 |
Rules of Debit and Credit |
| << Dual Aspect of Transactions |
| Steps in Accounting Cycle >> |

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Lesson-3
ACCOUNTING
CYCLE/PROCESS
(Continued)
*Rules
of Debit and
Credit
From
our discussion up to this
point, we have established following rules
for Debit and Credit:
Any
account that obtains a
benefit is Debit.
OR
Anything
that will provide benefit to
the business is Debit.
Both
these statements may look
different but in fact if we consider
that whenever an account
benefits as
a
result of a transaction, it will have to
return that benefit to the
business then both the
statements will
look
like different sides of the
same picture.
For
credit,
Any
account that provides a
benefit is Credit.
OR
Anything
to which the business has a
responsibility to return a benefit in
future is Credit.
As
explained in the case of Debit,
whenever an account provides
benefit to the business the
business
will
have a responsibility to return that
benefit at some time in
future and so it is Credit.
*Rules
of Debit and Credit for
Assets
Similarly
we have established that whenever a
business transfers a value /
benefit to an account and as
a
result
creates some thing that
will provide future benefit;
the `thing' is termed as Asset. By
combining
both
these rules we can devise following rules
of Debit and Credit for
Assets:
o When
an asset is created or purchased,
value / benefit is transferred to that
account, so it
is
Debited
I.
Increase
in Asset is Debit
Reversing
the above situation if the asset is sold,
which is termed as disposing off,
for
o
say
cash, the asset account
provides benefit to the cash account.
Therefore, the asset
account
is Credited
II.
Decrease in Asset is
Credit
*Rules
of Debit and Credit for
Liabilities
Anything
that transfers value to the
business, and in turn
creates a responsibility on part of the
business
to
return a benefit, is a Liability.
Therefore, liabilities are the exact
opposite of the assets.
When
a liability is created the benefit is
provided to business by that
account so it is
o
Credited
III.
Increase in Liability is
Credit
When
the business returns the benefit or
repays the liability, the liability
account
o
benefits
from the business. So it is
Debited
10
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
IV.
Decrease in Liability is
Debit
*Rules
of Debit and Credit for
Expenses
Just
like assets, we have to pay
for expenses. From assets,
we draw benefit for a long
time whereas the
benefit
from expenses is for a short
run. Therefore, Expenditure is
just like Asset but for a
short run.
Using
our rule for Debit and
Credit, when we pay cash
for any expense that
expense account
benefits
from
cash, therefore, it is
debited.
Now
we can lay down our
rule for Expenditure:
o
V.
Increase in Expenditure is
Debit
Reversing
the above situation, if we return any
item that we had purchased,
we will
o
receive
cash in return. Cash account
will receive benefit from
that Expenditure account.
Therefore,
Expenditure account will be
credited
VI.
Decrease in Expenditure is
Credit
*Rules
of Debit and Credit for
Income
Income
accounts are exactly
opposite to expense accounts
just as liabilities are
opposite to that of
assets.
Therefore,
using the same principle we
can draw our rules of Debit
and Credit for Income
VII.
Increase
in Income is Credit
VIII.
Decrease
in Income is Debit
Khizr introduced a
capital of Rs.180,000 in his business
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
2006
1-Jul
Cash
Account
1
180,000
Khizr,
Capital
1
180,000
Purchased land for
cash for Rs.141,000
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
3-Jul
Land
Account
141,000
Cash
Account
141,000
Purchased
Land for
Rs.
141,000
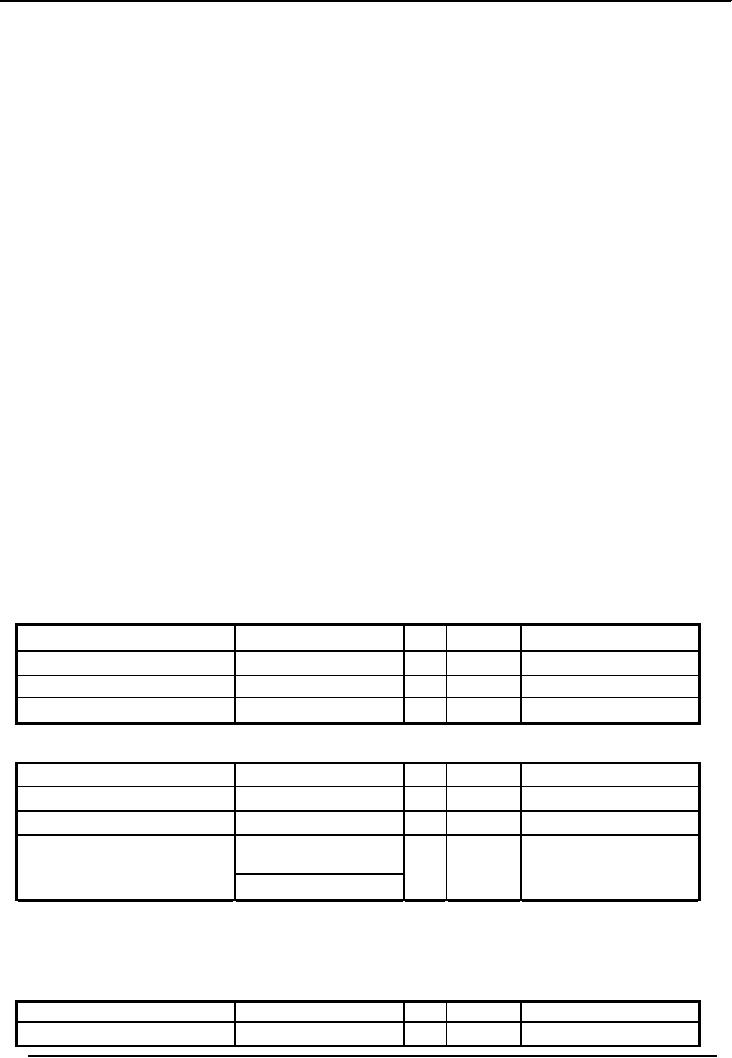
Purchase of
building partly on cash (Rs.15,000) and partly
on credit
(Rs.21,000)
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
5-Jul
Building
Account
36,000
11
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Cash
Account
15,000
Accounts
Payables
21,000
Sale of part of
land on credit for Rs.11,000
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
10-Jul
Accounts
receivables
11,000
11,000
Land
Account
Sold
a portion of land
for
Rs. 11,000.
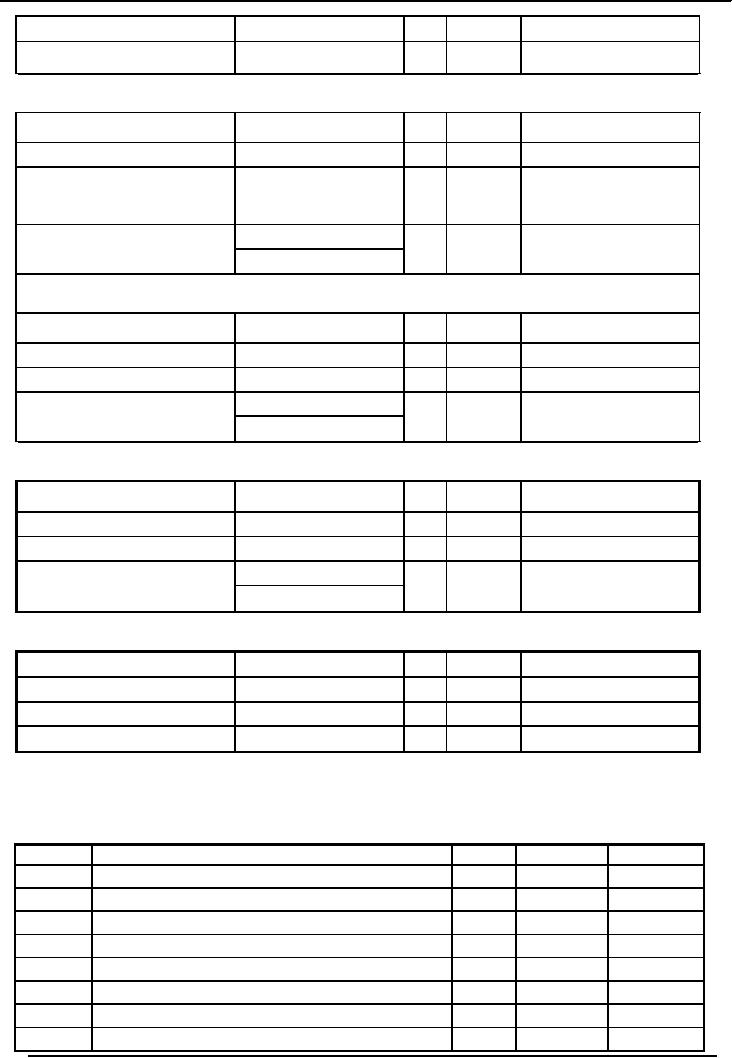
Purchase of Office
Equipment for Rs.5400 on credit
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
14-Jul
Office
equipment
5,400
Accounts
Payables
5,400
Purchased
Equipment
on
credit
Partial collection
of Accounts Rs.1500
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
20-Jul
Cash
account
1,500
Accounts
receivables
1,500
Collection
of accounts
receivables
Payment of
liability (A/C Payable)
Rs.3, 000.
Date
Explanation
Ref
Dr.
Cr.
31-Jul
Accounts
payables
3,000
Cash
account
3,000
Payment of
liability
Khizr
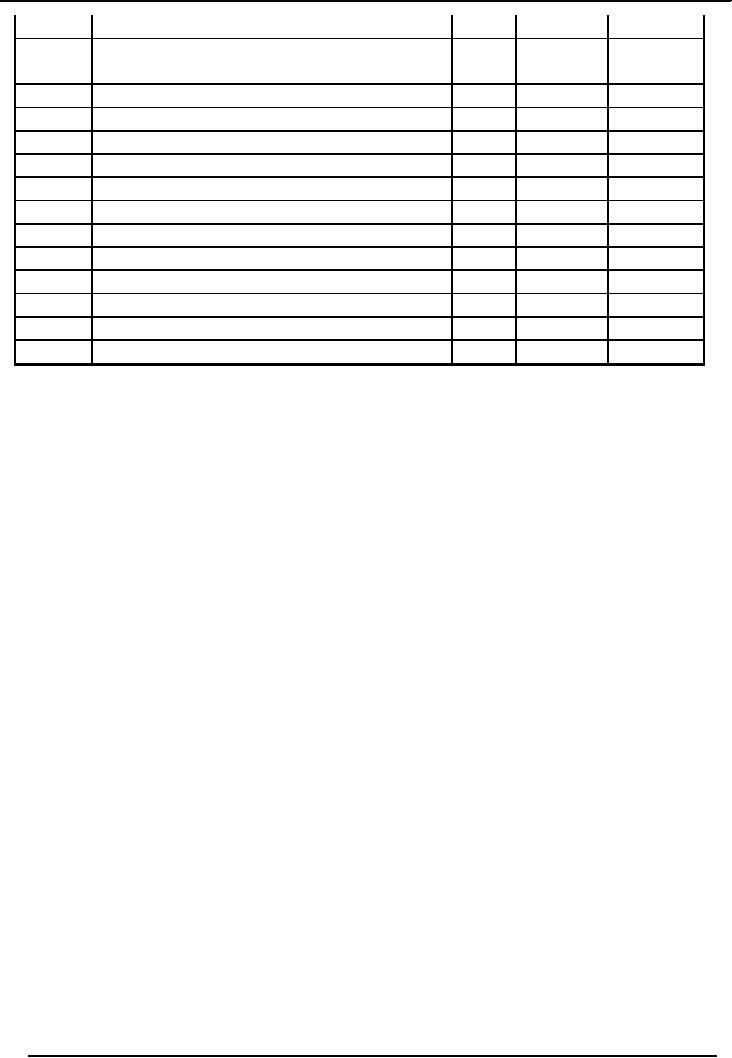
Limited
General
Journal
For the month of
July 2006
Date
Description
L/F
Dr.
Cr.
1-Jul
Cash
Account
180,000
Khizr,
Capital
180,000
Capital
Invested by owner
3-Jul
Land
Account
141,000
Cash
Account
141,000
Purchased
Land for Rs.
141,000
5-Jul
Building
Account
36,000
Cash
Account
15,000
12
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Accounts
Payables
21,000
Purchased
Building partly for cash and
partly on
credit
10-Jul
Accounts
receivables
11,000
Land
Account
11,000
Sold
a portion of land for Rs.
11,000.
14-Jul
Office
equipment
5,400
Accounts
Payables
5,400
Purchased
Equipment on credit
20-Jul
Cash
account
1,500
Accounts
receivables
1,500
Collection
of accounts receivables
31-Jul
Accounts
payables
3,000
Cash
account
3,000
Payment of
liability
13
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- Dual Aspect of Transactions
- Rules of Debit and Credit
- Steps in Accounting Cycle
- Preparing Balance Sheet from Trial Balance
- Business transactions
- Adjusting Entry to record Expenses on Fixed Assets
- Preparing Financial Statements
- Closing entries in Accounting Cycle
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Preparing Cash Flows
- Additional Information (AI)
- Cash flow from Operating Activities
- Operating Activities’ portion of cash flow statement
- Cash flow from financing Activities
- Notes to Financial Statements
- Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement
- First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO)
- Depreciation Accounting Policies
- Accelerated-Depreciation method
- Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate
- Management Discussion & Analyses (MD&A)
- TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
- Incorporation of business
- Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital
- Book Values of equity, share
- SUMMARY
- SUMMARY
- Analysis of income statement and balance sheet:
- COMMON –SIZE AND INDEX ANALYSIS
- ANALYSIS BY RATIOS
- ACTIVITY RATIOS
- Liquidity of Receivables
- LEVERAGE, DEBT RATIOS
- PROFITABILITY RATIOS
- Analysis by Preferred Stockholders
- Efficiency of operating cycle, process
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 1
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 2
- BALANCE SHEET AND INCOME STATEMENT RATIOS
- Financial Consultation Case Study
- ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET & INCOME STATEMENT
- SUMMARY OF FINDGINS