 |
Accelerated-Depreciation method |
| << Depreciation Accounting Policies |
| Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate >> |
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Lesson-22
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Continued)
Depreciation
expenses for year would be:
=cost-(estimated) Residual value =
17,000-2000 = 3000
*(Estimated
years of useful life-5)
ii)
Accelerated-Depreciation
method: In
this method higher depreciation rate is
charged
in
early years and lower rate
in later years. Since new plants
are most efficient in
early
years,
matching principle demands
that higher depreciation may
be charged in earlier
years.
Depreciation
= Book Value x Accelerated
Dep. Rate
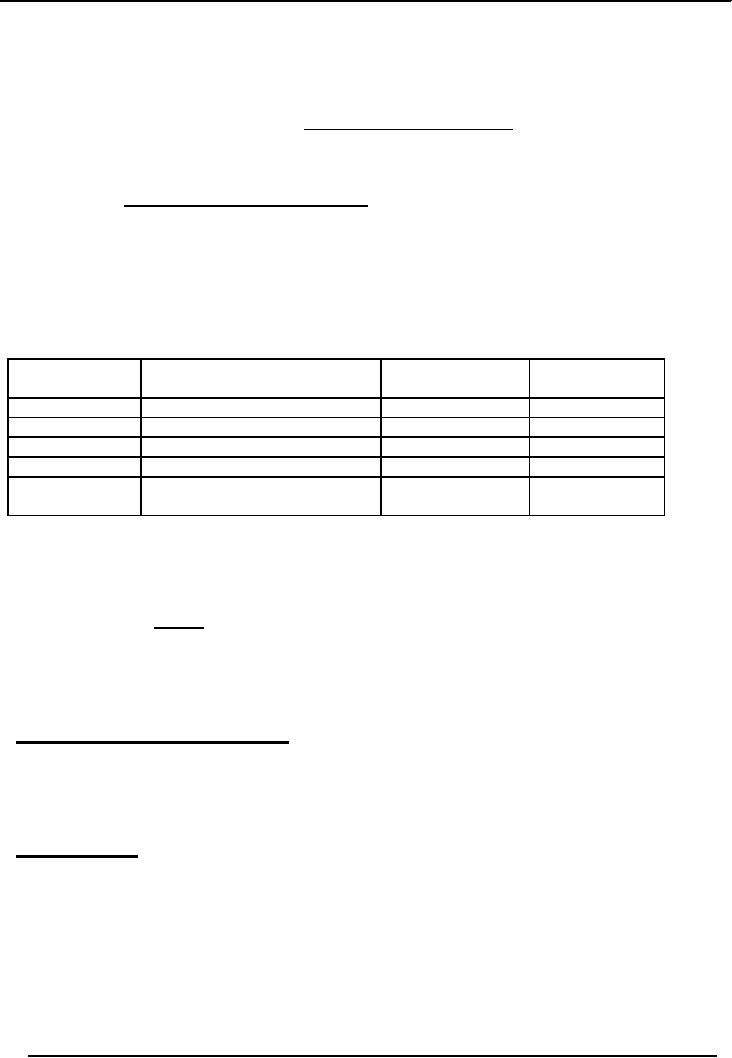
Example:
Taking the above case of plant
asset acquired for Rs.17,
000
Year
Depreciation
Accumulated
Book
Value
Depreciation
1
17,000
X 40%
6800
6800
10200
2.
10,200
X 40%
4080
10880
6120
3.
6,120
X 40%
2448
13328
3672
4.
3,672
X 40%
1469
14797
2203
5.
2,203
X 40%
881
15000
2000
(reduced to
203)
Note
that sine total depreciation
in five years is Rs.15, 000
(Rs.17, 000 2,000), the
depreciation for the
last
year is reduced from 881 to
203 to bring the total
depreciation amount in 5 years to Rs.17,
000.
Principles
of disclosure and Consistency of Accounting Methods.
This is the basic
concept
underlying reliable financial
statements, i.e. consistently
following the Inventory
valuation/
pricing
and Depreciation calculation Methods.
Disclosure of the Accounting methods
used, in Balance
Sheet
or in the Notes is also an essential
requirement of Disclosure Principle. If
however, Accounting
Method
(s) are changed disclosure
must be made of reasons for
such change, and of the effect of
change
upon
the company's net income.
Annual
Report Generated By Business
Annual
Report is part of Financial
Reporting Process which contains
Financial
Statements,
Notes to financial statements,
Auditors' Report, Five-year summary of
key financial and
non-financial
data, and Management's discussion and analysis of
operations (MD&A).
Auditor's
Report
Audit
of financial statements is independent of
the business issuing these.
Financial
Statements
preparation is Management's
responsibility, whereas expressing
opinion as to their fairness
is the
Auditor's responsibility, Audit
Report is issued along with
financial statements to persons
outside
the
business. It provides assurance to
outside users about the
completeness and reliability
(not
necessarily
accuracy) of Financial
Statements.
Auditor
is hired by the company being audited.
Usually a Management letter is
also
issued
by Auditors to Company's management,
recommending steps for improving
company's internal
control
structures.
98

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Fairness' in the
context of Auditor's Report
means that financial
statements
are
not
misleading.
Audit is conducted according to Generally
Accepted Auditing Standards.
During Audit, the
Auditors
obtain reasonable assurance
that financial statements
are free of "material"
misstatements.
Audit
is conducted by examining, on a test
basis, evidence supporting the amounts
and disclosures in
the
financial statements. It assesses the
accounting principles used and
significant estimates made
by
management.
It must also be noted that
Audit`s purpose is to determine fairness
of financial statements
and
not to detect frauds, as such. In the
context of materiality, it is to be noted
that an item is material
if
knowledge
of this might reasonably be expected to
influence user's decisions. Also to be
noted is the
fact
an auditor can also make
errors like a physician does
in diagnosis.
End
product of every audit is the
auditor's report. An audit
involves collection of audit evidence
about
the
truth and fairness of
financial statements or other
proposition under review. By
careful examination
of the evidence so
called the auditor draws
appropriate conclusions and forms his
opinion. The
auditor's
report
summarizes results of the work conducted
by the auditor and formally communicates
the
auditor's
opinion.
It is
important to note that the
auditor's report simply
expresses the auditor's opinion on
truth and
fairness
of financial statements as absolutely
correct. An auditor's report is a formal
statement that
includes
the reporting auditor's opinion
formed after careful
examination of books of accounts
and
related
documents. Where as, a certificate is
written conformation of absolute accuracy
of the facts
stated
therein and does not involve
any estimate or
opinion.
Types
of auditor's opinion
An
auditor's opinion may be
unqualified, qualified or adverse. In
certain circumstances the auditor
may
disclaim
an opinion i.e states his
inability to express an
opinion.
Unqualified
opinion
Opinion
of an auditor is termed as unqualified
when the auditor concludes
that that the
financial
statements
give a true and fair view in
accordance with the identified
financial reporting
framework.
There
is no statuary definition of the words "true
and fair". However, true and
fair has been taken
to
mean
the following: (I) free from
prejudice or bias, (II) presentation of an
objective picture, (III) in
accordance
with generally accepted
accounting principles, (IV) consistent
and having clarity,(V)
not
misleading
and understandable by the reader of financial
statements,. (V) presented
fairly, in all
material
respects.
Identified
financial reporting framework
means the set of statutes,
rulers, and standards etc.
That apply
to the
preparation and presentation and presentation of such
financial statements.
According
to the companies ordinance 1984, in an
unqualified audit report the
auditor is required to
make
some statutory affirmations
without reservations, as prescribed in section
255(3).
In an
unqualified opinion the auditor
also impliedly undertakes that
any changes in
accounting
principles
or in the method of their application, and the effects
thereof, have been properly
determined
and
disclosed in the financial
statements.
Modified
opinion
An
auditor may not be able to
express an unqualified opinion.
When either of the
following
circumstances
exists and, in the auditor's judgment, the
effect of which is or may be
material to the
financial
statements:-
99

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
(a)
There is a limitation on the scope of the
auditor's work; or
(b)
There is a disagreement with management
regarding the acceptability of the
accounting policies
selected,
the method of their application or the
adequacy of financial statement
disclosures.
The
circumstances described in (a) could
lead to a qualified opinion or a
disclaimer of opinion.
The
circumstances
described in (b) could lead
to a qualified opinion or an adverse
opinion.
(i)
Qualified Opinion
Opinion
of an auditor is termed as qualified
opinion when the auditor
concludes that an
unqualified
opinion
cannot be expressed but that the
effect of any disagreement with
management, or limitation on
scope
is not so material and pervasive as to
require and adverse opinion or a
disclaimer of opinion. A
qualified
opinion is expressed as being `except
for' the effects of the matter to which the
qualification
relates.
(ii)
Disclaimer of opinion
A
disclaimer of opinion should be
expressed when possible effect of a
limitation on scope of audit is
so
material
and pervasive that the
auditor has not been
able to obtain sufficient
appropriate audit evidence
an
accordingly is unable to express an
opinion on the financial
statements
(iii)
Adverse opinion.
An
adverse opinion should be
expressed when the effect of a
disagreement is so material and
pervasive
to the
financial statements that the
auditor concludes that a
qualification of the report is not
adequate to
disclose
the misleading or incomplete nature of the
financial statements.
100
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- Dual Aspect of Transactions
- Rules of Debit and Credit
- Steps in Accounting Cycle
- Preparing Balance Sheet from Trial Balance
- Business transactions
- Adjusting Entry to record Expenses on Fixed Assets
- Preparing Financial Statements
- Closing entries in Accounting Cycle
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Preparing Cash Flows
- Additional Information (AI)
- Cash flow from Operating Activities
- Operating Activities’ portion of cash flow statement
- Cash flow from financing Activities
- Notes to Financial Statements
- Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement
- First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO)
- Depreciation Accounting Policies
- Accelerated-Depreciation method
- Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate
- Management Discussion & Analyses (MD&A)
- TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
- Incorporation of business
- Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital
- Book Values of equity, share
- SUMMARY
- SUMMARY
- Analysis of income statement and balance sheet:
- COMMON –SIZE AND INDEX ANALYSIS
- ANALYSIS BY RATIOS
- ACTIVITY RATIOS
- Liquidity of Receivables
- LEVERAGE, DEBT RATIOS
- PROFITABILITY RATIOS
- Analysis by Preferred Stockholders
- Efficiency of operating cycle, process
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 1
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 2
- BALANCE SHEET AND INCOME STATEMENT RATIOS
- Financial Consultation Case Study
- ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET & INCOME STATEMENT
- SUMMARY OF FINDGINS