 |
ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES |
| Dual Aspect of Transactions >> |

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Lesson-1
ACCOUNTING
& ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
Accounting
Almost
every organization and individual
maintains accounts and deals
with
accounting.
In simple terms, it can be
described as a record of Income and
expenditure of a business
organization,
or budget vs. utilization, in the
case of a government non-commercial
organization. In the
case
of the business entity, accounting
would deal with measuring,
recording and communicating
the
results
of business activities. That is
why; Accounting is often
called "Language of Business".
Purpose
of Accounting
Accounting
provides decision-makers with sufficient,
relevant information to make
prudent
and intelligent business decisions. This
information is provided through
accounting reports
called
financial statements. The
whole process is called
"financial reporting"
�
The
purpose of accounting is to organize the
financial details of
business.
�
To
identify the financial
transactions.
�
To
organize the financial data
into useful
information
�
To
measure the value of these
information in terms of
money
�
To analyze,
interpret, and communicate the
information to persons or groups,
both
inside
or outside the business.
Financial
Statements Generated by a
Business
A
business generates four
financial statements at the end of its
accounting period:-
i)
Income
statement: shows
operational results of business
during/over the accounting
period.
ii)
Statement of owners'
equity: showing
changes in owner's equity
through
profit/additional
investment or through losses/drawl by
owner.
iii)
Balance
sheet showing
financial position at the end of the
accounting period i.e.
a
picture
of what the business owns and
what it owes.
iv)
Statement of
cash flows giving
a picture of cash inflows (receipts) and
cash outflows
(payments)
over/during the accounting period. It is
prepared from the two
major
financial
statements viz Income
Statement and Balance
Sheet.
Notes
to Financial Statements:
In
addition to above, notes
containing additional information
(financial & non-
financial)
about the business are also
attached to financial
statements.
Accounting
Period
Accounting
period is the period of time covered by
an Income Statement. It is usually
one
year.
It can either be calendar year
(Jan to Dec) or financial year
(July to June). Financial Statements
are
prepared at the
end of accounting period and are the
end product of accounting
process/cycle.
1

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Different
Types of Business
Organizations
1. Sole
Proprietorship
According
to D.W.T. Stafford, "It is the simplest
form of business organization,
which is owned and
controlled
by one man"
Sole
proprietorship is the oldest form of
business organization which is
owned and controlled by one
person.
In this business, one man
invests his capital himself. He is
all in all in doing his
business. He
enjoys
the whole of the profit. The
features of sole proprietorship
are:
�
Easy
Formation
�
Unlimited
Liability
�
Ownership
�
Profit
�
Management
�
Easy
Dissolution
2.
Partnership
According
to Partnership Act, 1932, "Partnership is
the relation between persons who have
agreed to
share
the profits of a business carried on by
all or any of them acting
for all."
Partnership
means a lawful business
owned by two or more persons.
The profit of the business
shared
by the
partners in agreed ratio.
The liability of each
partner is unlimited. Small and
medium size
business
activities are performed
under this organization. It
has the following features:
�
Legal
Entity
�
Profit
and Loss Distribution
�
Unlimited
Liability
�
Transfer
of Rights
�
Management
�
Number
of Partners
3.
Joint Stock
Company
According
to S. E. Thomas, "A company is an incorporated
association of persons formed usually
for
the
pursuit of some commercial
purposes"
A
joint stock company is a voluntary association of
persons created by law. It
has a separate legal
entity
apart
from its members. It can
sue and be sued in its
name. In the joint stock
company, the work of
organization
begins before its incorporation by
promoters and it continues after incorporation.
The joint
stock company
has the following
feature:
�
Creation
of Law
�
Separate
Legal Entity
�
Limited
Liability
�
Transferability
of shares
�
Number
of Members
�
Common
Seal
2

Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Generally
Accepted Accounting Principles
(GAAP)
These
are `Ground rules' i.e.
Principles for preparing
financial statements. These
are
constantly
evolving. These embody
accounting concepts, measurement
techniques and standards of
presentation of
financial statements. These
Accounting Principles enable
comparability between various
enterprises
and of the operational performance of the
same enterprise over many
years. These give
reliability
to Financial Statements.
Following
are some of the Generally
Accepted Accounting
Principles:
i)
Entity
principle:
specific
business entity separate
from personal affairs of the
owner(s).
ii)
Cost
principle:
valuation and recording of assets at
cost.
iii)
Going-concern
assumption: connected
with cost principle, assets
acquired for use
and
not
for resale.
iv)
Objectivity
principle:
definite, factual basis for
assets valuation; measuring
transactions
objectively.
v)
Stable
currency principle. The
currency remains more or
less
stable and rate of
inflation
is almost zero.
vi)
Adequate
disclosure concept: facts
necessary for proper
interpretation of statements;
"subsequent
events", lawsuits against the
business, assets
pledged as
securities/collaterals,
contingent liabilities etc; reflected in
Notes.
ACCOUNTING
EQUATION
ASSETS
= LIABILITIES + OWNER'S
EQUITY
Balance
Sheet is based on Accounting
Equation. It is in fact, a detailed
statement of the
Equation.
The Equation in a way shows,
utilization of Funds and Sources of
Funds. In other words, it
shows
what a business OWNS and
what it OWES. Alternately, the Accounting
Equation or Balance
Sheet
is a description of Total Assets of a
business against the claimants of these
Assets. Therefore,
this
Equation
shows financial position on a
specific date. The three titles in the
Equation are Elements of
Balance
Sheet. Similarly Elements of
Income Statement would be
Revenues & Expenses and their
net
affects
Owner's equity.
Within
the Elements, there would be sub-elements,
for example, the Element or
Account
"Assets"
would consist of cash,
Accounts Receivable, Land, and
Building etc. Each
financial
transaction
affects two or more elements or
sub-elements of the Accounting Equation.
Therefore, we
can
say that each financial
transaction affects Balance Sheet i.e.
financial position of the business.
This
would
be clear from the following
illustration.
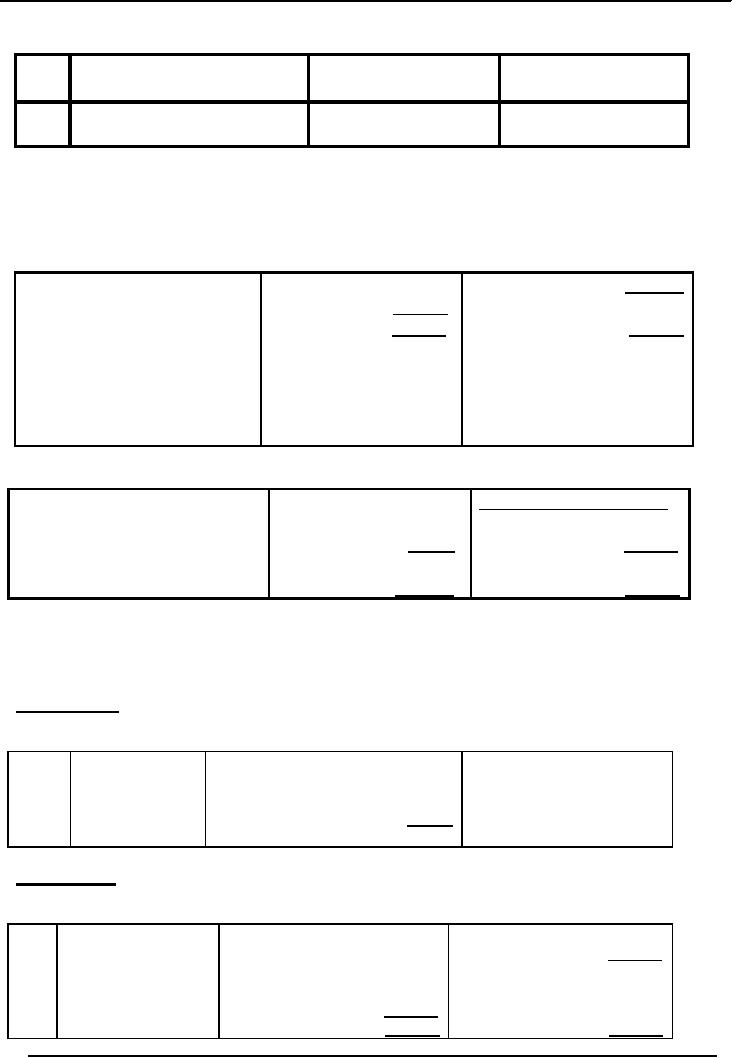
Khizr
property dealer:
The
proprietor starts business
with deposit of Rs.180, 000. On
July 1, 2006
3
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
Financial
Position as on July 1,
2006
Assets
(Rs)
Owner's
equity (Rs)
i)
Deposit
in business by proprietor/ Cash
180,000
Khizr,
Capital 180,000
owner.
Jul 3,
06
Land
Valuing Rs. 141, 000 is
purchased for cash on July
3.
Financial
Position on that date would
be
II)
Purchase of land for
cash
Cash
39,000
Khizr,
Capital
180,
000
(Rs.141,000)
Land
141,000
Total
assets
180,000
Total
owner's equity
180,000
(Cash
is reduced by
Rs.141,
000, but
correspondingly
a new
asset
land has come
up)
Jul 5,
06
III)
Purchase of building
for
Cash
24,000
Liabilities
& Owner's equity
(Rs.36,000)
partly on cash
Land
141,000
Accounts/Notespayable21,000
Rs.15,000) and
partly on credit
Building
36,000
Owner's
equity
180,000
(Rs.21,000)
Total
assets
2,01,000
Total
201,000
Rs.15,
000 is paid in cash for the
building which further
reduces cash from Rs.39,
000 to Rs.24, 000.
For
remaining amount of Rs.21, 000, a
liability in the form of accounts or
notes payable involve
interest, where as
accounts payable are without
interest.
July
10, 2006: A
part of land valuing Rs.11,
000 was sold on credit. A
new asset "Accounts
Receivable"
has been introduced. The
new financial position as a
result of this transaction would
be:
24,000
Accounts Payable
21,000
iv)
Sale
of part of Cash
11,000
Owner's equity
180,000
land
on credit for Accounts
Receivable
Rs.11,000
Land
130,000
_______
Building
36,000
201,000
Total
201,000
July
14, 2006: Office
equipment for Rs.5400/- was
purchased on credit. A new
liability of Rs.5400 has
accrued,
raising Accounts Payable from
Rs.21, 000 to Rs.26,
400.
v)
Purchase
of Office Cash
24,000
A/C
Payable
26,400
Equipment
for
A/Cs Receivable
11,000
Owner's
equity
180,000
Rs.5400 on
credit.
Land
130,000
Building
36,000
Office
equipment
5,400
206,400
Total
206,400
4
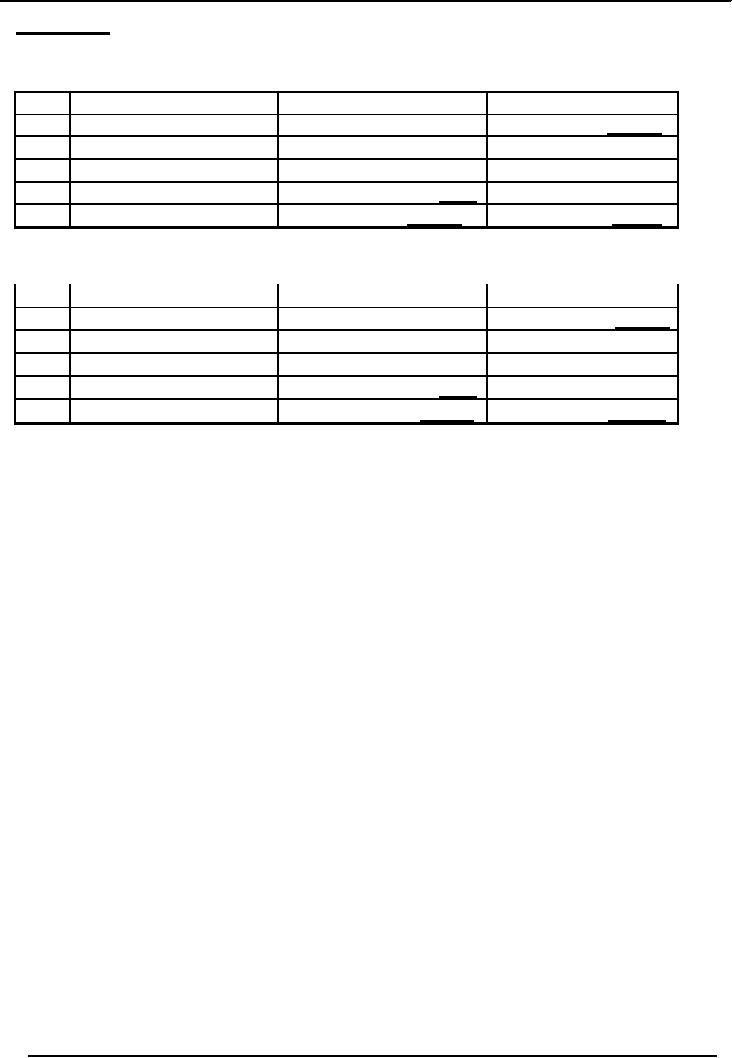
Financial
Statement Analysis-FIN621
VU
July
20, 2006.
Accounts receivable which were
Rs.11, 000 on July 14, have
been converted into cash
to
the
extent of Rs.1, 500. Cash
has therefore increased from
Rs.24, 000 to Rs.25, 500 and
accounts
receivable
have correspondingly decreased to Rs.9,
500
(VI)
Partial
collection of
Cash
25,500
A/Cs
payable
26,400
Accounts
(Rs.15,00)
A/C
receivable
9,500
owner's
equity
180,000
Land
130,000
Building
36,000
Office
equipment
5,400
Total
206,400
Total
206400
July
31, 2006
(VII)
Payment of
liability
Cash
22,500
A/Cs
payable
23,400
(A/C
payable) Rs.3,000
A/C
receivable
9,500
owner's
equity
180,000
Land
130,000
Building
36,000
Office
equipment
5,400
Total
203,400
Total
2,03,400
It is
thus clear from the above
illustration that each
financial transaction affects
financial
position,
(which in effect is the balance
sheet). Accounting period in the
example was one month.
It
must
also be noted no business
activity (commissions/ fees/ Revenues
& Expenses) was involved
in
above
example. Only setting up of
business was involved and
therefore owner's equity
remains the
same.
5
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING & ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
- Dual Aspect of Transactions
- Rules of Debit and Credit
- Steps in Accounting Cycle
- Preparing Balance Sheet from Trial Balance
- Business transactions
- Adjusting Entry to record Expenses on Fixed Assets
- Preparing Financial Statements
- Closing entries in Accounting Cycle
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Preparing Cash Flows
- Additional Information (AI)
- Cash flow from Operating Activities
- Operating Activities’ portion of cash flow statement
- Cash flow from financing Activities
- Notes to Financial Statements
- Charging Costs of Inventory to Income Statement
- First-in-First - out (FIFO), Last-in-First-Out (LIFO)
- Depreciation Accounting Policies
- Accelerated-Depreciation method
- Auditor’s Report, Opinion, Certificate
- Management Discussion & Analyses (MD&A)
- TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
- Incorporation of business
- Authorized Share Capital, Issued Share Capital
- Book Values of equity, share
- SUMMARY
- SUMMARY
- Analysis of income statement and balance sheet:
- COMMON –SIZE AND INDEX ANALYSIS
- ANALYSIS BY RATIOS
- ACTIVITY RATIOS
- Liquidity of Receivables
- LEVERAGE, DEBT RATIOS
- PROFITABILITY RATIOS
- Analysis by Preferred Stockholders
- Efficiency of operating cycle, process
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 1
- STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY SECTION OF THE BALANCE SHEET 2
- BALANCE SHEET AND INCOME STATEMENT RATIOS
- Financial Consultation Case Study
- ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET & INCOME STATEMENT
- SUMMARY OF FINDGINS