 |
MODIFIED AUDITOR’S REPORT |
| << AUDITOR’S REPORT ON A COMPLETE SET OF GENERAL PURPOSE FINANCIALSTATEMENTS |
Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
Lesson
45
MODIFIED
AUDITOR'S REPORT
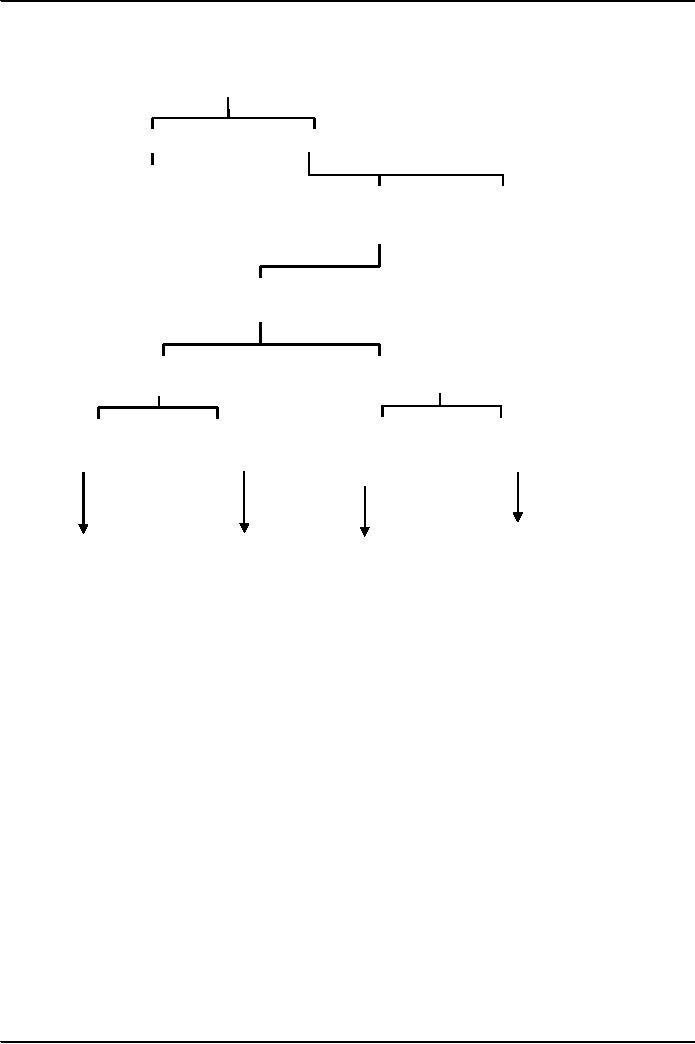
REPORTS/OPINIONS
TREE
STANDARD
MODIFIED
Unqualified
Affect
the
Do not
affect
Auditor's
opinion
auditor's
opinion
(Emphasis
of the matter)
DEPENDS
UPON NATURE
OF
CIRCUMSTANCES
LIMITATION
ON
DISAGREEMENT
SCOPE
OF WORK
WITH
MANAGEMENT
Material
but not so
Material
Material
but
Material
&
Material
& Pervasive
&
Pervasive
not so
material
Pervasive
and
Pervasive
Adverse
opinion
Qualified
Disclaimer
of opinion
Qualified
(Financial
statement
Opinion
(we do
not express an
opinion
do not
give a true
(Except
for)
opinion
on the financial
(Except
for)
and
fair view)
statements)
MODIFICATIONS
TO THE AUDITOR'S REPORT
(Effective
for auditor's reports dated
on or after December 31,
2006).
Here we
shall discuss the
circumstances when the independent
auditor's report should be
modified
and
the form and the content of
the modifications to the auditor's report
in those circumstances.
The
wording of auditor's report is
modified in the following
situations:
Matters that Do
Affect the Auditor's
Opinion
�
Qualified
opinion,
�
Disclaimer
of opinion, or
�
Adverse
opinion.
Matters that Do
Not Affect the Auditor's
Opinion
�
Emphasis
of matter
MATTERS
THAT DO AFFECT THE AUDITOR'S
OPINION
An
auditor may not be able to
express an unqualified opinion when
either of the following
circumstances
exists and, in the auditor's
judgment, the effect of the
matter is or may be material
to
the
financial statements:
(a)
There
is a limitation on the scope of
the auditor's work;
or
146

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
(b)
There
is a disagreement with management
regarding the acceptability of
the accounting
policies
selected, the method of their application
or the adequacy of financial
statement
disclosures.
Limitation
on Scope
(a)
Imposed by
the entity
A
limitation on the scope of the auditor's
work may sometimes be
imposed by the entity
(for
example,
when the terms of the
engagement specify that the auditor
will not carry out an
audit
procedure
that the auditor believes is necessary).
However, when the limitation in
the terms of a
proposed
engagement is such that the auditor
believes the need to express
a disclaimer of opinion
exists;
the auditor would ordinarily
not accept such a limited
engagement as an audit engagement,
unless
required by statute. Also, a
statutory auditor would not
accept such an audit engagement
when
the
limitation infringes on the auditor's
statutory duties.
(b)
Imposed by
circumstances
A
scope limitation may be
imposed by circumstances (for
example, when the timing of
the auditor's
appointment is
such that the auditor is unable to
observe the counting of physical
inventories). It may
also
arise when, in the opinion
of the auditor, the entity's
accounting records are
inadequate or when
the
auditor is unable to carry
out an audit procedure believed to be
desirable. In these
circumstances,
the
auditor would attempt to
carry out reasonable
alternative procedures to obtain
sufficient
appropriate
audit evidence to support an unqualified
opinion.
When
there is a limitation on the scope of
the auditor's work that
requires expression of a qualified
opinion
or a disclaimer of opinion, the auditor's
report should describe the
limitation and indicate
the
possible
adjustments to the financial statements that
might have been determined
to be necessary had
the
limitation not
existed.
A
qualified opinion should
be expressed when the auditor concludes
that an unqualified opinion
cannot
be expressed but that the
effect of any limitation on
scope is not so material and
pervasive as
to
require a disclaimer of opinion. A
qualified opinion should be expressed as
being `except for'
the
effects
of the matter to which the qualification
relates.
A disclaimer
of opinion should
be expressed when the
possible effect of a limitation on
scope is so
material
and pervasive that the
auditor has not been
able to obtain sufficient appropriate
audit
evidence
and accordingly is unable to
express an opinion on the financial
statements.
Whenever
the auditor expresses an opinion
that is other than unqualified, a clear
description of all the
substantive
reasons should be included in
the report and, unless
impracticable, a quantification of the
possible
effect(s) on the financial statements.
Ordinarily, this information
would be set out in a
separate
paragraph preceding the opinion or
disclaimer of opinion on the financial
statements and
may
include a reference to a more
extensive discussion, if any, in a note
to the financial statements.
Illustrations
of these matters are set out
below.
Limitation
on Scope--Qualified Opinion
We
have audited........................
Management
is responsible .............................
Our
responsibility is to express an opinion on
these financial statements based o
our audit. Except as
discussed
in the following paragraph, we
conducted our audit in accordance
with
.................................
We did
not observe the counting of
the physical inventories as of December
31, 20X1, since that
date
was
prior to the time we were
initially engaged as auditors
for the Company. Owing to
the nature of
the
Company's records, we were
unable to satisfy ourselves as to
inventory quantities by other
audit
procedures.
In our
opinion, except for the
effects of such adjustments, if
any, as might have been
determined to
be
necessary had we been able
to satisfy ourselves as to physical
inventory quantities, the
financial
statements
give a true and fair view of
... (remaining words are
the same as illustrated in the
opinion
paragraph)
Limitation
on Scope--Disclaimer of Opinion
We
were not able to observe all
physical inventories and
confirm accounts receivable
due to
limitations
placed on the scope of our
work by the Company.)
147

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
Because
of the significance of the matters
discussed in the preceding paragraph, we
do not express an
opinion
on the financial statements."
Disagreement
with Management
The auditor
may disagree with management
about matters such as the
acceptability of accounting
policies
selected, the method of their
application, or the adequacy of
disclosures in the financial
statements.
If such disagreements are
material to the financial statements,
the auditor should express
a
qualified or an
adverse opinion.
A
qualified opinion should
be expressed when the auditor concludes
that an unqualified opinion
cannot
be expressed but that the effect of
any disagreement with
management is not so material
and
pervasive
as to require an adverse opinion. A
qualified opinion should be expressed as
being `except
for'
the effects of the matter to which the qualification
relates.
An
adverse opinion should
be expressed when the effect
of a disagreement is so material
and
pervasive
to the financial statements that the auditor
concludes that a qualification of the
report is not
adequate
to disclose the misleading or
incomplete nature of the financial
statements.
Illustrations
of these matters are set out
below.
Disagreement
on Accounting Policies--Qualified Opinion
We
have audited........................
Management
is responsible .............................
Our
responsibility is to express an opinion on
these financial statements based o
our audit. Except as
discussed
in the following paragraph, we
conducted our audit in accordance
with
.................................
As
discussed in Note (Ref no.) to
the financial statements, no depreciation
has been provided in
the
financial
statements which practice, in our
opinion, is not in accordance
with International
Financial
Reporting
Standards. The provision for
the year ended December
31, 2007, should be Rs.___
based
on the
straight-line method of depreciation
using annual rates of x% for
the building and y% for
the
equipment.
Accordingly, the fixed assets should be
reduced by accumulated depreciation of
Rs. __
and
the loss for the year
and accumulated deficit
should be increased by Rs.__
and Rs.__,
respectively.
In our
opinion, except for the
effect on the financial statements of the
matter referred to in the
preceding
paragraph, the financial statements
give a true and fair view of
... (remaining words are
the
same
as illustrated in the opinion
paragraph)
Disagreement
on Accounting Policies--Inadequate Disclosure--Adverse
Opinion
"We
have audited ... (remaining
words are the same as
illustrated in the introductory
paragraph
Management
is responsible for ... (remaining
words are the same as
illustrated in the
management's
responsibility
paragraph
Our
responsibility is to ... (remaining words
are the same as illustrated in the
auditor's responsibility
paragraphs)
(Paragraph(s)
discussing the disagreement.)
In our
opinion, because of the effects of
the matters discussed in the
preceding paragraph(s), the
financial
statements do not give a true
and fair view of (or `do
not present fairly, in all
material
respects,')
the financial position of ABC Company as
of December 31, 2007, and of
its financial
performance
and its cash flows for
the year then ended in
accordance with International
Financial
Reporting
Standards."
MATTERS
THAT DO NOT AFFECT THE AUDITOR'S
OPINION
In
certain circumstances, an auditor's
report may be modified by
adding an emphasis of
matter
paragraph
to highlight a matter affecting the financial
statements which is included in a note to
the
financial
statements that more
extensively discusses the
matter.
The
addition of such an emphasis of
matter paragraph does not
affect the auditor's opinion.
The
paragraph
would preferably be included
after the paragraph containing the
auditor's opinion but
before the
section on any other reporting
responsibilities, if any. The emphasis of
matter paragraph
would
ordinarily refer to the fact
that the auditor's opinion is not
qualified in this respect.
For
example:
The auditor
should modify the auditor's
report by adding a paragraph to
highlight a material
matter
regarding
a going
concern problem.
148

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
"Without
qualifying our opinion, we draw
attention to Note (Ref no)
in the financial statements
which
indicates that the Company
incurred a net loss of Rs.__
during the year ended
December 31,
2007
and, as of that date, the
Company's current liabilities exceeded
its total assets by Rs.__.
These
conditions,
along with other matters as
set forth in Note (Ref no),
indicate the existence of a
material
uncertainty
which may cast significant
doubt about the Company's ability to
continue as a going
concern."
The
auditor should consider
modifying the auditor's report by
adding a paragraph if there is
a
significant
uncertainty (other than a going concern problem), the
resolution of which is dependent
upon
future events and which may
affect the financial statements. An
uncertainty is a matter
whose
outcome
depends on future actions or
events not under the
direct control of the entity
but that may
affect
the financial statements.
An
illustration of an emphasis of matter
paragraph for a significant
uncertainty in an
auditor's
report
follows:
"Without
qualifying our opinion we draw attention
to Note X to the financial statements.
The
Company
is the defendant in a lawsuit alleging
infringement of certain patent rights
and claiming
royalties
and punitive damages. The
Company has filed a counter
action, and preliminary hearings
and
discovery
proceedings on both actions
are in progress. The ultimate outcome of
the matter cannot
presently
be determined, and no provision
for any liability that
may result has been
made in the
financial
statements."
The
addition of a paragraph emphasizing a
going concern problem or significant
uncertainty is
ordinarily
adequate to meet the
auditor's reporting responsibilities
regarding such matters.
However,
in
extreme cases, such as
situations involving multiple
uncertainties that are significant to the
financial
statements,
the auditor may consider it appropriate
to express a disclaimer of opinion
instead of
adding
an emphasis of matter
paragraph.
In
addition to the use of an emphasis of
matter paragraph for matters
that affect the financial
statements,
the auditor may also modify
the auditor's report by
using an emphasis of
matter
paragraph,
preferably after the paragraph containing
the auditor's opinion but before
the section on
any
other reporting responsibilities, if any, to
report on matters other than those
affecting the
financial
statements. For example, if an
amendment to
other information in a
document containing
audited
financial statements is necessary and
the entity refuses to make
the amendment, the
auditor
would
consider including in the auditor's
report an emphasis of matter
paragraph describing the
material
inconsistency.
"Without
qualifying our opinion we draw
attention to the fact that the
figures of dividend
proposed
and
earning per share appearing
in the director's report
being part of annual report
are incorrect and
in
conflict with those
disclosed in financial statements. The
matter has been brought to
the notice of
the
management but no corrective
action has been taken by
them in this regard."
149
Table of Contents:
- AN INTRODUCTION
- AUDITORS’ REPORT
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Auditing
- OBJECTIVE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES GOVERNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- What is Reasonable Assurance
- LEGAL CONSIDERATION REGARDING AUDITING
- Appointment, Duties, Rights and Liabilities of Auditor
- LIABILITIES OF AN AUDITOR
- BOOKS OF ACCOUNT & FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Contents of Balance Sheet
- ENTITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENT AND ASSESSING THE RISKS OF MATERIAL MISSTATEMENT
- Business Operations
- Risk Assessment Procedures & Sources of Information
- Measurement and Review of the Entity’s Financial Performance
- Definition & Components of Internal Control
- Auditing ASSIGNMENT
- Benefits of Internal Control to the entity
- Flow Charts and Internal Control Questionnaires
- Construction of an ICQ
- Audit evidence through Audit Procedures
- SUBSTANTIVE PROCEDURES
- Concept of Audit Evidence
- SUFFICIENT APPROPRIATE AUDIT EVIDENCE AND TESTING THE SALES SYSTEM
- Control Procedures over Sales and Debtors
- Control Procedures over Purchases and Payables
- TESTING THE PURCHASES SYSTEM
- TESTING THE PAYROLL SYSTEM
- TESTING THE CASH SYSTEM
- Controls over Banking of Receipts
- Control Procedures over Inventory
- TESTING THE NON-CURRENT ASSETS
- VERIFICATION APPROACH OF AUDIT
- VERIFICATION OF ASSETS
- LETTER OF REPRESENTATION VERIFICATION OF LIABILITIES
- VERIFICATION OF EQUITY
- VERIFICATION OF BANK BALANCES
- VERIFICATION OF STOCK-IN-TRADE AND STORE & SPARES
- AUDIT SAMPLING
- STATISTICAL SAMPLING
- CONSIDERING THE WORK OF INTERNAL AUDITING
- AUDIT PLANNING
- PLANNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Audits of Small Entities
- AUDITOR’S REPORT ON A COMPLETE SET OF GENERAL PURPOSE FINANCIALSTATEMENTS
- MODIFIED AUDITOR’S REPORT