 |
First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO) |
| << Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement |
| Depreciation Accounting Policies >> |

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Lesson-20
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Continued)
In
cost-flow assumptions, three methods
for measuring "cost of good
sold", under GAAP are
used.
In
these three methods, assumptions
are made as to the sequence in
which units were
withdrawn
from inventory. The three
flow assumptions are:-
i)
Average
cost: Values
all merchandise (units sold
and in balance) at the
Average
per-unit cost, under the assumption of
random withdrawal of inventory
units.
Average
cost in the above example: Rs.23,
000 per AC. That would be
the cost of goods
sold.
Ending Inventory to be recorded on
balance sheet would also
take into account
this
figure
of reduction in Inventory.
ii)
First-in-First
- out (FIFO): goods
sold are assumed to be the
first units
that
were purchased.
iii)
Last-in-First-Out
(LIFO): units
sold are assumed to be those
which were most
recently
acquired.
During
Inflation, FIFO shows less
expense on income statement
and higher inventory
valuation
on balance sheet and values ending
inventory at current cost, whereas
LIFO shows higher
expenses
on income statement and lower
inventory valuation on balance
sheet.
It
should be noted that
Inventory valuation significantly affects
both b/sheet and
income
statements.
Each valuation method/cost-assumption
produces different results in
financial statements
and
tax returns.
Valuation
of Stock
Any
manufacturing organization purchases
different material through
out the year. The prices
of
purchases
may be different due to inflationary
conditions of the economy. The question
is, what item
should
be issued first & what
item should be issued later
for manufacturing. For this
purpose, the
organization
has to make a policy for
issue of stock. All the issues for
manufacturing and valuation of
stock
are recorded according to the policy of
the organization. Mostly these three
methods are used
for
the
valuation of stock:
�
First
in first out (FIFO)
�
Last
in first out (LIFO)
�
Weighted
average
First
in first out (FIFO)
The
FIFO method is based on the assumption
that the first merchandise
purchased is the first
merchandised
issued. The FIFO uses actual
purchase cost. Thus, if merchandise
has been purchased at
several
different costs, the inventory
(stock) will have several different
cost prices. The cost of
goods
sold
for a given sales transaction
may involve several different
cost prices.
Characteristics
�
This
is widely used method for
determining values of cost of goods
sold and closing stock.
74

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
�
In the
FIFO method, oldest available purchase
costs are transferred to cost of
goods sold. That
means
the cost if goods sold has a
lower value and the profitability of the
organization becomes
higher.
�
As the
current stock is valued at recent
most prices, the current
assets of the company have the
latest
assessed values.
Last in
first out (LIFO)
As the
name suggests, the LIFO method is
based on the assumption that the
recently purchased
merchandise
is issued first. The LIFO
uses actual purchase cost. Thus, if
merchandise has been
purchased
at several different costs, the inventory
(stock) will have several different
cost prices. The
cost
of goods sold for a given
sales transaction may involve several
different cost prices.
Characteristics
�
This
is alternatively used method for
determining values of cost of goods
sold and closing stock.
�
In the
LIFO method recent available
purchase costs are transferred to
cost of goods sold.
That
means
the cost of goods sold has a
higher value and the profitability of the
organization
becomes
lower.
�
As the
current stock is valued at oldest prices, the
current assets of the company have the
oldest
assessed
values.
Weighted
average method
When
weighted average method is in use, the
average cost of all units in
inventory, is computed after
every
purchase. This average cost
is computed by dividing the total cost of
goods available for sale
by
the number of
units in inventory. Under the
average cost assumption, all items in
inventory are
assigned
the
same per unit cost. Hence, it
does not matter which units
are sold; the cost of goods
sold is always
based
on current average unit
cost.
Characteristics
�
Under
the average cost assumption, all items in
inventory are assigned same
per unit cost (the
average
cost). Hence it does not matter
which units are sold
first. The cost of goods
sold is
always
on the current average unit
cost.
� Since
all inventories are assigned
same cost, this method does
not make any effect on
the
profitability
and does not
increase/decrease any asset in the
financial statements.
� This
is the alternatively used method for
determining values of cost of goods
sold and closing
stock.
Example
�
Receipts:
01
Jan 20--,
10
units @ Rs. 150 per
unit
02
Jan 20--,
15
units @ Rs. 200 per
unit
10
Jan 20--,
20
units @ Rs. 210 per
unit
�
Issues:
05
Jan 20--,
05
units
06
Jan 20--,
10
units
15
Jan 20--,
15
75
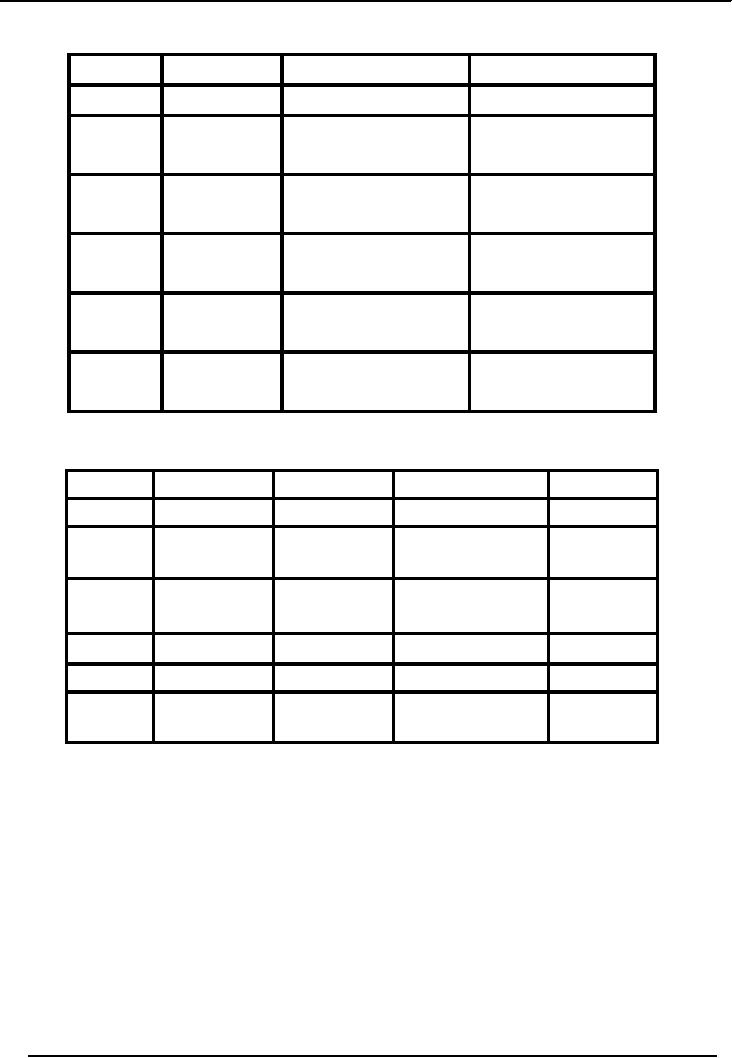
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
FIFO
Method of Stock
Valuation
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock
01-01-20--
10 @
Rs. 150
10 x
150 = 1500
02-01-20--
15 @
Rs. 200
10 x
150 = 1500
15 x
200 = 3000
4500
05-01-20--
5 @
150 = 750
750
5 x
150 = 750
15 x
200
=
3000
3750
06-01-20--
5 @
150 = 750
0 x
150 =
0
5 @
200 = 1000 1750
10 x
200
=
2000
2000
10-01-20--
20 @
Rs. 210
10 x
200 = 2000
20 x
210
=
4200
6200
15-01-20--
10 @
200 = 2000
0 x
200 =
0
5 @
210 = 1050 3050
15 x
210
=
3150
3150
Weighted
Average Method of Stock
Valuation
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock
Average
Cost
01-01-20--
10x150 = 1500
1500
1500/10=150
02-01-20--
15x200 = 3000
1500
+ 3000 = 4500
4500/25=180
05-01-20--
5x180
= 900
4500
900 = 3600
3600/20=180
06-01-20--
10x180
= 1800
3600
1800 = 1800
1800/10=180
10-01-20--
20x210 = 4200
1800
+ 4200 = 6000
6000/30=200
15-01-20--
15x200
= 3000
6000
3000 = 3000
3000/15=200
Effects
of valuation method on profit
FIFO
Method
�
Cost of Sales
= 750
+ 1750 + 3050
=
5,550
Gross
Profit
=
7500 5550
=
1,950
Weighted
Average Method
�
Cost of Sales = 900 +
1800 + 3000
=
5,700
Gross
Profit
=
7500 5700
=
1,300
76
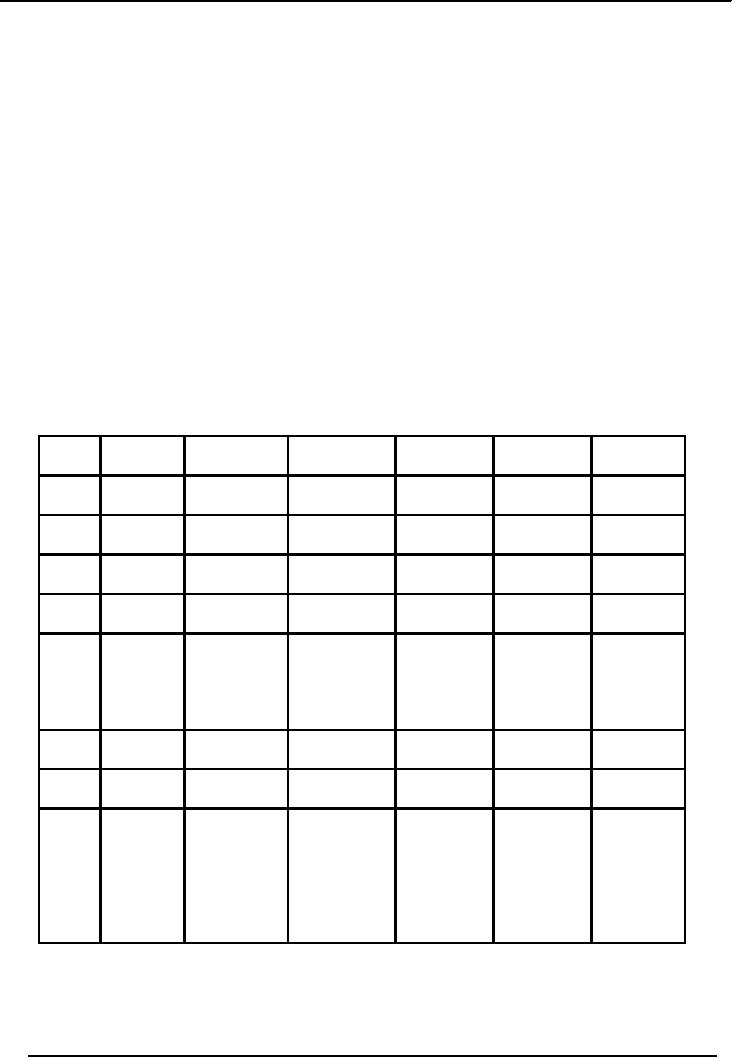
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Illustration
XYZ
Company is a manufacturing concern.
Following is the receipts & issues record
for the month of
May,
2002
Date
Receipts
Issues
May
7
200
units @ Rs. 50/unit
May
9
60
units
May
13
150
units @ Rs. 75/unit
May
18
100
units @ Rs. 60/unit
May
22
150
units
May
24
100
units
May
27
100
units @ Rs. 50/unit
May
30
200
units
Calculate
the value of closing stock by
� FIFO
Method
� Average
Method
Solution
Valuation
of Stock by FIFO
Method
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock Total
Remaining
Net
Balance
Amount
No. of
units
May
7
200
units @
200 x
50 = 10,000
200
10,000
Rs.
50/unit
10,000
May
9
60
units @ Rs. 60 x 50 = 3,000
(3,000)
140
7,000
50/unit
May
13
150
units @
75 x
150 = 11,250
290
18,250
Rs.
75/unit
11,250
May
18
100
units @
60 x
100 = 6,000
390
24,250
Rs.
60/unit
6,000
140
units @ 50 x 140 =
(7,750)
240
16,500
May
22
Rs.
50/unit
7,000
10
units @ Rs.
75/unit
10 x 75
=
750
May
24
100
units @ 75
x
100
(7,500)
140
9,000
Rs.
75/unit
=7,500
May
27
100
units @
50 x
100 = 5,000
240
14,000
Rs.
50/unit
5,000
40
units @ Rs. 75 x 40 = 3,000
(12,000)
40
2,000
May
30
75/unit
100
units @ 60 x 100 =
6,000
Rs.
60/unit
60
units @ Rs.
50 x 60 =
3,000
50/unit
77
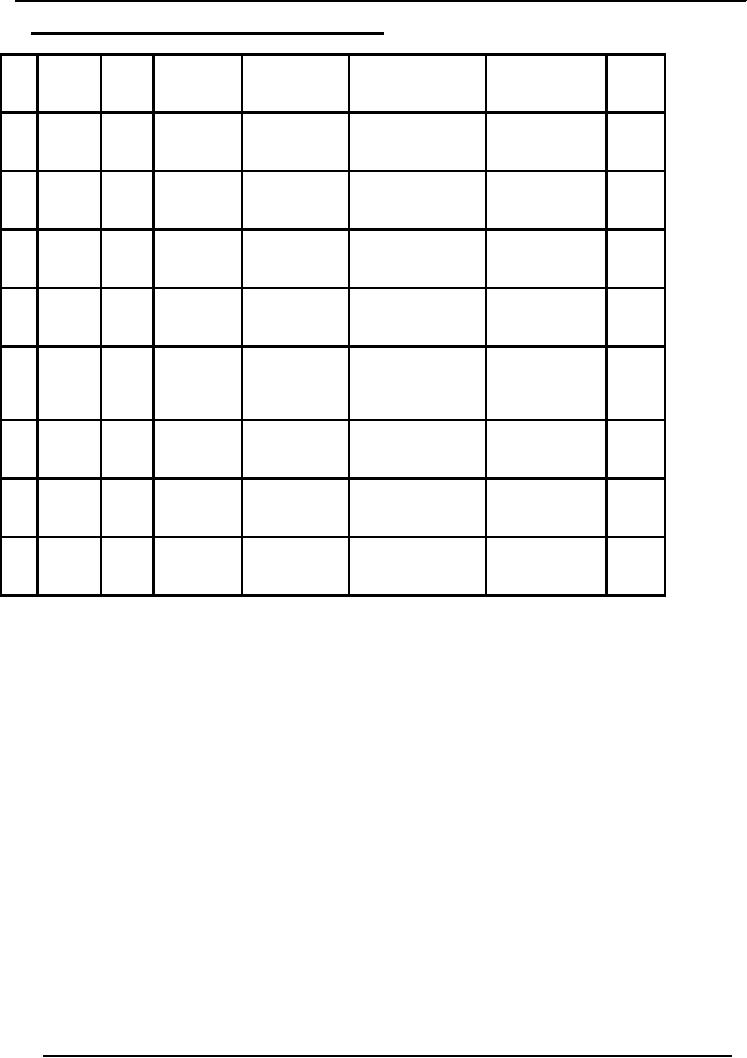
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Valuation
of Stock by Weighted Average
Method:
Date
Receipts Issues
Value
of
Total
Total
Units
Average
Net
Stock
Amount(Rs.)
Cost(Rs.)/unit
Balance
(Rs.)
May
200 units
200 x
50
10,000
200
50
10,000
7
@
Rs.
=
50/unit
10,000
May
60
60 x
50
(3,000)
140
7,000
9
units
=
3,000
May
150 units
150 x
75
7,000+11250
140+150=290
18250/290=62.9 18,250
13
@
Rs.
=
=
75/unit
11,250
18250
May
100 units
100 x
60
18250+6000
290+100
24250/390
24,250
18
@
Rs.
=
=
=
=
60/unit
6,000
24250
390
62.2
May
150
150 x
62.2
(9,330)
390-150
14,920
22
units
=
=
9330
240
May
100
100 x
62.2
(6,220)
240-100
8,700
24
units
=
=
6220
140
May
100 units
100 x
50
8,700+5,000
140+100
13700/240
13,700
27
@
Rs.
=
=
=
=
50/unit
5,000
13,700
240
57.1
May
200
200 x
57.1
(11,420)
240-200
2,280
30
units
=
=
11,420
40
78
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- Dual Aspect of Transactions
- Rules of Debit and Credit
- Steps in Accounting Cycle
- Preparing Balance Sheet from Trial Balance
- Business transactions
- Adjusting Entry to record Expenses on Fixed Assets
- Preparing Financial Statements
- Closing entries in Accounting Cycle
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Preparing Cash Flows
- Additional Information (AI)
- Cash flow from Operating Activities
- Operating Activities’ portion of cash flow statement
- Cash flow from financing Activities
- Notes to Financial Statements
- Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement
- First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO)
- Depreciation Accounting Policies
- Accelerated-Depreciation method
- Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate
- Management Discussion & Analyses (MD&A)
- TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
- Incorporation of business
- Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital
- Book Values of equity, share
- SUMMARY
- SUMMARY
- Analysis of income statement and balance sheet:
- COMMON –SIZE AND INDEX ANALYSIS
- ANALYSIS BY RATIOS
- ACTIVITY RATIOS
- Liquidity of Receivables
- LEVERAGE, DEBT RATIOS
- PROFITABILITY RATIOS
- Analysis by Preferred Stockholders
- Efficiency of operating cycle, process
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 1
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 2
- BALANCE SHEET AND INCOME STATEMENT RATIOS
- Financial Consultation Case Study
- ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET & INCOME STATEMENT
- SUMMARY OF FINDGINS