninety days of
such appointment.
vii)
A
person disqualified for appointment as an
auditor due to above reasons
is disqualified
from
holding the office of auditor of another
company which is a subsidiary or
holding
company
of that company
254(4).
18
Table of Contents:
- AN INTRODUCTION
- AUDITORS’ REPORT
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Auditing
- OBJECTIVE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES GOVERNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- What is Reasonable Assurance
- LEGAL CONSIDERATION REGARDING AUDITING
- Appointment, Duties, Rights and Liabilities of Auditor
- LIABILITIES OF AN AUDITOR
- BOOKS OF ACCOUNT & FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Contents of Balance Sheet
- ENTITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENT AND ASSESSING THE RISKS OF MATERIAL MISSTATEMENT
- Business Operations
- Risk Assessment Procedures & Sources of Information
- Measurement and Review of the Entity’s Financial Performance
- Definition & Components of Internal Control
- Auditing ASSIGNMENT
- Benefits of Internal Control to the entity
- Flow Charts and Internal Control Questionnaires
- Construction of an ICQ
- Audit evidence through Audit Procedures
- SUBSTANTIVE PROCEDURES
- Concept of Audit Evidence
- SUFFICIENT APPROPRIATE AUDIT EVIDENCE AND TESTING THE SALES SYSTEM
- Control Procedures over Sales and Debtors
- Control Procedures over Purchases and Payables
- TESTING THE PURCHASES SYSTEM
- TESTING THE PAYROLL SYSTEM
- TESTING THE CASH SYSTEM
- Controls over Banking of Receipts
- Control Procedures over Inventory
- TESTING THE NON-CURRENT ASSETS
- VERIFICATION APPROACH OF AUDIT
- VERIFICATION OF ASSETS
- LETTER OF REPRESENTATION VERIFICATION OF LIABILITIES
- VERIFICATION OF EQUITY
- VERIFICATION OF BANK BALANCES
- VERIFICATION OF STOCK-IN-TRADE AND STORE & SPARES
- AUDIT SAMPLING
- STATISTICAL SAMPLING
- CONSIDERING THE WORK OF INTERNAL AUDITING
- AUDIT PLANNING
- PLANNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Audits of Small Entities
- AUDITOR’S REPORT ON A COMPLETE SET OF GENERAL PURPOSE FINANCIALSTATEMENTS
- MODIFIED AUDITOR’S REPORT