 |
Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital |
| << Incorporation of business |
| Book Values of equity, share >> |
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Lesson-27
TYPES
OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
(Continued)
Authorized
Share Capital
The
maximum amount with which a company
gets registration/incorporation is called
authorized share
capital
of that company.
This
capital can be increased
with the prior approval of
security and exchange commission.
This capital
is
further divided in to smaller
denominations called shares.
Each share usually has a
face value equal to
Rs.
10. According to Companies Ordinance,
this face value can be
increased but can not be
decreased.
The
value of share written on
its face is called face
value or par value or nominal
value
Issued
Share Capital
When
a company issues its shares to general
public at large, the amount raised by the
company with
such
an issue is called issued
share capital. This is also
called Paid up Share
Capital.( total amount
received
by the company). Accounting entry is
recorded for issued share
capital; no such entry
is
recorded
for authorized share
capital.
Preliminary
Expenses
All
expenses incurred up to the stage of
incorporation of the company are called
Preliminary Expenses.
All
these expenses are incurred
by subscribers of the company.
The
maximum amount with which a company
gets registration/incorporation is called
authorized share
capital
of that company. This capital
can be increased with the
prior approval of security
and exchange
commission.
This capital is further
divided in to smaller denominations
called shares.
Each share
usually
has a face value equal to
Rs. 10. According to
Companies Ordinance, this face
value can be
increased
but can not be decreased.
The value of share written
on its face is called face
value.
Shares
are issued for cash as
well as for any asset.
For example, if any member
of the company sell
his/her
land to the company. In return, company
issue him/her fully paid
shares instead of paying
cash.
Those
shares are also part of
paid up capital because company
has received the benefit of
that amount.
Share
Certificate
Share
Certificate is the evidence of ownership of the number
of shares held by a member of
the
company.
When a company issue more than
one share to its member, it
does not issue that number
of
shares
to him/her. Instead, it issues a
certificate under the stamp of the
company that a particular number
of
shares are issued to members
of the company.
Shares
Issued At Premium
When
a company has a good reputation
and earns huge profits, the
demand of its shares
increases in the
market.
In that case, the company is allowed by
the Companies Ordinance 1984, to issue
shares at a
higher
price than their face
value. Such an issue is
called Shares Issued at Premium.
The amount
received
in excess of the face value of the
shares is transferred to an account
called "Share Premium
Account".
This account is used
to:
� Write
off Preliminary Expenses of the
company.
� Write
off the balance amount, in
issuing shares on
discount.
� Issue
fully paid Bonus
Shares.
112

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Shares
Issued On Discount
When
a company is not making huge profits,
rather it is sustaining loss, the demand
of its shares
decreases
in the market. If the company needs extra
funds, then it is allowed by the
Companies
Ordinance
1984, to issue shares at
lesser price than their
face value. Such an issue is
called Shares
Issued
on discount.
The
difference of face value and
the amount received is met by share
premium account, if available. If
there is no
share premium account
available, this difference is shown in
the profit and loss account
of
that
period, in which shares are
issued as loss on issue of
shares at discount.
Capital
stock: This
signifies ownership of a corporation in
the form of shares issued or
sold for cash
and
sometimes in exchange of assets like
land, buildings etc., and
services (e.g. legal), using
market
value
of shares issued in exchange. It includes
common and preferred stock. When only
one type of
stock is
issued, the words "common stock" is
used. It is the amount invested by stockholders
i.e. paid-
in-capital.
It is also called "Outstanding
Shares" i.e. shares in the
hands of stockholders.
Stockholders'
equity
Rs.
Cumulative
8% preferred stock, convertible
Rs.100
par value callable or
redeemable
at Rs.110,
authorized 20,000
shares;
Issued
10,000 shares.
1,000,000
Common stock
Rs.10
Par/stated
value, authorized 100,000
shares,
Issued
and outstanding 50,000
shares.
500,000
Paid-in-capital
1,500,000
Plus
additional paid-in-capital+
donated
Capital/assets
at market value +
Retained
Earning
(or minus accumulated losses).
Retained
earning transferred to B/Sheet= Opening
balance + Net Profit for the
year Dividends.
Additional
paid-in-capital: shows excess amount
received, when stock is sold
for more
than
par value. Underwriters, (banks,
investment companies etc) make
profit by selling share at
higher
prices.
Retained earnings is an element of stockholders
equity, does not indicate
the form in which
these
resources
are currently held. These
may have been invested in
land, building, equipment or
any other
assets,
or might have been used in
liquidating debts.
Balance
Sheet as on June 30
Assets
Rs.
_____
Current
assets.
1,000,000
Fixed
assets.
1,692,000
Total
assets.
2,692,000
Liabilities
& Stockholders' equity
Liabilities
Current.
112,000
12%
long-term Notes
payable
200,000
Outside
liabilities.
312,000
Paid-in-capital
(from previous slide)
1,500,000
113

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Additional
Paid-in-Capital, Common stock.
750,000
Retained
earnings
130,000
Total
Stockholders' equity.
2,380,000
Total
Liabilities & Stockholder equity.
2,692,000
Dividend
Profit
distributed to the share holders for
their investment in the company is called
Dividend. Dividend
is
approved by the share holders in the
annual general meeting at the recommendation of the
directors.
Dividend
is paid out of profits. If,
in any year, company could
not make any profit. No
dividend will be
paid
to share holders. Dividend is
paid to registered share holders of the
company. Registered share
holders
are those members of the
company, who are enlisted in
the register of share holders of the
company.
Subscribers
/ Sponsors Of The
Company
Subscribers
/ Sponsors are the persons
who sign articles and memorandum of the company
and
contribute
in the initial share capital of the
company.
Issuance
Of Further Capital
Where a company
wants to issue further
capital (called raising the
capital), shares are first
offered to
current
shareholders. The issuance of
further capital to Present Shareholders
is called Right
Issue. This
issue
is in proportion to current shares
held by the shareholders. The
shareholders can accept or
reject
the
offer. If shareholders refuse to
accept these shares then
these are offered to other
people.
Journal
Entries
�
Shares
issued against cash
Debit:
Cash
/ Bank Account
Credit:
Share
Capital Account
�
Shares
issued against transfer of asset:
Debit:
Asset
Account
Credit:
Share
Capital Account
This
is called issuance of asset in
kind.
Bonus
Shares
This
is another way of distributing dividend.
When a company decides, not to
give cash to the
share
holders as
dividend, it issued shares
called bonus shares, to the
share holders for which it
receives no
cash.
These are fully paid
shares.
Financial
Statements Of Limited
Companies
In Pakistan,
Financial Statements of limited
companies are prepared in accordance
with:
� International
accounting standards adopted in
Pakistan.
� Companies
Ordinance 1984.
In
case of conflict the requirements of
Companies Ordinance would
prevail over Accounting
Standards.
Components
Of Financial Statements
Components of
companies' financial statements
are as follows:
114
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
�
Balance
Sheet
�
Profit
and Loss Account
�
Cash
Flow Statement
�
Statement
of Changes in Equity
�
Notes
to the Accounts
�
Comparative
figures of Previous
Period
Equity
Equity
is the total of capital, reserves and
undistributed profit. That
means the amount contributed by
share
holders plus accumulated profits of the company.
Equity, therefore, represents
the total of
shareholders
fund in the company.
Statement Of
Changes In Equity
The
statement of changes in equity
shows the movement in the shareholders
equity (capital and
reserves)
during the year. We can say
that it replaces profit and
loss appropriation account
of
partnership
business.
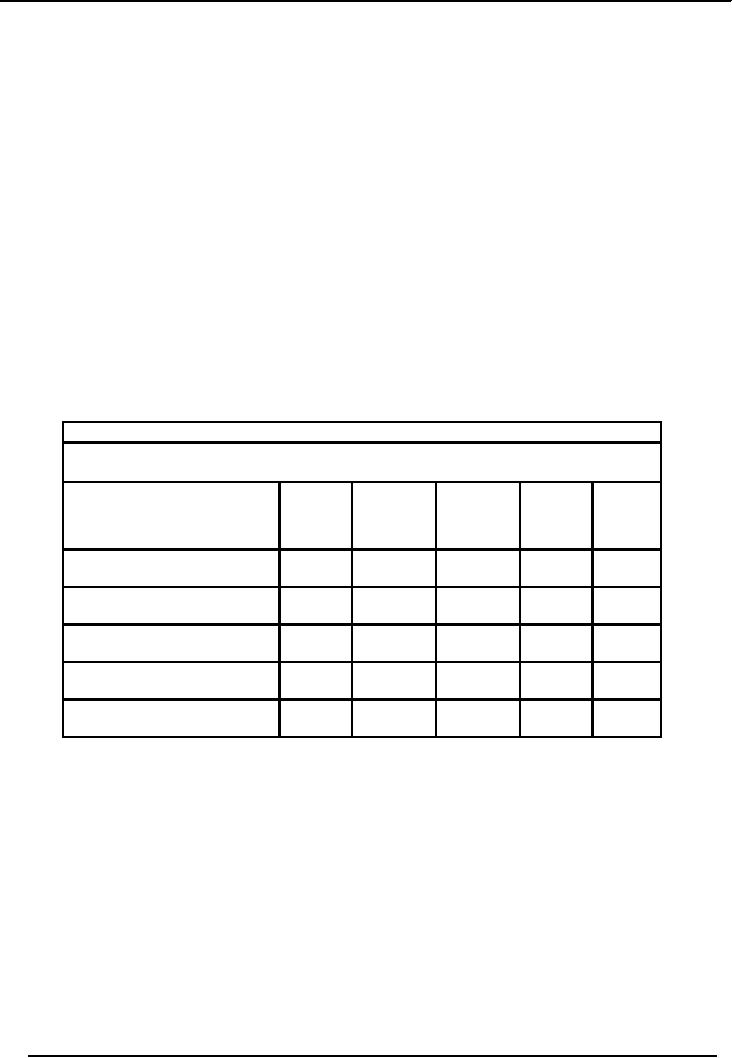
FORMAT
OF STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN
EQUITY
Name of
the Company
Statement of
Changes in Equity
For
Year Ended June 30,
2002
Share
Share
Reserves
Profit
& Total
Capital
Premium
Loss
A/c
Account
Balance On Jun
30, 2000
X
X
X
X
X
Movements
During the Year
X
X
Balance On Jun
30, 2001
X
X
X
X
X
Movements
During the Year
X
X
Balance On
June 30, 2002
X
X
X
X
X
115
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- Dual Aspect of Transactions
- Rules of Debit and Credit
- Steps in Accounting Cycle
- Preparing Balance Sheet from Trial Balance
- Business transactions
- Adjusting Entry to record Expenses on Fixed Assets
- Preparing Financial Statements
- Closing entries in Accounting Cycle
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Preparing Cash Flows
- Additional Information (AI)
- Cash flow from Operating Activities
- Operating Activities’ portion of cash flow statement
- Cash flow from financing Activities
- Notes to Financial Statements
- Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement
- First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO)
- Depreciation Accounting Policies
- Accelerated-Depreciation method
- Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate
- Management Discussion & Analyses (MD&A)
- TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
- Incorporation of business
- Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital
- Book Values of equity, share
- SUMMARY
- SUMMARY
- Analysis of income statement and balance sheet:
- COMMON –SIZE AND INDEX ANALYSIS
- ANALYSIS BY RATIOS
- ACTIVITY RATIOS
- Liquidity of Receivables
- LEVERAGE, DEBT RATIOS
- PROFITABILITY RATIOS
- Analysis by Preferred Stockholders
- Efficiency of operating cycle, process
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 1
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 2
- BALANCE SHEET AND INCOME STATEMENT RATIOS
- Financial Consultation Case Study
- ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET & INCOME STATEMENT
- SUMMARY OF FINDGINS