 |

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-8
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
�
After
studying this chapter, you will be
able to:
o Draw
up Profit & Loss account
from the information given in trial
balance.
o Differentiate
the term, Receipt & Payment,
Income & Expenditure and
Profit & Loss
account.
FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
� Different
reports generated from the books of
accounts to provide information to the
relevant
persons.
� Every
business is carried out to
make profit. If it is not
run successfully, it will
sustain loss. The
calculation of
such profit & loss is
probably the most important objective of
the accounting function.
Such
information is acquired from
"Financial Statements".
� Financial
Statements are the end
product of the whole accounting
process. These show us
the
profitability
of the business concern and the financial
position of the entity at a specified
date.
� The
most commonly used Financial Statements
are `profit & loss
account' `balance sheet' &
`cash
flow
statement'.
Income
and Expenditure Vs Profit and Loss
�
Income
and Expenditure Account is
used for Non-Profit Organizations
like Trusts, NGOs.
�
Profit
and Loss Account is
used for Commercial
organizations like limited
companies.
PROFIT
& LOSS ACCOUNT
�
Profit
& Loss account is an account
that summarizes the profitability of the
organization for a
specific
accounting period.
�
Profit
& Loss account has two
parts:
o In the
first part, Gross Profit is
calculated.
o Gross
profit is the excess of sales
over cost of goods sold in
an accounting period.
o In
trading concern, cost of
goods sold is the cost of
goods consumed plus any
other charge
paid in
bringing the goods in salable
condition. For example, if
business purchased
certain
items
for resale purpose and
any expense is paid in respect of
carriage or bringing the
goods
in
store (transportation charges).
These will also be grouped under the
heading of `cost of
goods
sold' and will become part
of its price.
o In
manufacturing concern, cost of goods
sold comprises of purchase of
raw material plus
wages
paid to staff employed for converting this
raw material into finished
goods plus any
other
expense in this connection.
o In the
2nd part, Net Profit
is calculated.
o Net
Profit is what is left of the gross
profit after deducting all other
expenses of the
organization in a
specific time period.
How
to prepare Profit & Loss
account
� One
way is to write down all the
Debit and Credit entries of
Income and Expense accounts
in the
Profit
and Loss Account. But it is
not sensible to do
so.
� The
other way is that we
calculate the net balance or we can
say Closing Balance of each
income and
expense
account. Then we note all
the credit balances on the credit side
and all the debit balances
on
the
debit of profit and loss
account.
� If the net
balance of profit and loss
is Credit (credit side is greater
than debit side) it is
Profit and if
the net
balance is Debit (Debit side
is greater than credit side) it is a
loss.
28

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Income,
expenditure, profit and loss
�
Income
is
the value of goods and
services earned from the
operation of the business. It
includes
both
cash & credit. For example, if a
business entity deals in
garments. What it earns from
the sale of
garments,
is its income. If somebody is rendering
services, what he earned from rendering
services is
his
income.
�
Expenses
are
the resources and the efforts
made to earn the income,
translated in monetary
terms.
It
includes both expenses,
i.e., paid and to be paid (payable).
Consider the above mentioned
example,
if any
sum is spent in running the
garments business effectively or in
provision of services, is
termed
as
expense.
�
Profit
is
the excess of income over
expenses in a specified accounting
period.
Profit=
Income-expenses
In the
above mentioned example, if the business
or the services provider earn
Rs. 100,000 &
their
expenses
are Rs. 75,000. Their
profit will be Rs. 25,000
(100,000-75,000).
�
Loss
is the excess of expenses over
income in a specified period of time. In
the above example, if
their
expenses are Rs. 100,000
& their income is Rs.
75,000. Their loss will be
Rs. 25,000.
RULES
OF DEBIT & CREDIT
�
Increase
in expense is Debit
(Dr.)
�
Decrease
in expense is credit (Cr.)
�
Increase
in income is credit (Cr.)
�
Decrease
in income is Debit
(Dr.)
Classification
of expenses
�
It has
already been mentioned that a
separate account is opened
for each type of expense.
Therefore,
in
large business concerns,
there may be a large number of
accounts in organization's books.
�
As
profit & loss account is a
summarized record of the profitability of
the organization. So, similar
accounts
should be grouped for reporting
purposes.
�
The
most commonly used groupings of expenses
are:
o COST
OF GOODS SOLD
o ADMINISTRATION
EXPENSES
o SELLING
EXPENSES
o FINANCIAL
EXPENSES
�
Cost
of goods sold is the
cost incurred in purchasing or manufacturing the
product, which an
organization is
selling plus any other
expense incurred in bringing the product
in salable condition.
Cost
of goods sold contain the following
heads of accounts:
o Purchase
of raw material/goods
o Wages
paid to employees for manufacturing of
goods
o Any
tax/freight is paid on purchases
o Any
expense incurred on carriage/transportation of
purchased items.
�
Administrative
expenses are
the expenses incurred in running a
business effectively. Main
components
of this group are:
o Payment
of utility bills
o Payment
of rent
o Salaries
of employees
o General
office expenses
o Repair
& maintenance of office equipment &
vehicles.
29

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
�
Selling
expenses are
the expenses incurred directly in connection with the
sale of goods. This
head
contains:
o Transportation/carriage
of goods sold
o Tax/freight
paid on sale
�
If the
expense head `salaries'
includes salaries of sales staff. It
will be excluded from
salaries & appear
under the
heading of `selling
expenses'.
�
Financial
expenses are
the interest paid on bank loan & charges
deducted by bank on entity's bank
accounts.
It includes:
o Mark
up on loan
o Bank
charges
Receipt
& Payment Account
�
A
receipt & payment account is the
summarized record of actual
cash receipts and actual
cash
payment
of the organization for a given period of time. This
is a report that provides cash
movement
during
the reported period. In other words, it
can be defined as the summarized
record of the cash
book
for a specific
period.
Receipt
& Payment vs. Profit & Loss
Account
�
Receipt
& payment account is the summarized
record of actual cash
receipts and actual cash
payment
during
the period while profit &
loss account also includes
Receivable and
Payable.
�
Income
& expenditure Vs. Profit & Loss
Account
�
These
are two similar terms.
Only difference between these
two terms is that income
& expenditure
account
is prepared for non profit
oriented organizations, e.g.
Trusts, N.G.O's, whereas
profit & loss
account
is prepared in profit oriented
organizations, e.g. Limited
companies, Partnership firms
etc.
�
In
case of Income and
Expenditure Surplus/Deficit is to be find
and in case of Profit and
loss
account
profit or loss is to be
find.
30
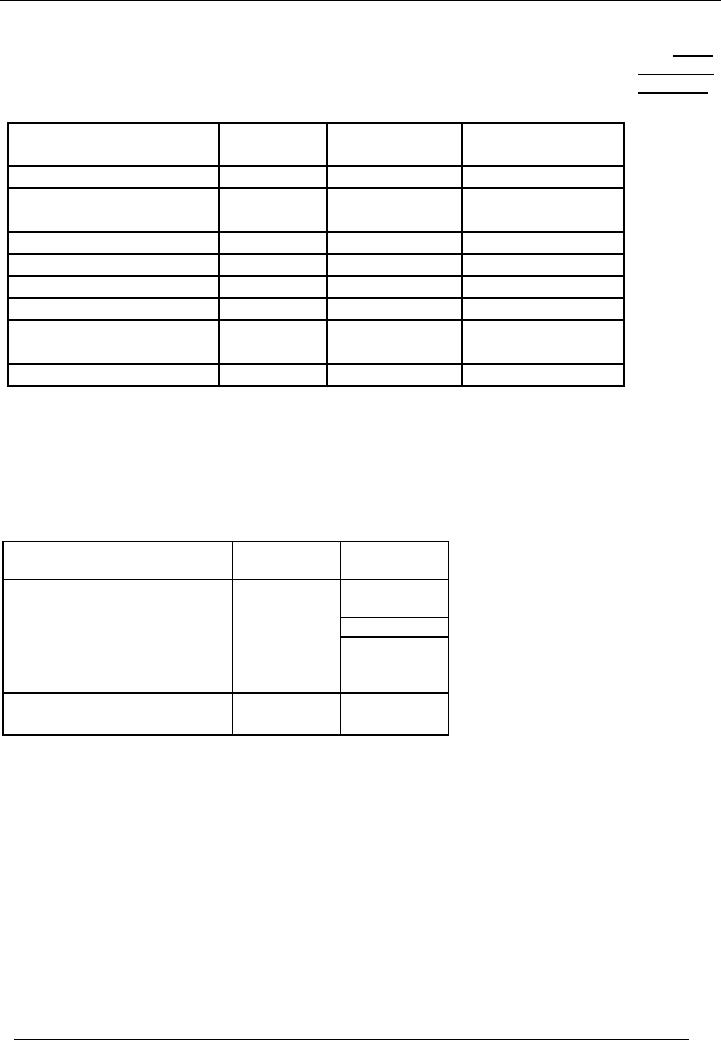
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
A sample of
Profit and Loss Account
Gross
Name
of the Entity
profit
and
Profit and
Loss Account
Net
profit
for
the period Ending
----
DEBIT
CREDIT
Gross
PARTICULARS
AMOUNT
PARTICULARS
AMOUNT
profit
=
Rs.
Rs.
Income
Cost
of sale
60000
income
100000
cost
of
Gross
profit c/d
40000
sales
(Income
cost of sales)
=
100000-
Total
100000
Total
100000
60000
Admin
expenses
15000
Gross
profit b/d
40000
Selling
expenses
5000
=
Rs.40000
Financial
expenses
5000
Net
profit
=
Gross
Net
profit (Gross profit
profit
expenses)
Expenses
Total
40000
Total
40000
=
40000 15000 5000 -
5000
=Rs.15000
A sample of
Income Statement
Name
of the Entity
Income
statement
For
the period Ending
----
PARTICULARS
AMOUNT
AMOUNT
Rs.
Rs
Income/Sales/Revenue
100000
Less:
Cost of sales
(60000)
Gross
profit
40000
Less:
Administration expenses
15000
Selling
expenses
5000
Financial
expenses
5000
(25000)
Net
profit
15000
Recognizing
Income and Expenditure
�
Income
should be recognized / recorded at the time
when goods are sold or
services are
rendered.
�
Expenses
should be recognized / recorded
when benefit relating to that
expense has been
drawn.
31
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES