 |
CONSIDERING THE WORK OF INTERNAL AUDITING |
| << STATISTICAL SAMPLING |
| AUDIT PLANNING >> |
Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
Lesson
40
CONSIDERING
THE WORK OF INTERNAL
AUDITING
Introduction
(Meaning of Internal Audit)
Internal
audit is part of internal control, set by
the management, delegating
its supervisory functions
to
specially assigned staff,
with the objective to see that the
internal controls are in operation and
to
assist
them in fulfilling their
responsibilities such as
1.
safeguarding of the assets
2.
reliability of financial records
and
3.
efficiency in operation
Definition
"Internal
auditing" means an appraisal activity
established
within an entity as a service to the
entity.
Its
functions include, amongst other things,
examining, evaluating and
monitoring the adequacy
and
effectiveness
of the accounting and internal control
system.
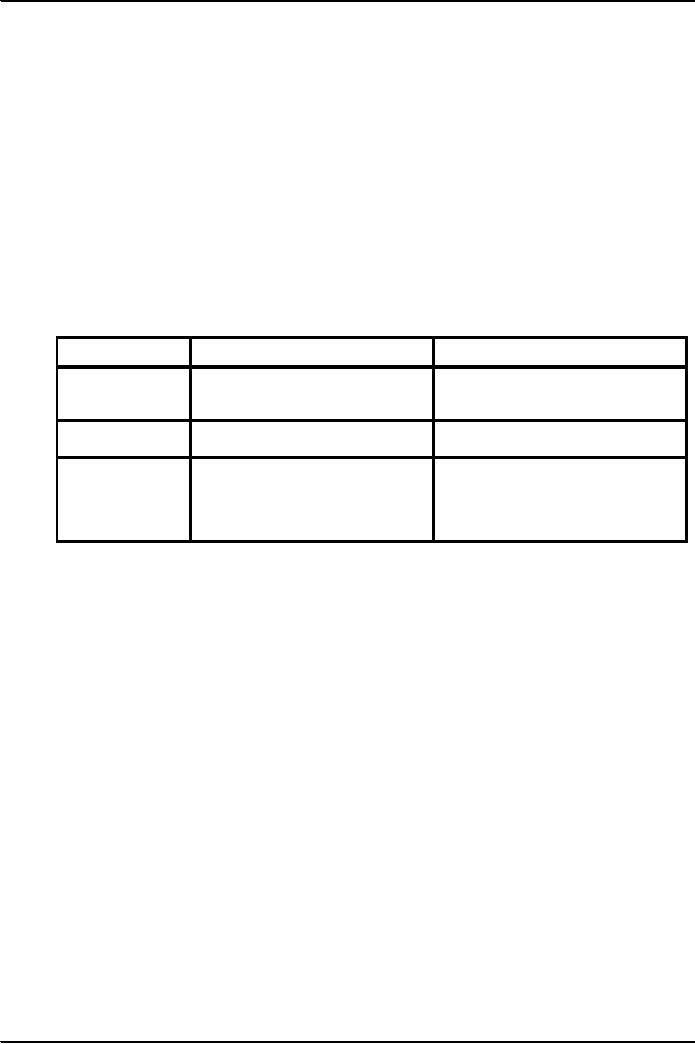
DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL
AUDITORS
INTERNAL
AUDITOR
EXTERNAL
AUDITOR
Objective:
Accounting
system and internal Report on
Financial statements.
control
are operating efficiently.
Responsibility
Responsibility
to the management.
Responsibility
to the share holders.
Scope
of work
Determined by
management.
Determined by
the statute;
otherwise
determined
through mutual
agreement
between
auditor and the client.
Scope
and Objectives of the Internal
Audit Function
Although
the exact nature of internal audit
function is determined by the management,
however,
generally
the aims and objectives of
the internal audit function
are:
i)
Review
and assessment of the internal control
procedures and accounting
system.
ii)
Examination of
financial and operating information
for management, including
detailed
testing
of transactions and
balances.
iii)
Review
of efficiency, economy and
effectiveness of operation.
iv)
Review
of compliance with laws,
regulations, management policy and other
internal
requirements.
Relationship
between Internal Auditing and
the External Auditor
Management's
Requirements Vs Independent Report on
Financial Statements
Unlike
the internal auditor who is an
employee of the enterprise, the external
auditor is required to be
independent
of the enterprise, usually having a
statutory responsibility to report on the
financial
statements
giving an account of management's
stewardship.
Common
Means
Some
of the means adopted by both
the auditors to achieve
their respective objectives
are common,
e.g.
evaluation of internal control. Therefore, certain
aspect of internal auditing may be useful
in
determining the
nature, timing and extent of
external audit procedures.
Dependence
Vs Independence
Whatever
be the degree of autonomy
given by the management to internal
auditing it cannot enjoy
the
same degree of independence as
external auditors. Moreover,
the responsibility for the
report is
that of the
external auditor alone, and therefore is
indivisible and is not
reduced by the reliance
on
internal
auditing.
128

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
As a
result, all final judgments
relating to matters which are
material to the financial statements
or
other
aspects on, which he is reporting, must be
made by the external auditor
himself.
Understanding
of Internal Auditing
The
external auditors should
obtain a sufficient understanding of internal audit
activities to assist in
planning the audit
and developing an effective audit
approach.
Effective
internal auditing will often allow a reduction in
the procedures performed by the
external
auditors
but cannot eliminate them
entirely. However, external auditor may
decide not to use
the
internal
auditor's work.
Preliminary
Assessment of Internal
Auditing
After
obtaining understanding of internal auditing, if it
appears that its work is
relevant for external
auditors,
the external auditor should, during
the course of planning perform
preliminary assessment
of internal
auditing function. An effective internal audit may
allow a modification in the nature,
timing
and
extent of procedures performed by external
auditors.
Criteria
while Obtaining Understanding and
Preliminary Assessment of Internal
Auditing
Before
relying on the work performed by the
internal auditor, it is necessary for the
external auditor
to
make an assessment of the
effectiveness and relevance of the
internal audit function by
considering
the
following:
Organizational
status: The internal
auditor is an employee of the entity and
therefore
i)
cannot
be independent, however the external
auditor should evaluate to what extent he
is
free
in performing his duties and
communicate with external
auditor and consider
any
constraints
placed upon his
work.
Ideally, internal
auditor should be reporting to the
highest level of management
and should
be
free from other operating
responsibility.
Scope
and Objectives of Internal
Audit Function: The
external auditor should
examine
ii)
the
range and aim of the
assignments assigned to internal auditors
by the management and
whether
management acts on internal audit
recommendations.
Technical
Competence: The
external auditor should ascertain
whether staff of the internal
iii)
audit
function has adequate
technical training and proficiency as
auditors.
Due
Professional Care: The
external auditor should consider
whether the internal auditor
iv)
has
performed his work with
reasonable care and skill
i.e. work is properly
planned,
supervised
and reviewed. He should also
consider existence of working
papers, work
programs,
audit manuals etc.
Liaison and
Coordination
The extent of
liaison would normally encompass
the following:
i)
Initial
planning to formulate a joint approach to
minimize the tests performed by
the two
auditors
i.e. tests level, sample
selection, documentation of work
performed, review and
reporting
procedures.
ii)
Regular
meetings between the internal and
external auditors during the
year.
iii)
Exchange
of knowledge between the two
auditors i.e. the external
auditors should be
informed
of any significant matter
that comes to the knowledge
of internal auditor which
he
believes may affect to work
of external auditor. Similarly the
external auditor should
inform
the internal auditor of any significant
matters which may affect his
work.
Evaluating
Internal Audit
Work/Review/Controlling
Where
the external auditor has
decided to place reliance on the
work of internal auditor, he
should
review
the working papers to
satisfy himself as
to:-
i)
Audit
programs are
adequate.
ii)
The
work is performed by trained staff and
the work of assistants is properly
supervised,
reviewed and
documented.
iii)
Sufficient
appropriate audit evidence was
obtained.
iv)
Conclusions
made are appropriate.
v)
Reports
prepared are based on the
work done.
129

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
vi)
Exceptions
or unusual items have been
properly resolved. The external
auditor
should
record all the working he
has received. The external auditor
should also
test
the work of internal auditor.
Testing
the Work of Internal
Auditing
It can
be done in the following
ways:
i)
Re-performing
the work done by internal auditor, on
test basis, to ensure that
the same
results
are achieved;
ii)
Selecting
a few similar items and
perform independent test;
and
iii)
Observation of
internal auditing procedures.
130
Table of Contents:
- AN INTRODUCTION
- AUDITORS’ REPORT
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Auditing
- OBJECTIVE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES GOVERNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- What is Reasonable Assurance
- LEGAL CONSIDERATION REGARDING AUDITING
- Appointment, Duties, Rights and Liabilities of Auditor
- LIABILITIES OF AN AUDITOR
- BOOKS OF ACCOUNT & FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Contents of Balance Sheet
- ENTITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENT AND ASSESSING THE RISKS OF MATERIAL MISSTATEMENT
- Business Operations
- Risk Assessment Procedures & Sources of Information
- Measurement and Review of the Entity’s Financial Performance
- Definition & Components of Internal Control
- Auditing ASSIGNMENT
- Benefits of Internal Control to the entity
- Flow Charts and Internal Control Questionnaires
- Construction of an ICQ
- Audit evidence through Audit Procedures
- SUBSTANTIVE PROCEDURES
- Concept of Audit Evidence
- SUFFICIENT APPROPRIATE AUDIT EVIDENCE AND TESTING THE SALES SYSTEM
- Control Procedures over Sales and Debtors
- Control Procedures over Purchases and Payables
- TESTING THE PURCHASES SYSTEM
- TESTING THE PAYROLL SYSTEM
- TESTING THE CASH SYSTEM
- Controls over Banking of Receipts
- Control Procedures over Inventory
- TESTING THE NON-CURRENT ASSETS
- VERIFICATION APPROACH OF AUDIT
- VERIFICATION OF ASSETS
- LETTER OF REPRESENTATION VERIFICATION OF LIABILITIES
- VERIFICATION OF EQUITY
- VERIFICATION OF BANK BALANCES
- VERIFICATION OF STOCK-IN-TRADE AND STORE & SPARES
- AUDIT SAMPLING
- STATISTICAL SAMPLING
- CONSIDERING THE WORK OF INTERNAL AUDITING
- AUDIT PLANNING
- PLANNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Audits of Small Entities
- AUDITOR’S REPORT ON A COMPLETE SET OF GENERAL PURPOSE FINANCIALSTATEMENTS
- MODIFIED AUDITOR’S REPORT