 |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-9
Learning
Objective
�
After
studying this chapter, you should be able
to:
o Explain
what are Assets and
Liabilities: and
o Draw
up simple Balance Sheet from
given information in trial
balance.
Assets
are
economic resources that are
owned by a business and are
expected to benefit future
operations.
In
most cases, the benefit to
future operations comes in the form of
positive future cash flows.
The positive
future
cash flows may come directly
as the asset is converted into
cash(collection of a receivable)or
indirectly
as the
asset is used in operating the business
to create other assets that
result in positive future
cash
flows(building
& land used to
Manufacture
a product for sale). Assets
may have definite physical
form such as building,
machinery or
stock.
On the other hand, some
assets exist not in physical
or tangible form, but in the form of
valuable legal
claims
or right; examples are
accounts receivables, investment in govt.
bonds, and patent rights.
Liabilities
are
debts. The person or organization to
which the debt is owed is
called creditors. All
businesses
have
liabilities; even the most
successful companies purchase
stocks, supplies, and
services on credit. The
liabilities
arising from such purchases
are called accounts
payable.
Rule
of Debit and Credit
Assets
(increase in assets is debit
and decrease in asset is
credit)
Liabilities
(Increase in liability is credit and
decrease in liability is
debit)
Classification
of Assets
�
Fixed
Assets Are
the assets of permanent nature
that a business acquires,
such as plant,
machinery,
building,
furniture, vehicles etc.
Fixed assets are subject to
depreciation.
�
Long
Term Assets These
are the assets of the business
that are receivable after twelve months
of the
balance
sheet date. For example, if
business has invested some
money for two years in
any saving
scheme
or has purchased saving
certificates for more than
one year, it is a long term
asset.
�
Current
Assets Are
the receivables that are
expected to be received within
one year of the
balance
sheet
date. Debtors, closing stock &
all accrued incomes are the
examples of Current Assets
because
these
are expected to be received
within one accounting period
from the balance sheet
date.
� The
year, in which long term
asset is expected to be received, long
term asset is transferred
to
current
assets in that
year.
Classification
of Liabilities
�
Capital
is the funds
invested by the owners of the business.
Business has a liability to
return these
funds to the
owner.
We
know that for the purpose of
accounting, business is treated
separately from its owners.
This is
known
as Separate Entity Concept
i.e. Business is a separate
entity. Therefore, if the owner
gives
something
(can be in form of Cash or
Some other Asset) to the
business then the business,
not only has
to
return the amount to the owner but it
also has to give some return
on that money. That is why
we
treat Capital
(Owners Funds) as a
Liability.
�
Profit and
Loss Account The
net balance of the profit and
loss account i.e. either
profit or loss also
belongs
to the owners.
32
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
While
explaining capital we said
that the business has to give
return to the owners. Now if the
business
is
managed successfully, then this
return would be a Favorable figure
(Profit). This return will,
therefore,
be
added to the Owners' investment.
�
On the
other hand, if the business is
managed un-successfully then this
return would be an
un-favorable
figure
(Loss). It will, therefore, be deducted
from the Owners'
Investment.
�
Long
Term Liabilities These
are the liabilities that
will become payable after a
period of more than
one
year of the balance sheet
date. For example, if
business has taken a loan
from bank or any
third
person
and it is payable after three
years, it is a long term liability of the
business.
�
Current
Liabilities These
are the obligations of the business that
are payable within twelve months
of
the
balance sheet date. Creditors
and all accrued expenses
are the examples of current liabilities
of the
business
because business is expected to
pay these back within
one accounting
period.
�
The
year in which long term
liability is to be paid back, long
term liability is transferred
to
current
liability in that year.
BALANCE
SHEET
� It is a
position statement that
shows the standing of the organization in
Monetary Terms at a
Specific
Time.
� Unlike
Profit and Loss that
shows the performance of the entity
over a period of time, the Balance
Sheet
shows
the Financial State of Affairs of the
entity at a given date.
� Balance
sheet is the summarized analysis in a
`T' form of all assets
and liabilities of the entity,
with
liabilities
listed on left hand side and
assets on right hand
side.
� Asset
is any owned physical object (tangible
asset) or a right (intangible
asset) having economic value
to
the
owner.
� Liability
is an obligation of the business to
deliver goods or to provide a
benefit in future.
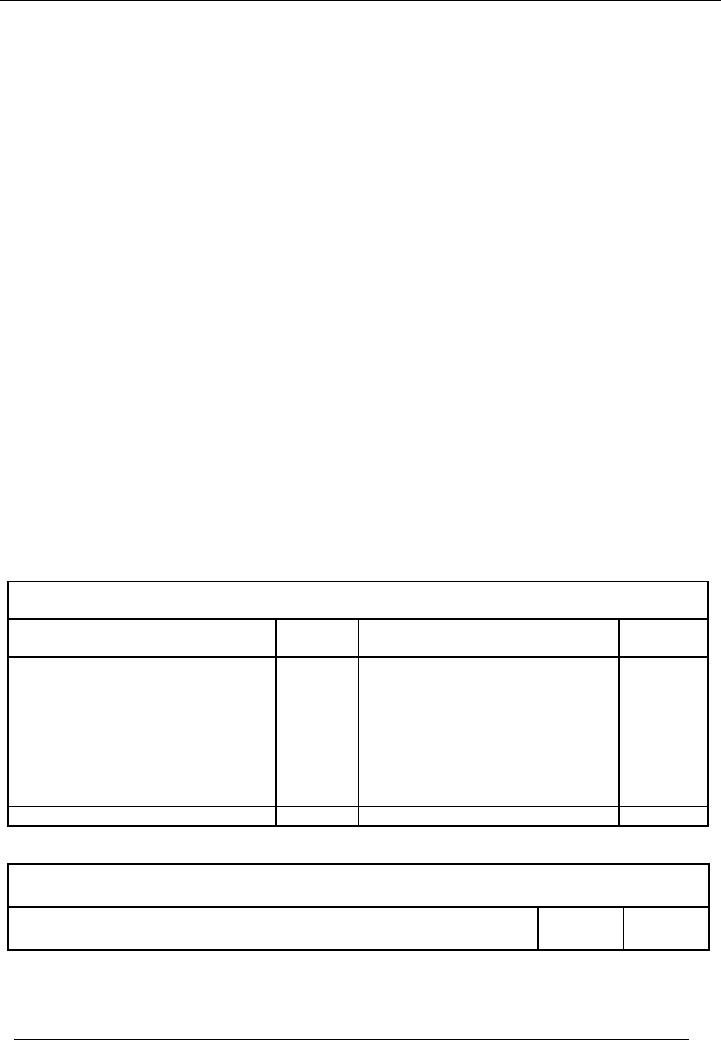
Format
of Balance Sheet (Account
Form)
Name
of the Entity
Balance
Sheet As At-------
Liabilities
Amount
Assets
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
Capital
100000
Fixes
Assets
75000
Profit
and loss Account +
15000
115000
Long
Term Assets
20000
Long
Term Liabilities
50000
Current
assets
80000
Current
liabilities
10000
Total
175000
Total
175000
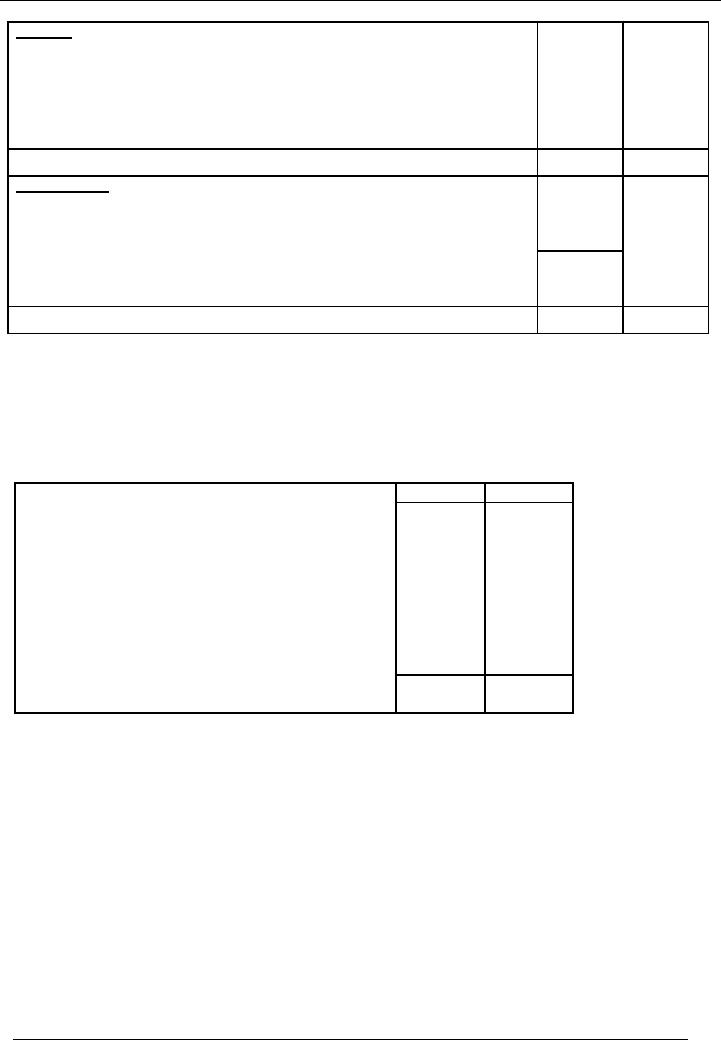
Format
of Balance Sheet (Report
Form)
Name
of the Entity
Balance
Sheet As At-------
PARTICULARS
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
33
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ASSETS
Fixes
Assets
75000
Long
Term Assets
20000
Current
Assets
80000
Total
175000
LIABILITIES
Capital
100000
Profit
15000
115000
Long
Term Liabilities
50000
Current
Liabilities
10000
Total
175000
SOLVED
EXAMPLES
ILLUSTRATION
# 1
The
following is the trial
balance extracted from the
books of Naeem & Sons as on
30/06/2002.
Prepare
a profit & loss account & balance
sheet for the year
ended June 30,
2002.
Particulars
Dr.
Cr.
Sales
100,000
Purchases
45,000
purchase
return
3,000
Salaries
12,000
Rent
5,000
Debtors
25,000
Creditors
16,000
Capital
368,000
Plant &
machinery
400,000
487,000
487,000
Grand
Total
34
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
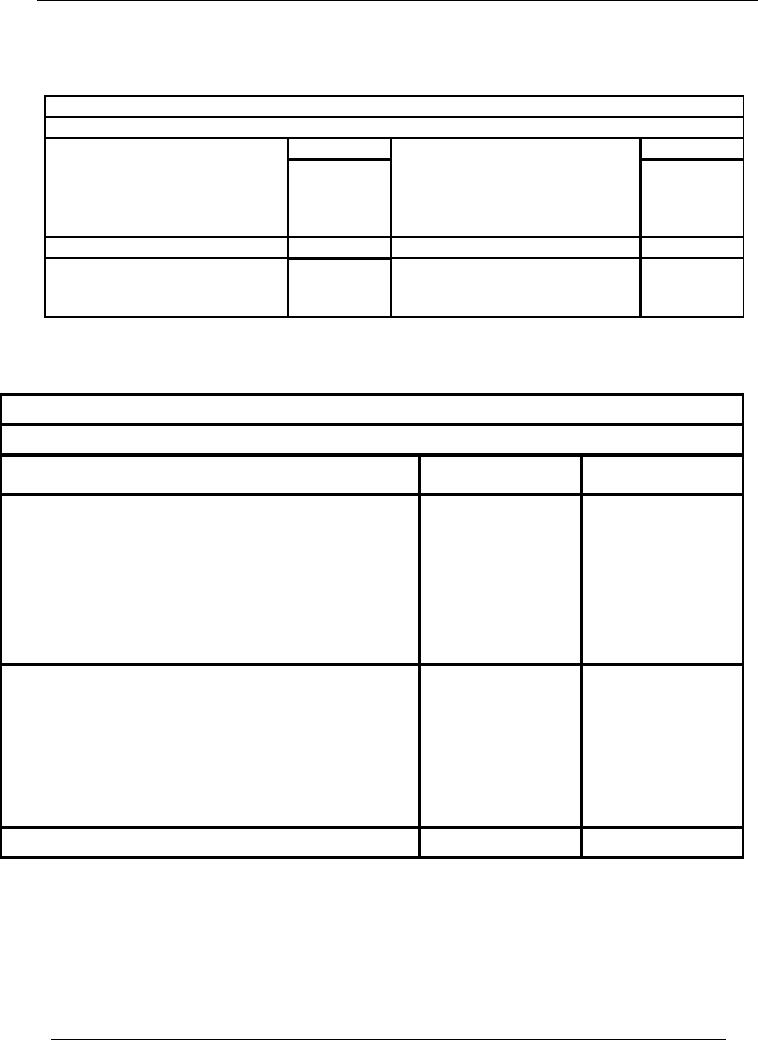
SOLUTION
Naeem
& Sons
Profit &
Loss Account for the
year ended June 30,
2002.
Rs.
Rs.
Sales
100,000
cost
of goods sold:
Purchases
45,000
Purchase return
3,000
Gross
Profit
58,000
103,000
103,000
Salaries
12,000
Gross Profit
58,000
Rent
5,000
Net
Profit
41,000
�
This
is a presentation of profit & loss
account in `T' account form.
Now same illustration is
presented in
statement
form.
Naeem
& sons
Profit &
Loss Account for the
year ended June 30,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
100,000
Income
/ Sales / Revenue
Less:
Cost of Goods
Sold
Purchases
45,000
Less:
Purchase Return
(3,000)
(42,000)
58,000
Gross
Profit
Less:
Administrative expenses
Salaries
(12,000)
Rent
(5,000)
(17,000)
Net
Profit
41,000
This is
not a correct way to present
profit & loss account in
statement form. In actual
practice only main
heads
of
expenses are presented in
profit & loss account along
with foot note number.
Detail of that head
of
expense
is given in the note. Correct presentation of profit
& loss account is
hereunder:
35
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Naeem
& sons
Profit &
Loss Account for the
year ended June 30,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
100,000
Income
/ Sales / Revenue
Less:
Cost of Goods
Sold
(42,000)
(See
Note # 1)
58,000
Gross
Profit
Less:
Administrative expenses
(17,000)
(See
Note # 2)
Net
Profit
41,000
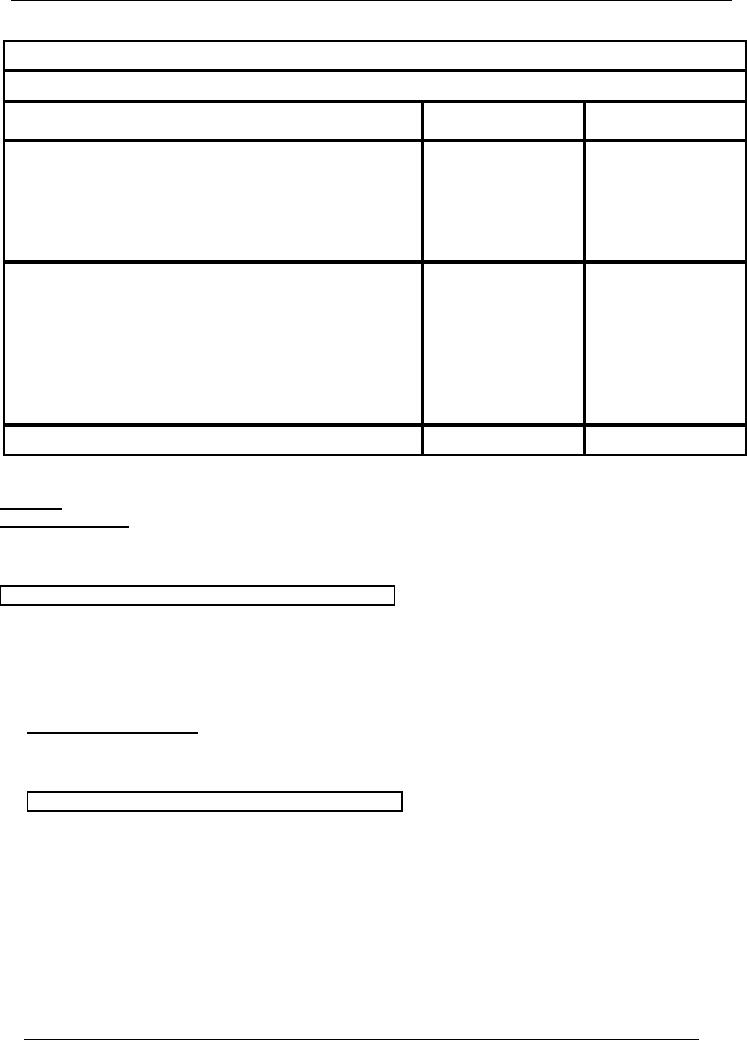
Note
# 1
Cost
of goods sold
Purchases
45,000
Less:
Purchase Return
(3,000)
Net
Purchases
42,000
Note
# 2
Administrative
expenses
Salaries
12,000
Rent
5,000
Total
Administrative expenses
17,000
It is
recommended that Profit &
loss account should be prepared in
above mentioned format.
36
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
BALANCE
SHEET
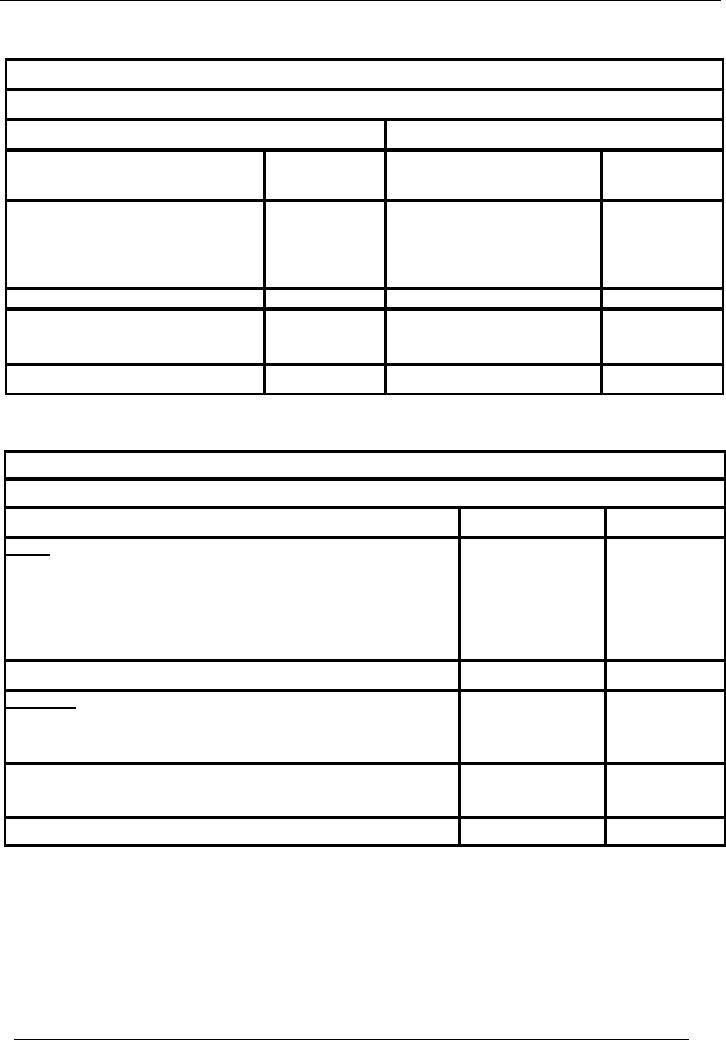
Naeem
& Sons
Balance
Sheet As At June 30,
2002
Liabilities
Assets
Particulars
Amount
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
Capital
368,000
Fixed Assets
Profit and
Loss Account
41,000
Plant &
Machinery
400,000
409,000
Current
Liabilities
Current
Assets
Creditors
16,000
Debtors
25,000
Total
425,000
Total
425,000
Balance
sheet in statement form is
presented hereunder:
Naeem
& Sons
Balance
Sheet As At June 30,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Amount
Rs.
Assets
Fixed
Assets
Plant &
machinery
400,000
Current
Assets
Debtors
25,000
Total
425,000
Liabilities
Capital
368,000
Profit
41,000
409,000
Current
Liabilities
Creditors
25,000
Total
425,000
425,000
37
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
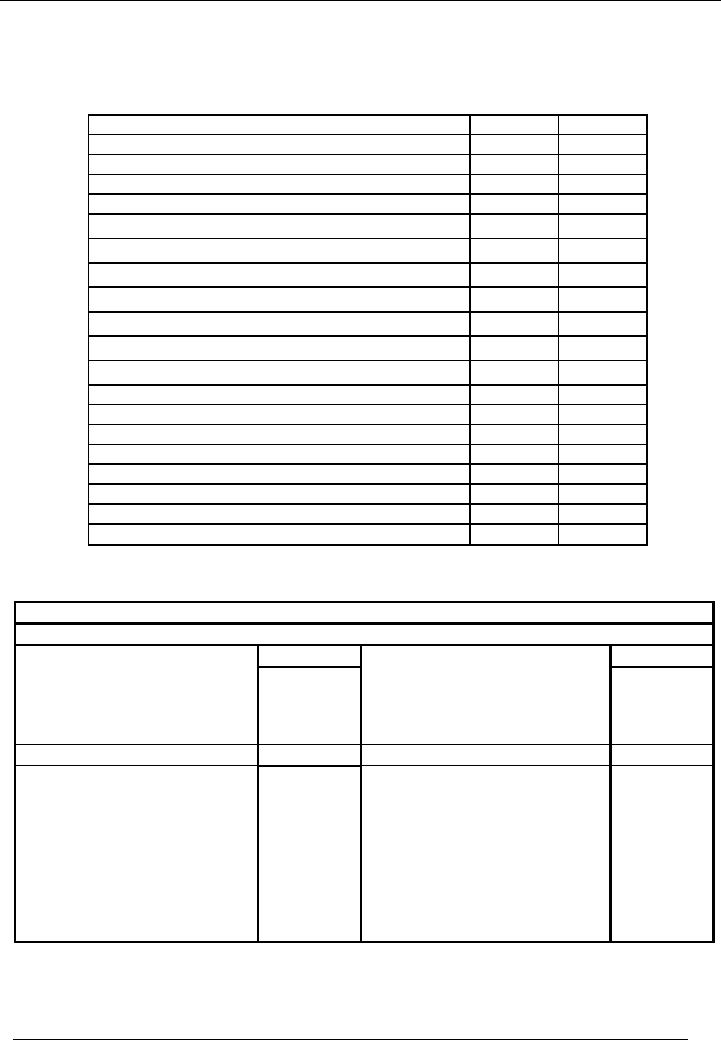
Illustration
# 2
The
following trial balance has
been extracted from the books of
Saeed & co. on 30-06-2002.
From this,
prepare
an income statement and
balance sheet for the year
ended 30-06-2002.
Dr.
Cr.
Sales
200,000
Purchases
180,000
purchase
return
2,500
Office
salaries
3,500
Furniture
& Fixture
16,000
Office
Equipment
11,000
Rent
5,000
Accounts
Payable(creditors)
28,000
Sales
Salaries
3,000
Freight
& custom duty on
purchases
6000
Repair
of office equipment
2,000
Accounts
Receivable(debtors)
52,000
Freight
on sales
1,000
Capital
41,500
Cash
in hand
37,000
Loan
from bank(for three
years)
50,000
Bank
charges
500
Interest
on loan
5,000
Grand
Total
322,000
322,000
SOLUTION
Saeed &
Co.
Profit &
Loss Account for the
year ended June 30,
2002.
Rs.
Rs.
Sales
200,000
Purchases
180,000
Purchase return
2,500
Freight,
custom duty on
purchases
6,000
Gross
Profit
16,500
202,500
202,500
Salaries
3,500
Gross Profit
16,500
Rent
5,000
Repair
of office equipment
2,000
Sales
salaries
3,000
Freight
on sales
1,000
Interest
on loan
5,000
Bank
charges
500
Net
loss
3,500
Total
20,000
20,000
Profit &
loss account in statement
form:
38
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Naeem
& sons
Profit &
Loss Account for the
year ended June 30,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
200,000
Income
/ Sales / Revenue
Less:
Cost of Goods
Sold
(183,500)
(See
Note # 1)
Gross
Profit
16,500
Less:
Administrative expenses
(10,500)
(See
Note # 2)
Less:
Selling expenses
(4,000)
(See
Note # 3)
Less:
Financial Expenses
(5,500)
(See
Note # 4)
Net
Profit/(Loss)
(3,500)
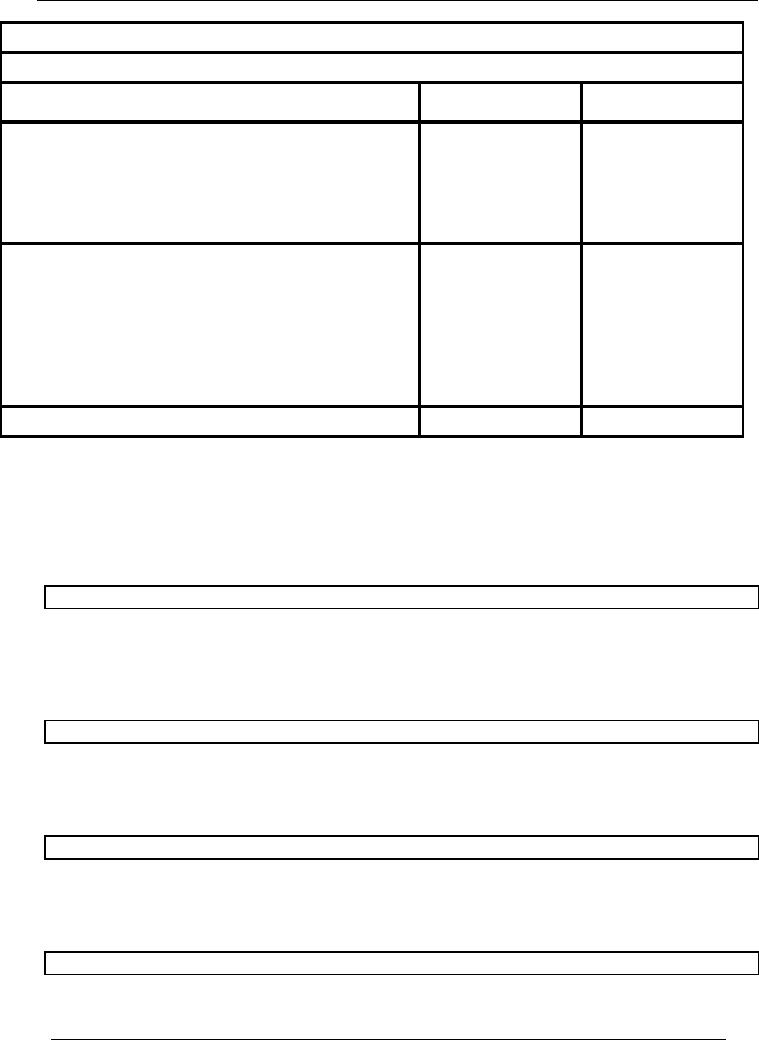
NOTE #
1
COST
OF GOODS SOLD
Purchases
180,000
Less:
purchase return
(2,500)
Add:
Freight, custom duty on
purchases
(6,000)
TOTAL
183,500
NOTE #
2
Administrative
expenses
Salaries
3,500
Rent
5,000
Repair
of office equipment
2,000
TOTAL
10,500
NOTE #
3
Selling
expenses
Sales
salaries
3,000
Freight
on sales
1,000
TOTAL
4,000
NOTE #
4
Financial
expenses
Interest
on loan
5,000
Bank
charges
500
TOTAL
5,500
39
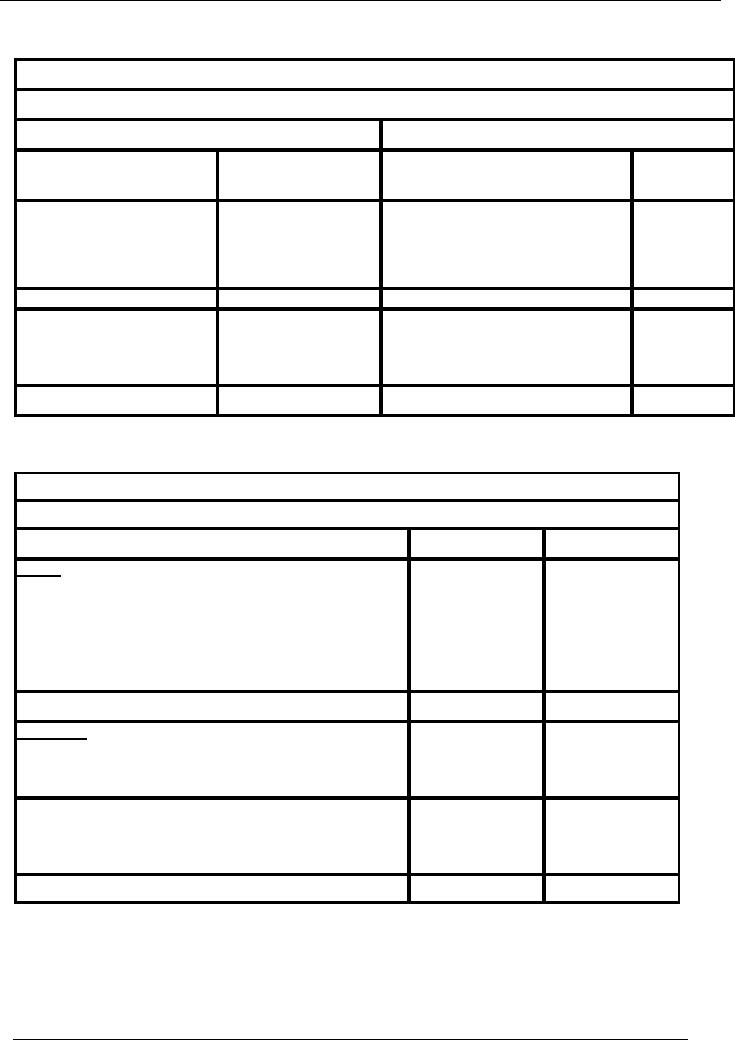
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
BALANCE
SHEET
Saeed
& co.
Balance
Sheet As At June 30,
2002
Liabilities
Assets
Particulars
Amount
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
Capital
41,500
Fixed Assets
Profit and
Loss Account
(3,500)
Furniture
& Fixture
16,000
38,000
Long
Term Liabilities
Current
Assets
Loan
from bank
50,000
Debtors
52,000
Current
Liabilities
Office
equipment
11,000
Creditors
28,000
Cash
37,000
Total
116,000
Total
116,000
Balance
sheet in statement
form
Saeed
& Co.
Balance
Sheet As At June 30,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Amount
Rs.
Assets
Fixed
Assets
Furniture
& Fixture
16,000
Current
Assets
Debtors
52,000
11,000
Office
Equipment
Cash
37,000
Total
116,000
Liabilities
Capital
41,500
Profit/(Loss)
(3,500)
38,,000
Long
Term Liabilities
Loan
from bank
50,000
Current
Liabilities
Creditors
28,000
Total
116,000
40
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES